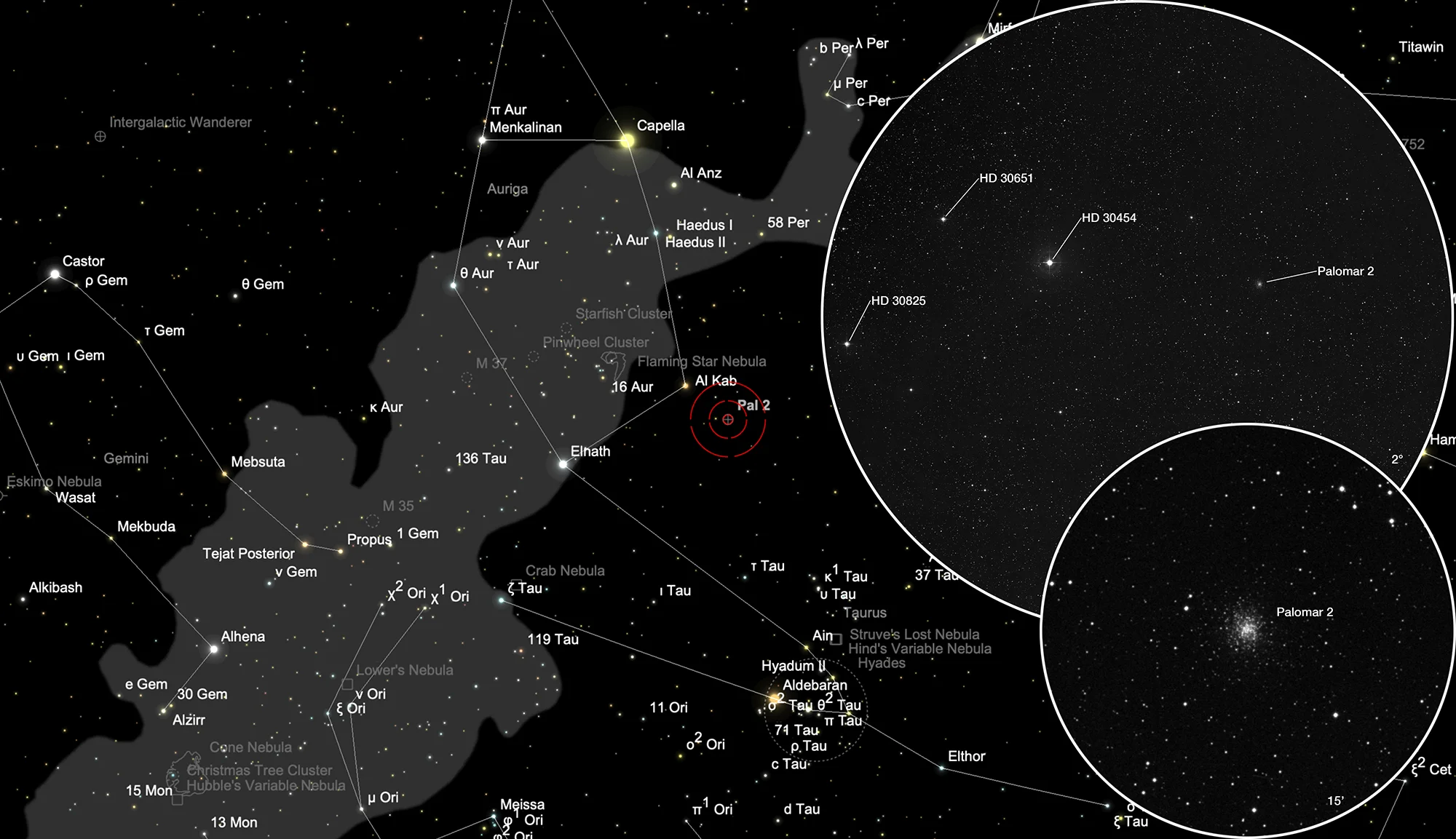
Globular Cluster Palomar 2

History
The globular cluster Palomar 2 was discovered in the 1950s by the American astronomer Albert George Wilson in the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey photo plates. George O. Abell published a list of 13 globular clusters and 73 planetary nebulae in 1955. He noted «highly obscured». [331]
Physical Properties
Palomar 2 is a loose globular cluster of Shapley–Sawyer concentration class IX. The stars appear reddened due to the high absorption by interstellar gas due to the great distance. [331]
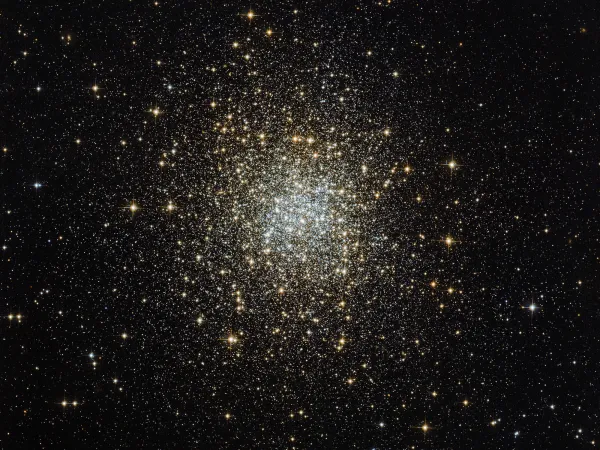

The globular cluster was studied in a study with the Hubble Space Telescope. The age has been estimated at 13.25 ± 0.12 billion years. It has about 140'000 solar masses. At a distance of 26.1 ± 1.5 kpc (about 85'000 light years) from the Sun, it is located in the outer halo of our Milky Way. [372]
| Name | Palomar 2 |
| Object Type | Globular Cluster |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 04h 46m 06s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +31° 22' 51" |
| Parallaxes | 0.042 mas |
| Radial velocity | -134.9 km/s |
| Redshift z | -0.00045 |
| Angular size | 1.62' × 1.426' |
| Magnitudes | J 8.876; H 8.005; K 7.68 |
| Identifiers | 2MASX J04460579+3122510; C 0443+313; Cl Pal 2; LEDA 15963; MCG+05-12-001; [KPS2012] MWSC 0418 |
Finder Chart
The globular cluster Palomar 2 is located in the constellation Auriga. The three stars of 7.6 to 5.5 mag within a 2° field of view help identifying the position of the globular cluster. On 6 December it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is August to May.
Visual Observation
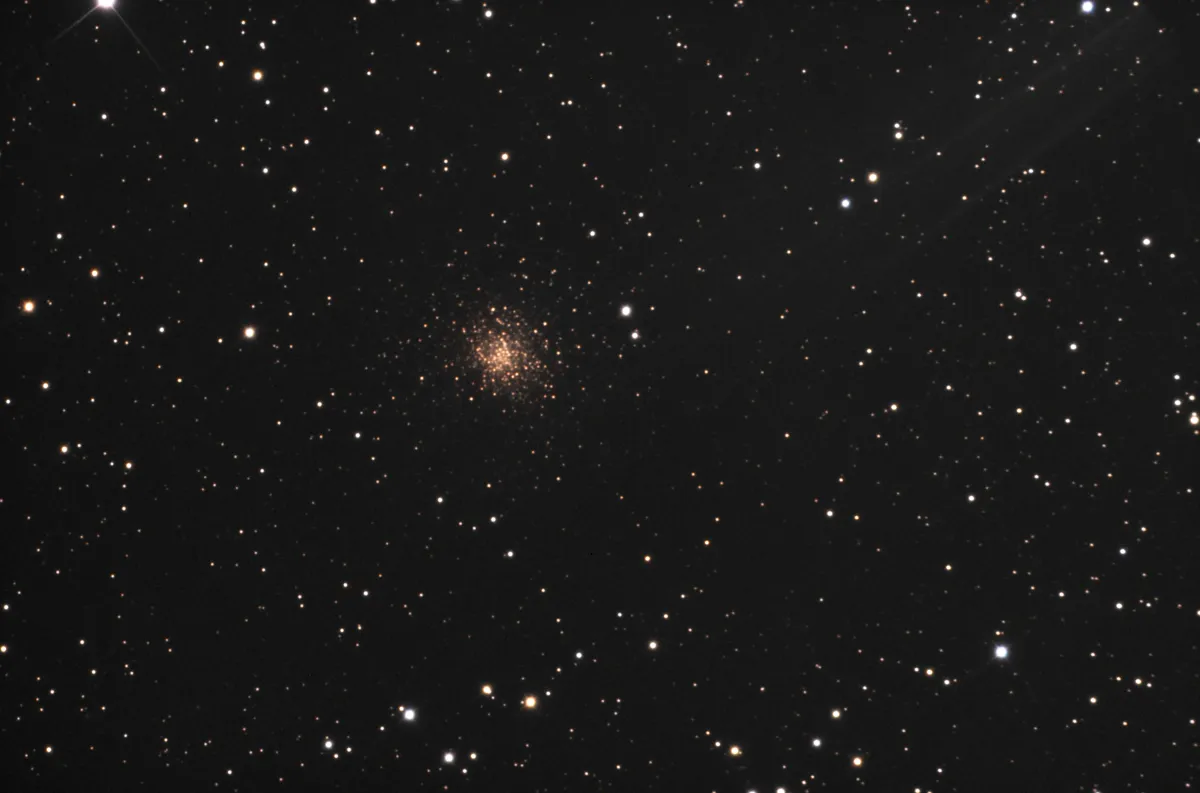
400 mm Aperture: The globular cluster is much dimmer than one would expect from the DSS closeups, probably due to reddening of galactic dust. Using averted vision, it is barely recognizeable as a fuzzy patch. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Hasliberg, SQM 21.0, 3. 2. 2024, Bernd Nies