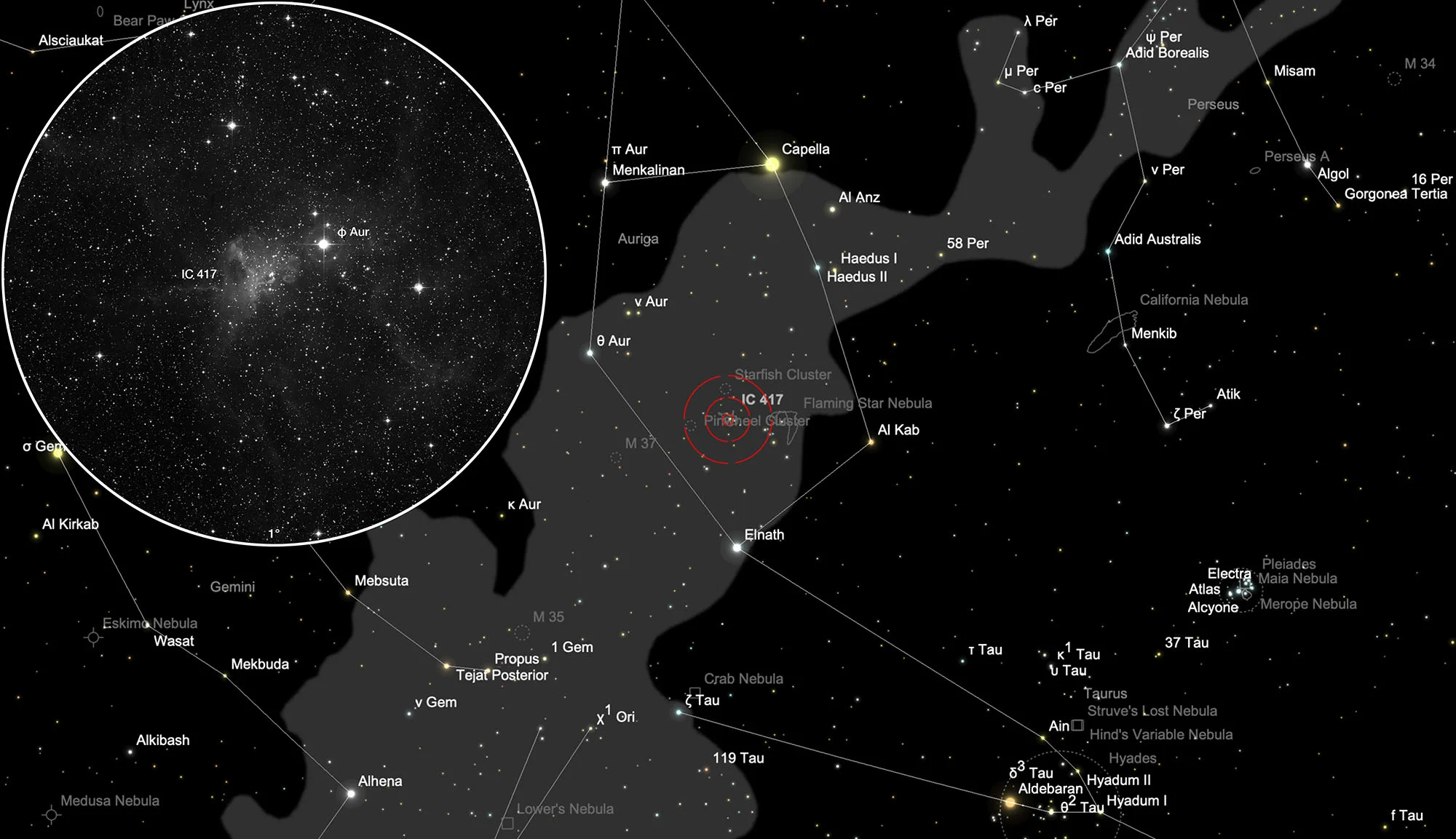
Galactic Nebula IC 417


Object Description
IC 417 was discovered on 25 September 1892 by the German astronomer Max Wolf. [196]
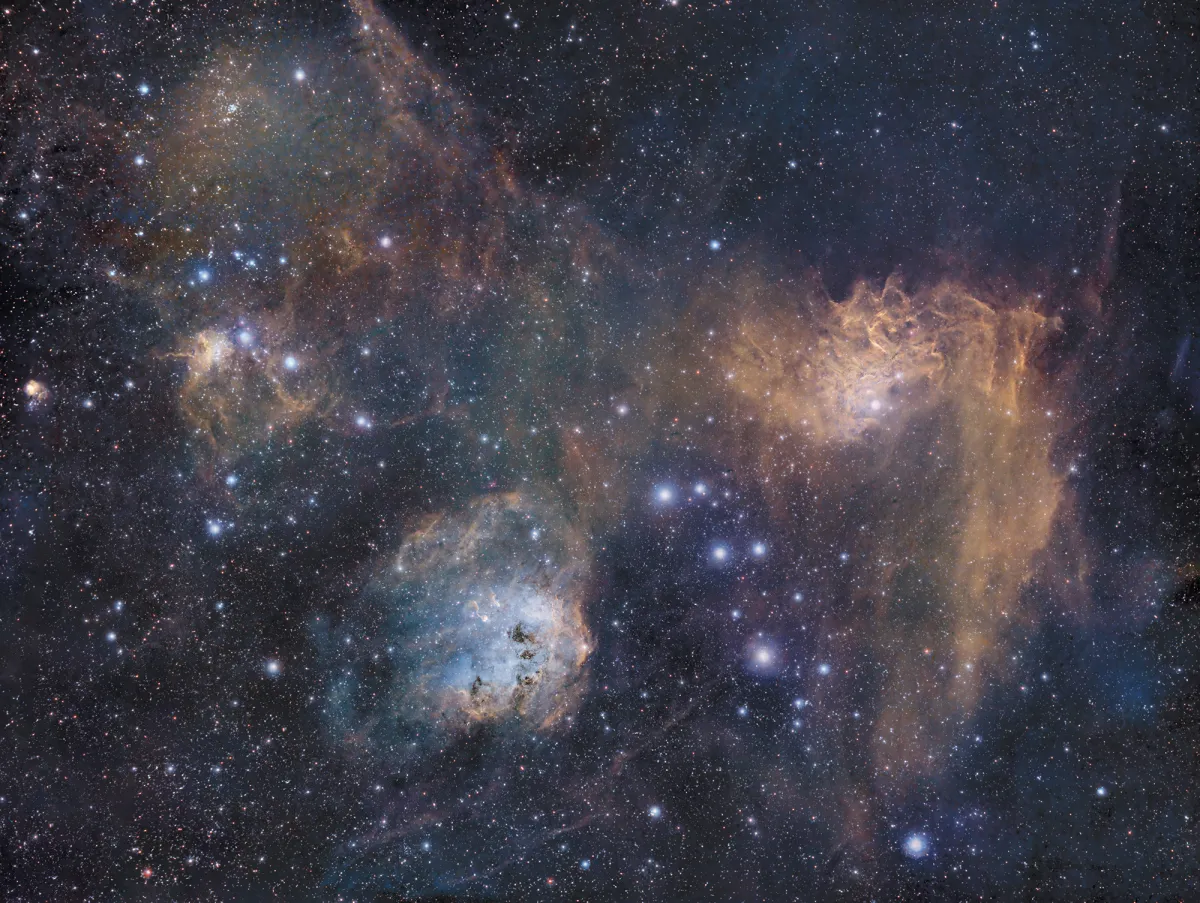
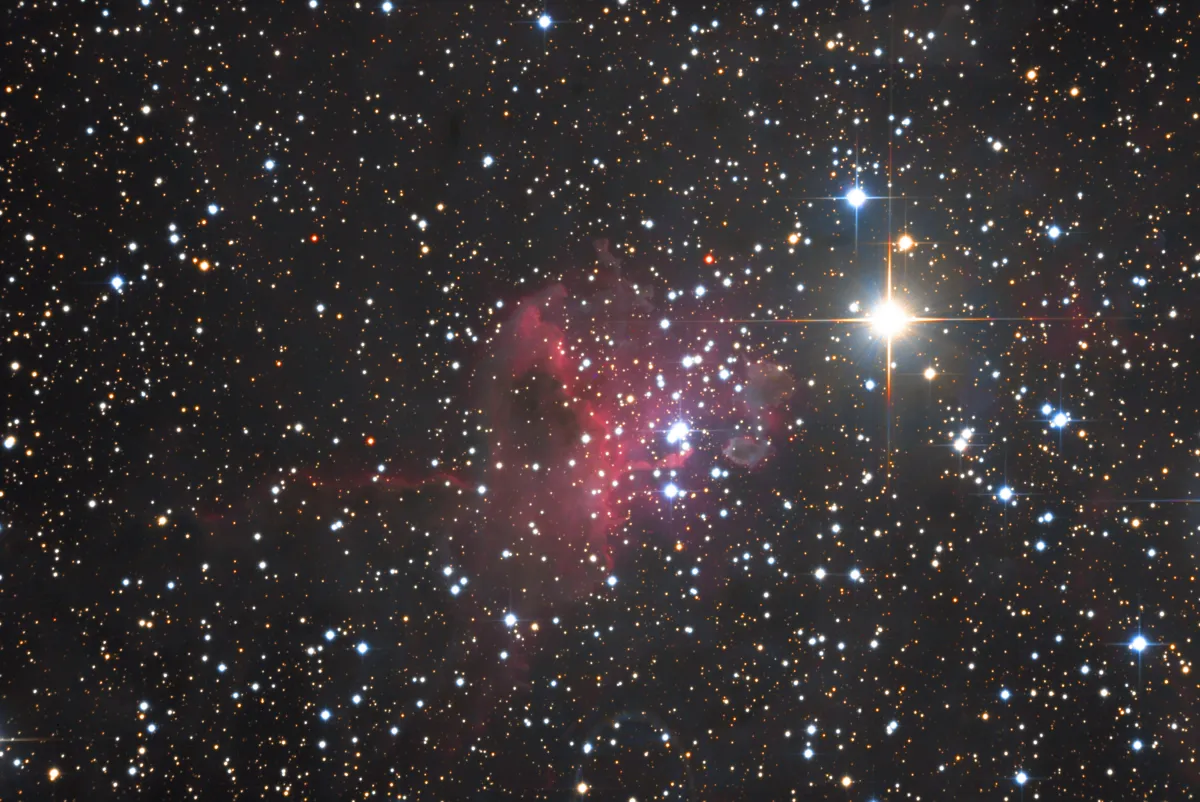
IC 417 is an emission and reflection nebula with an embedded star cluster, which is part of an extensive H-II nebula complex and star formation region in the Auriga constellation. The age is estimated to be less than 3 million years. The distribution of the young stellar objects (YSO) along with the ionized and molecular gas reveal two ring-like structures, both of which extend over a range of several degrees. The centre of these «Auriga Bubbles» is about 50 pc above the galactic mid-plane and their diameter is about 100 pc. This could be caused by past supernovae, the shock wave of which had stimulated star formation in this area. [358]

Other objects that seem to belong to the same molecular cloud are: NGC 1931, IC 410 and IC 405 (see Fig. 3). The distance from IC 417 to Earth is about 2.19 kpc, around 7100 light years. The distance from the star AE Aurigae, which is responsible for the flame star nebula IC 405, is given as 405 to 548 parsecs (approx. 1300 to 1800 light years) and is therefore much closer. [145] Either the distance information is incorrect, the nebula area is much larger, or it is a matter of different nebulae that lie in the same viewing direction.
| Designation | IC 417 |
| Type | EN+OCL |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 05h 28m 05.9s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +34° 25' 26" |
| Diameter | 13 × 10 arcmin |
| Metric Distance | 3.000 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | vL, dif, * 6 inv |
| Identification, Remarks | LBN 804; CED 46; Sh2-234 |
Finder Chart
The open star cluster with galactic nebula IC 417 is located in the constellation Auriga at the 5.1 mag bright star φ Aurigae. On 15 December it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is August to May.