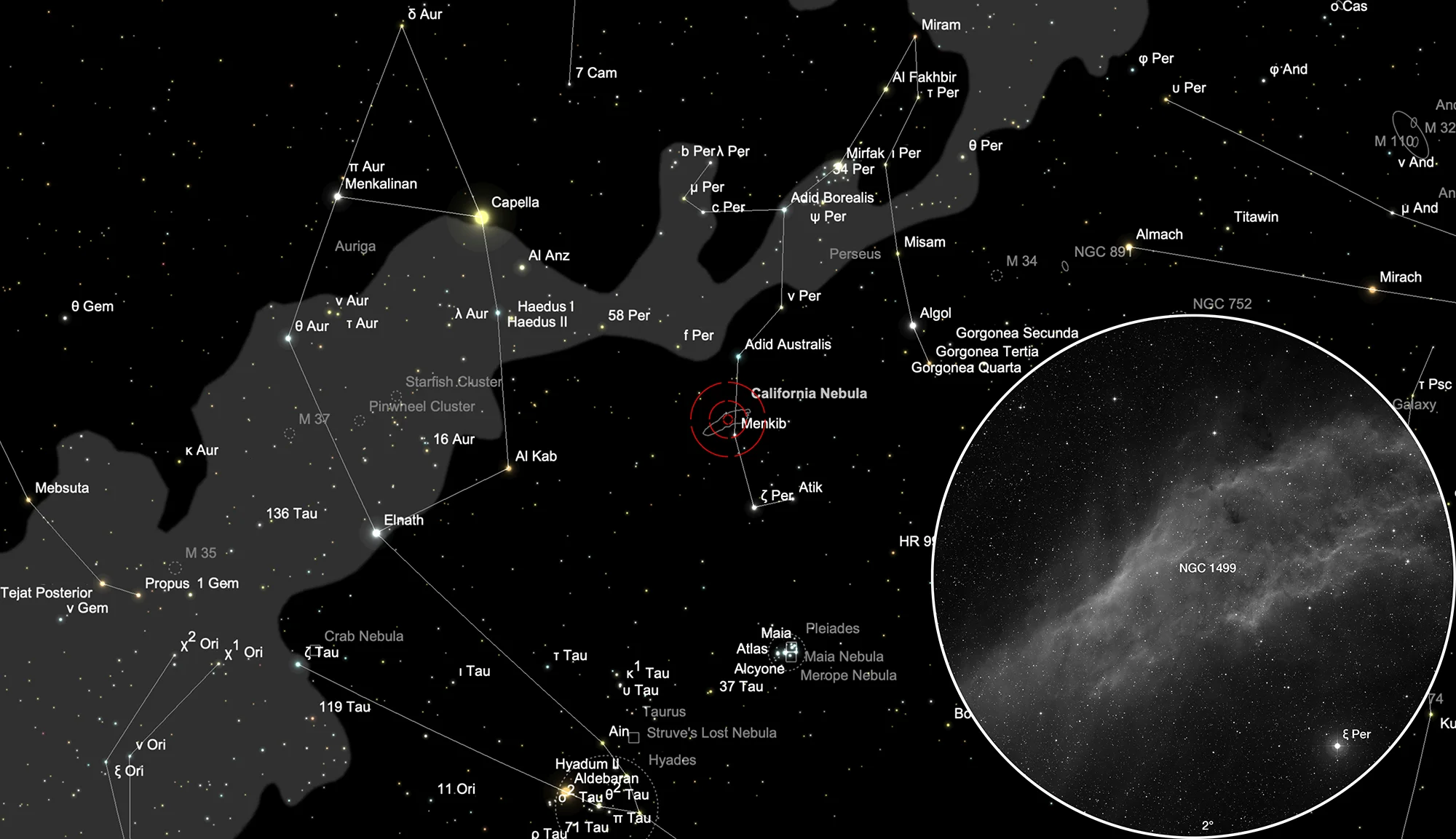
California Nebula (NGC 1499)




History
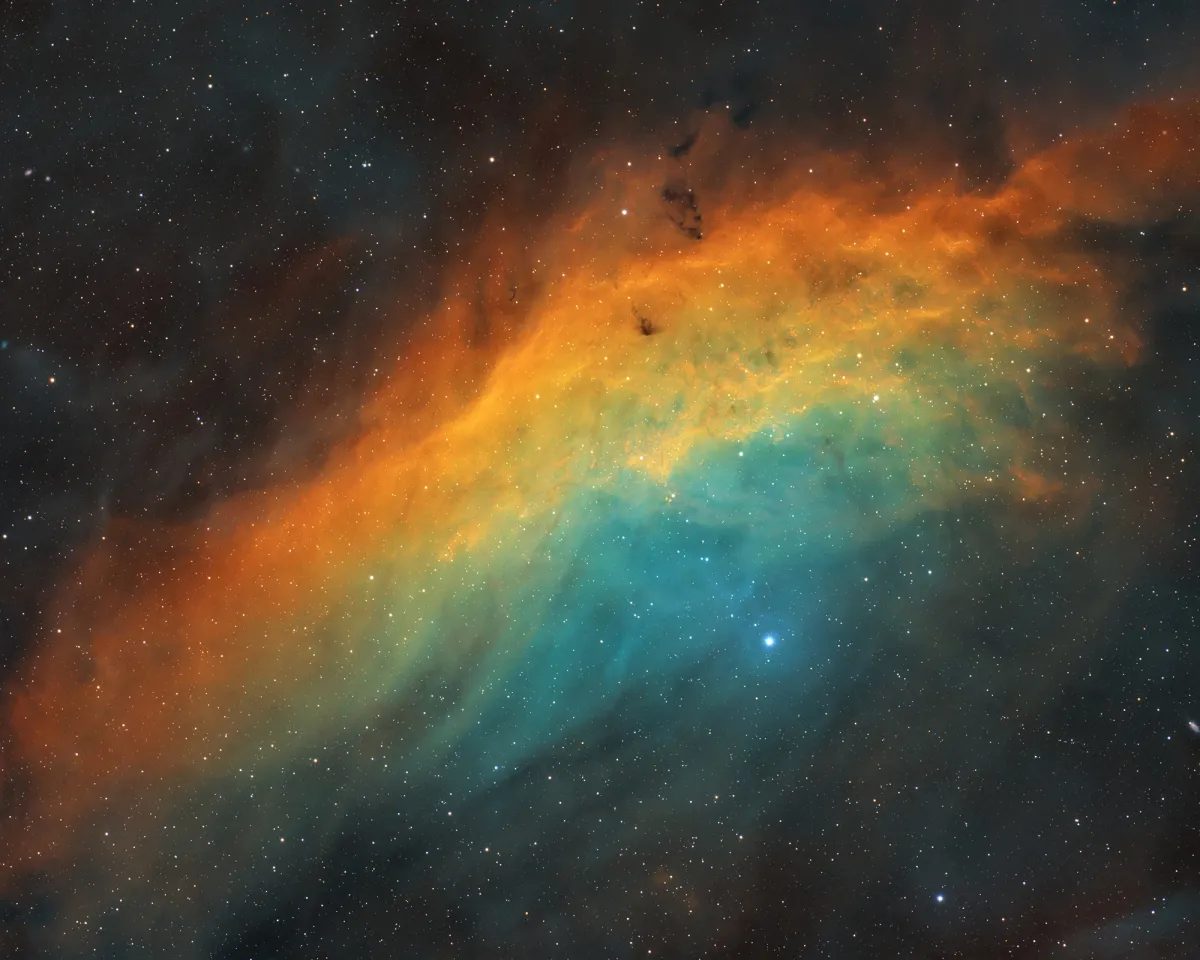
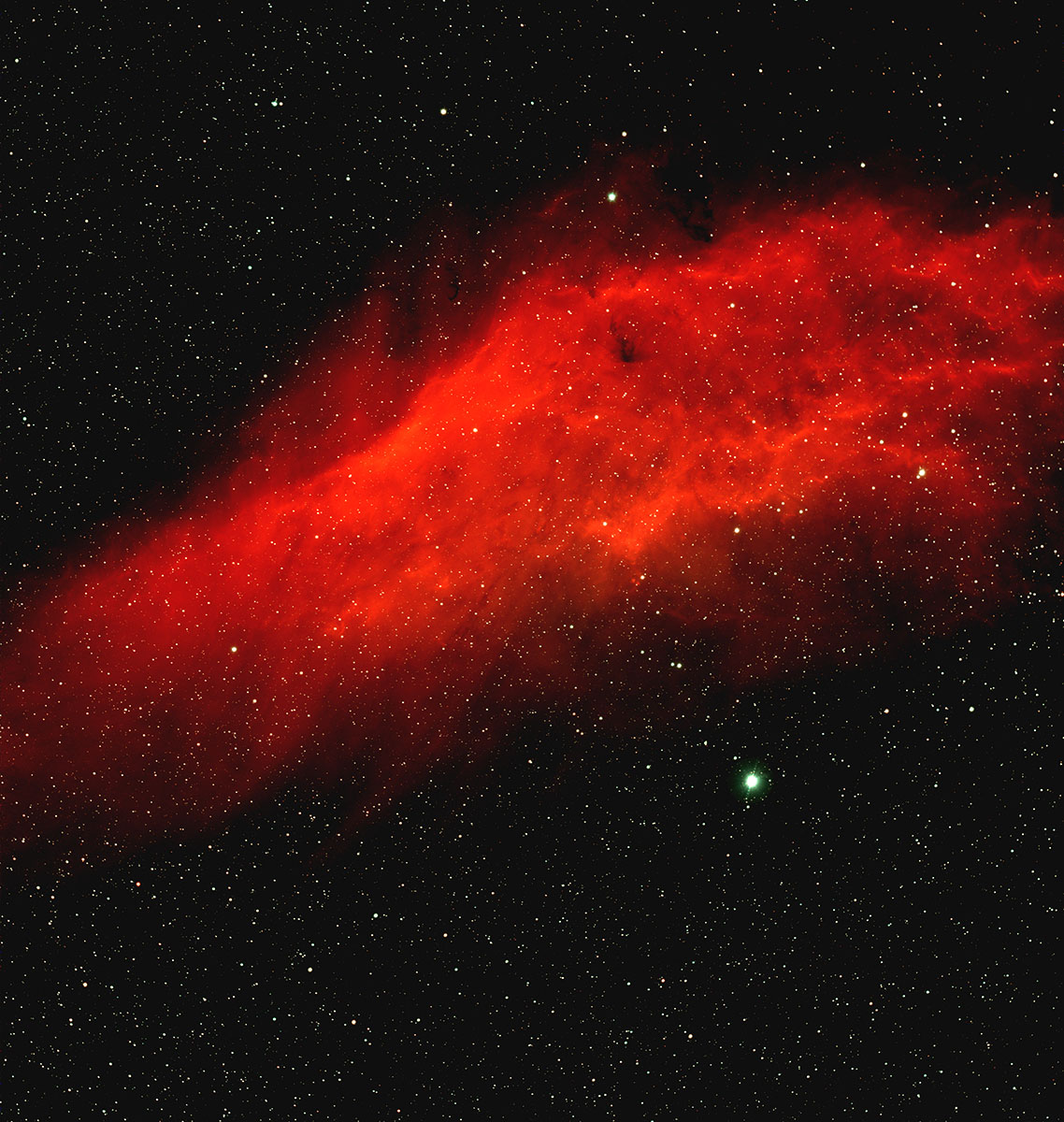
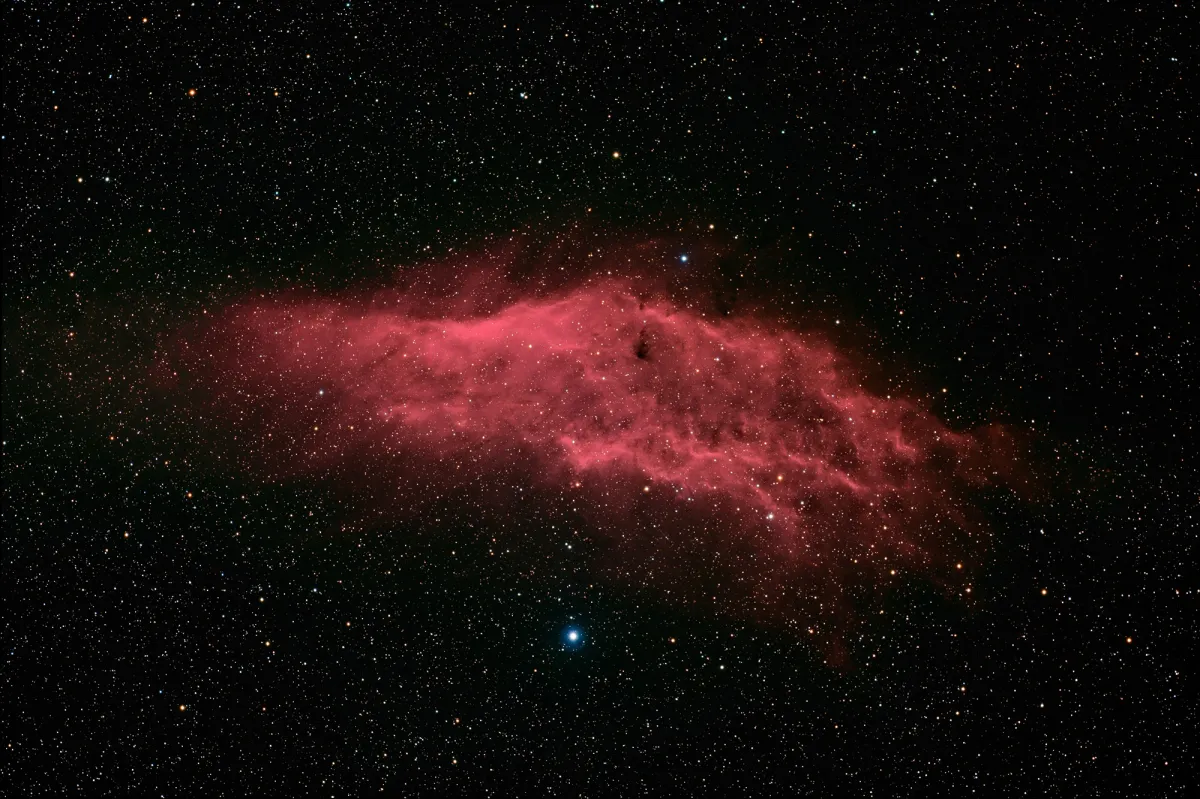
The galactic emission nebula NGC 1499 was discovered on 3 November 1885 by American astronomer Edward Emerson Barnard. It received the nickname because it is similar in shape to the US state of California. [196]
Physical Properties
With a surface area of around 2.5 ° x 1 °, the nebula is very large, but has a low surface brightness. It glows mainly in the red lines Hα (656 nm) and Hβ (486 nm). The nearby, high-energy O7 star ξ Persei (Menkib), located at a distance of about 420 pc to 486 pc (1370 to 1585 light years), is held responsible for this. [145, 196]
| Designation | NGC 1499 |
| Type | EN |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 04h 01m 10.0s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +36° 27' 36" |
| Diameter | 120 × 60 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 5.0 mag |
| Position Angle | 120° |
| Metric Distance | 0.400 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | vF, vL, E ns, dif |
| Identification, Remarks | LBN 756; California nebula |
Finder Chart
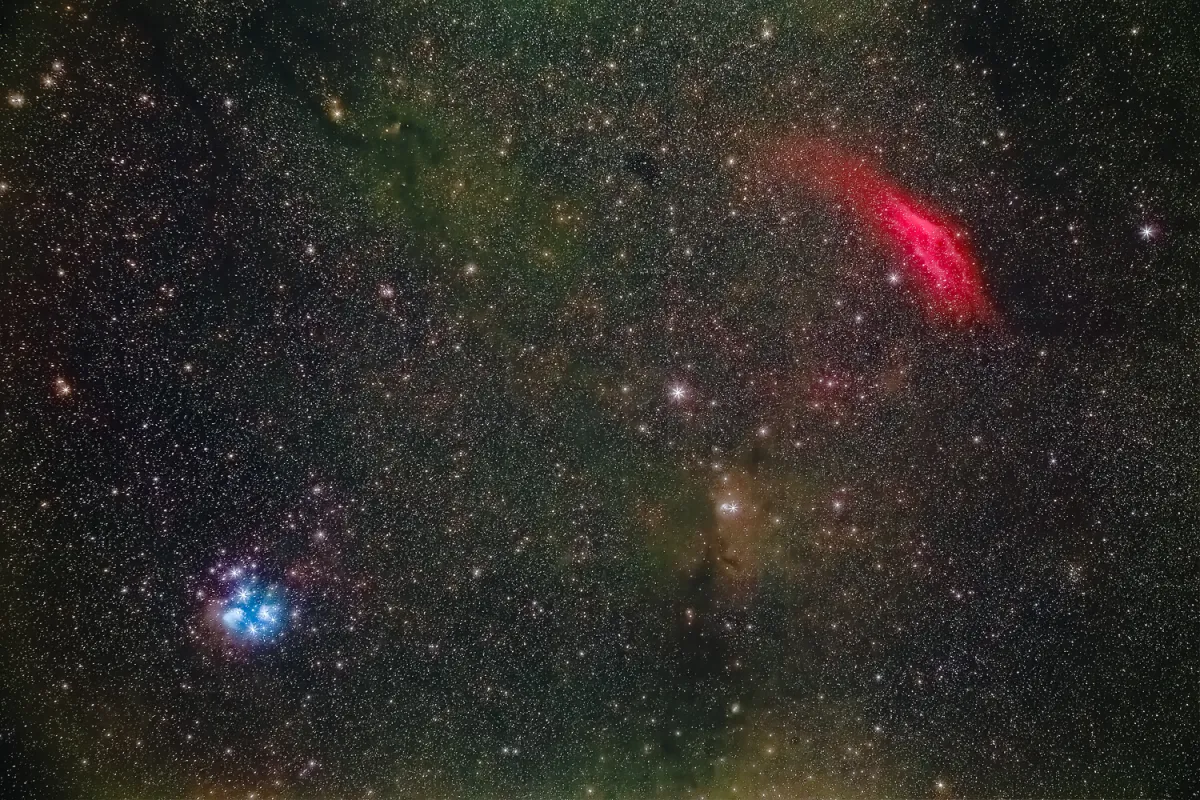
NGC 1499 is located in the constellation Perseus about 1° to the northeast from the 4 mag bright star ξ Persei (Menkib). It can best be observed in the months of July to April.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: With the 31 mm Tele Vue Nagler eyepiece (58x) and hβ filter, NGC 1499 is clearly defined as a large nebula, so that individual structures can also be recognised. However, the nebula extends far beyond the field of view of 1.4° of the eyepiece. In order to recognise it, the telescope must be moved along the edge of the nebula. For an even lower magnification, a shorter focal length is recommended. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Gurnigel, 19. 8. 2023, Bernd Nies