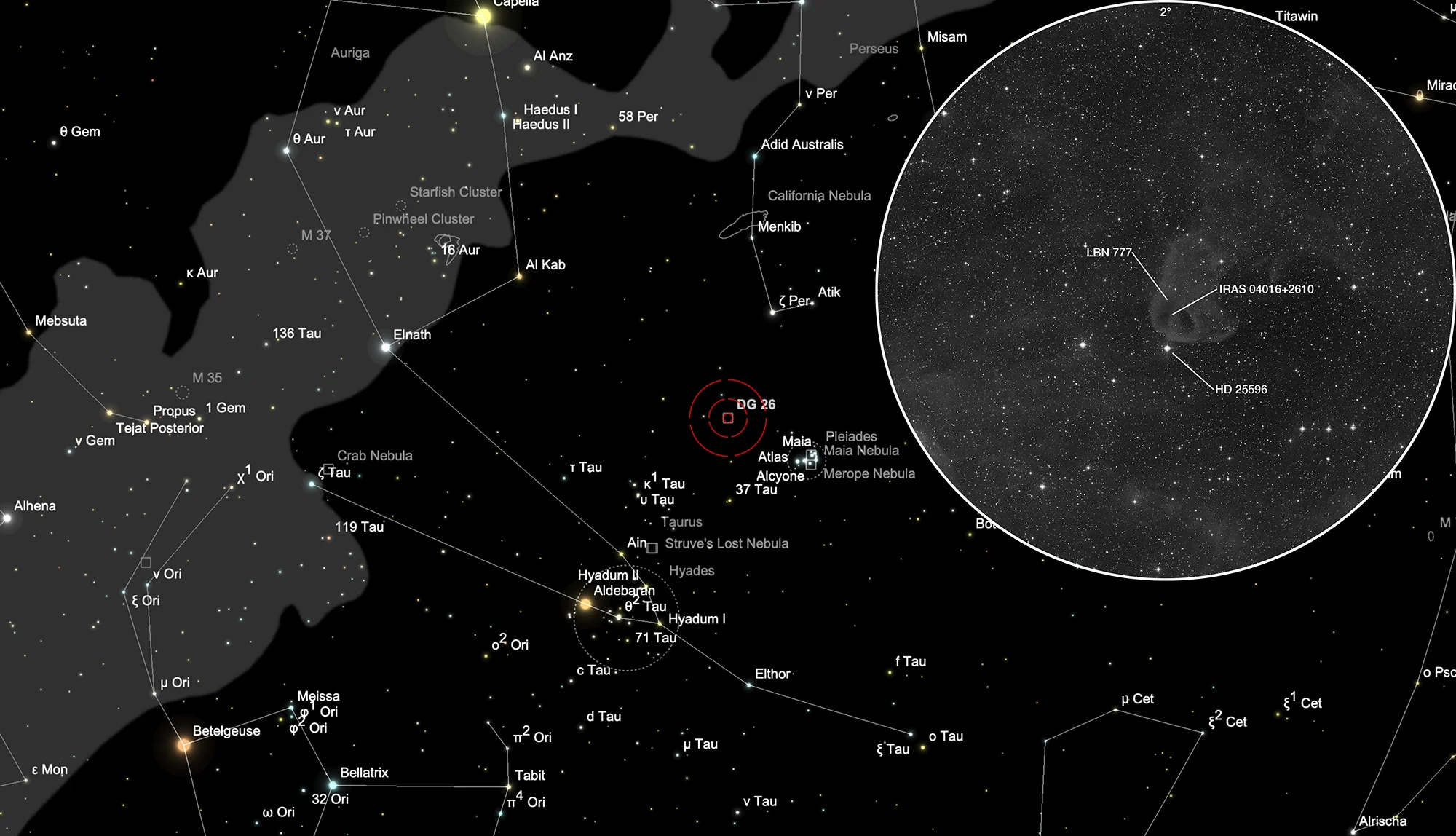
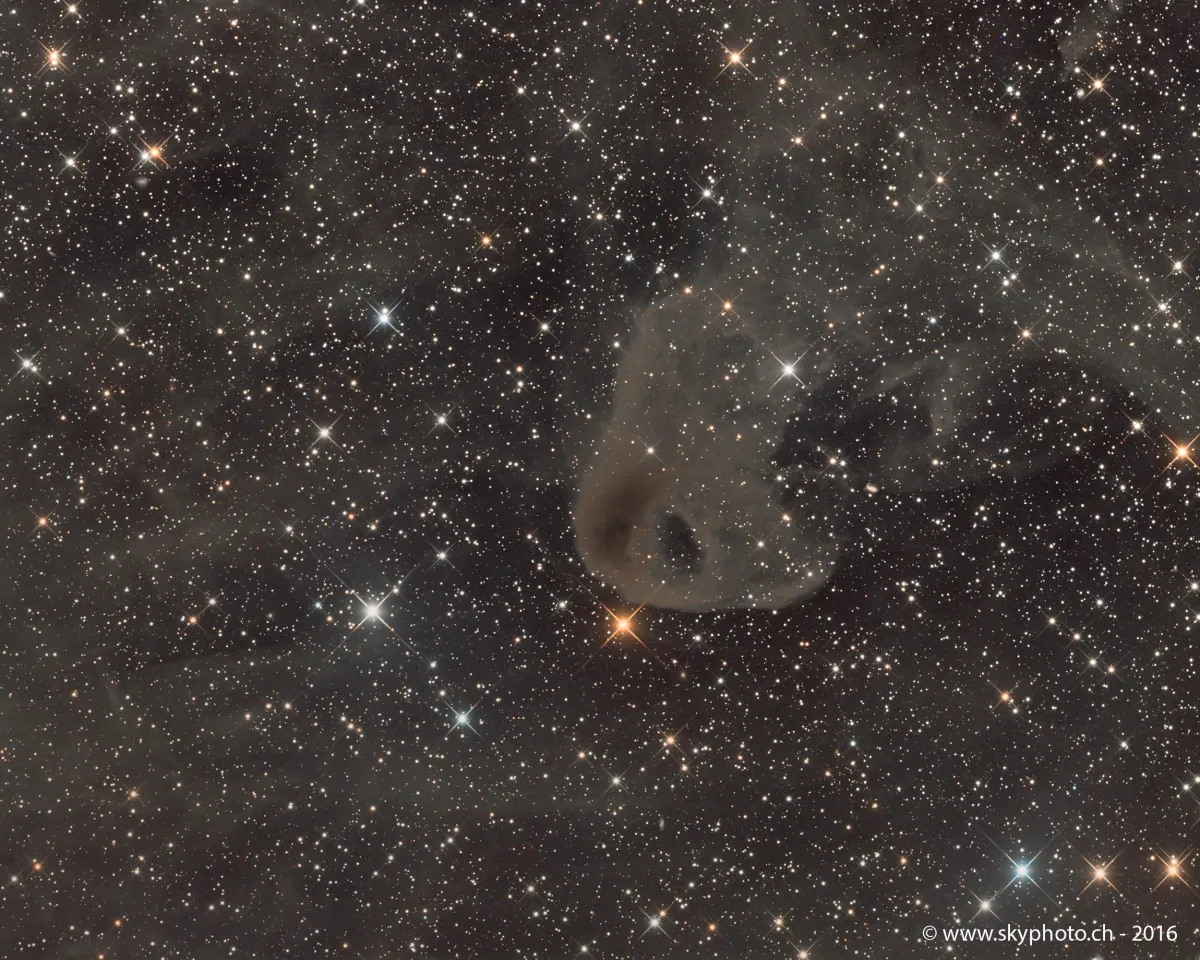
Baby Eagle Nebula (LBN 777)
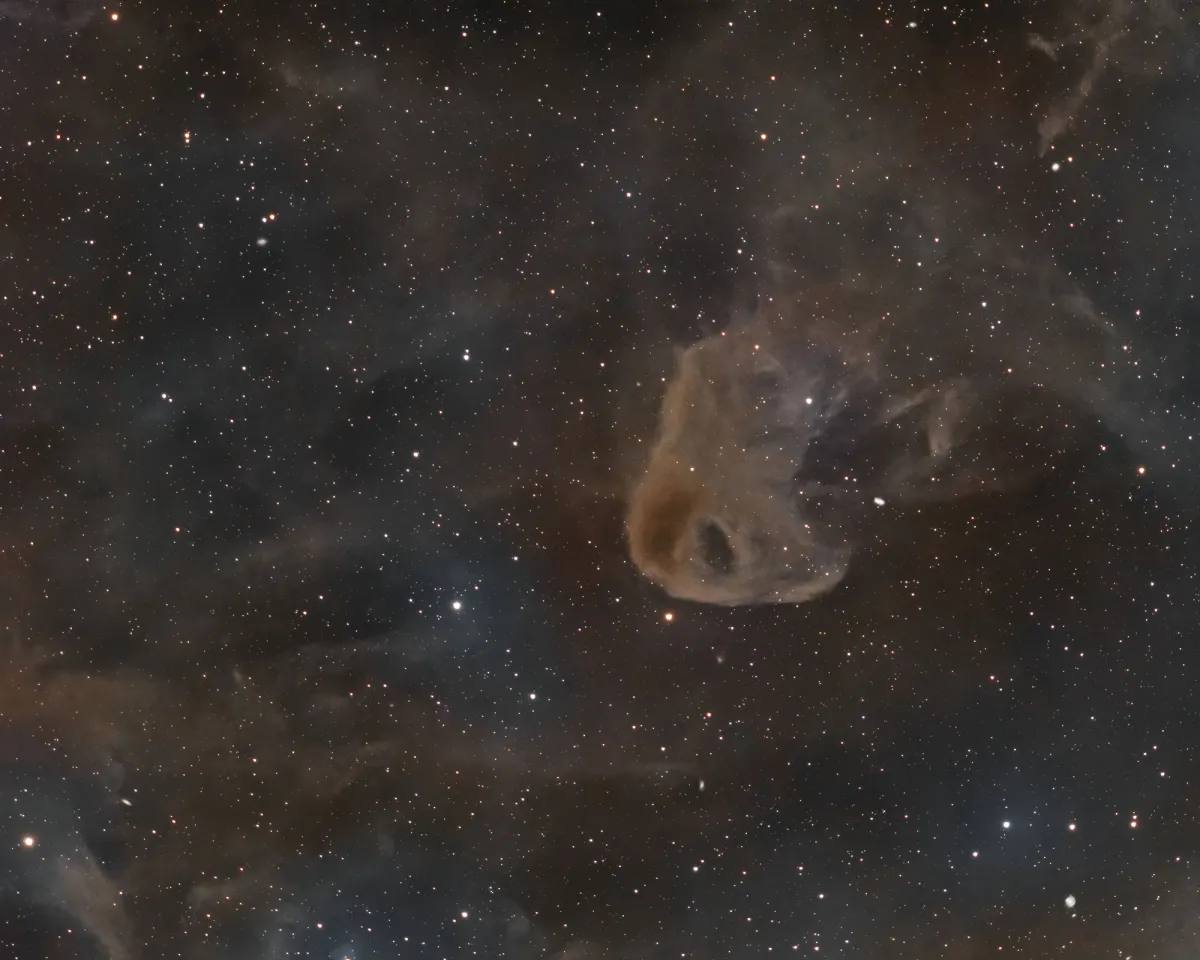


History
Edward. E. Barnard found on his photographs a «Small black spot, elongated nearly N and S, 7' N of BD+25°670 (8.3 mag).» After his death in 1923 this nebula was added as Barnard 207 to the «Photographic Atlas of Selected Regions of the Milky Way», published in 1927. [609] In 1962 by Otto Struve and W. C. Straka studied the POSS photo plates taken with the 48-inch telescope and listed this nebula as number 13 (SS62 13) with the notes «large figure-8 shape.» [716] In 1963 J. Dorschner and J. Gürtler also examined the POSS photo plates and listed the nebula as number 26 (DG 26) with estimated dimensions of 28'x22'. [594] In 1962 Beverly T. Lynds added the dark part of this nebula as LDN 1489 (LBN 167.78-19.21) in her «Catalogue of Dark Nebulae» and in 1965 the bright part as LBN 777 (LBN 168.10-19.04) in her «Catalogue of Bright Nebulae». [270, 473]
Due to its shape LBN 777 is also known as the «Baby Eagle Nebula» or also the «Vulture Head Nebula».
Physical Properties
LBN 777 is a cometary globule in the Taurus-Auriga-Perseus molecular cloud region, at a distance of 140 pc. It is known to host a Class I protostar, IRAS 04016+2610, located on the western edge from the dense core centre at a projected distance of ~8400 au. [717]
Finder Chart
The Baby Eagle Nebula LBN 777 is located approximately 4.5° northeast of the Pleiades in the constellation Taurus. Around 26 November it is in opposition to the sun and therefore culminates at local midnight.