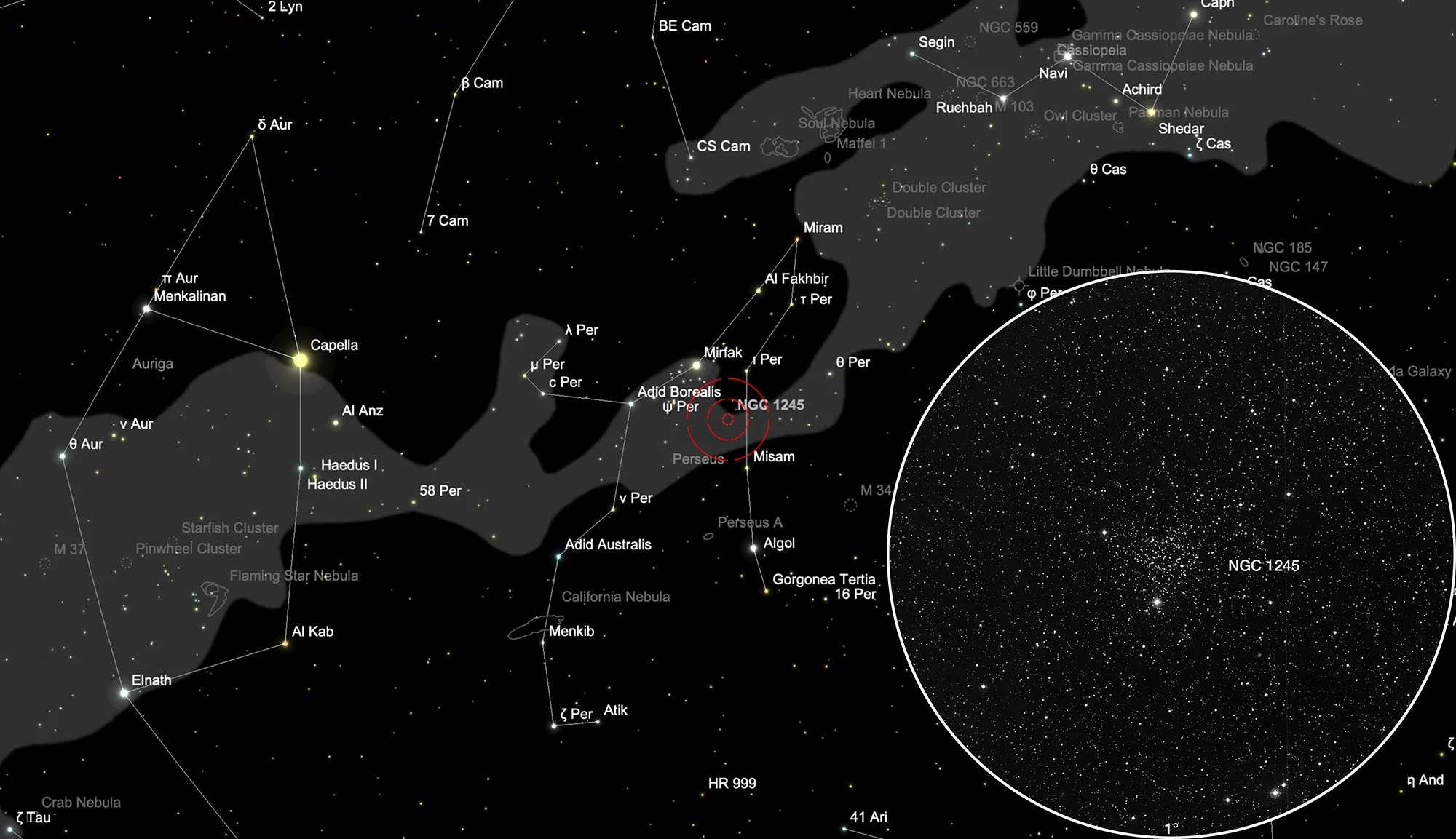
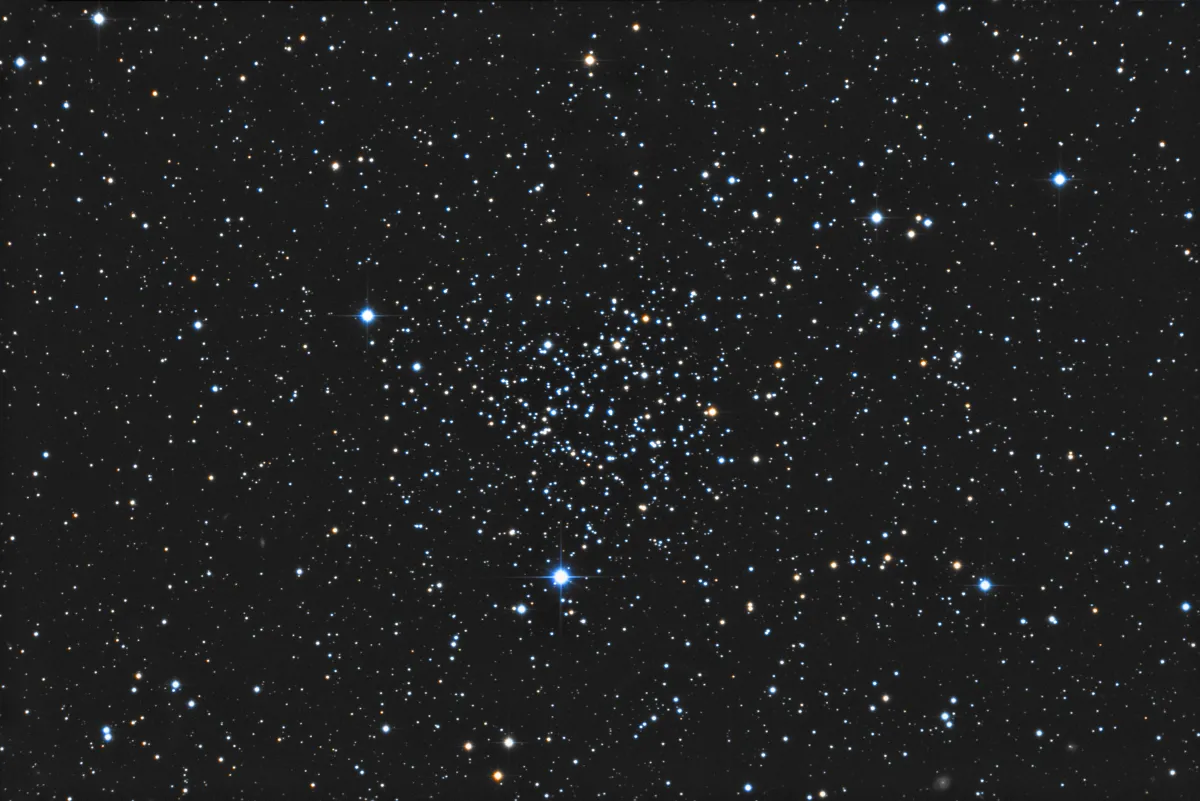
Open Cluster NGC 1245

History
The open star cluster NGC 1245 was discovered on 11 December 1786 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with its 18.7 inch reflector. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 8.4 magnitudes and is of the Tumpler type III1r. [196] [196]
Physical Properties
NGC 1245 is a rich, old, open star cluster with 870 stars. Its age is estimated to be 1.04 ± 0.09 billion years. Its metallicity [Fe/H] = -0.05 ± 0.08 is somewhat lower than that of the sun. The distance in the direction of the galactic anticentre is 2.8 ± 0.2 kpc. The radius of the cluster is 3.10 ± 0.52 arc minutes (2.57 ± 0.43 pc). The total mass of the cluster is estimated to be 2700 ± 600 solar masses. [379, 380]
| Designation | NGC 1245 |
| Type | OCL (III1r) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 03h 14m 41.4s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +47° 14' 19" |
| Diameter | 10 arcmin |
| Visual magnitude | 8.4 mag |
| Metric Distance | 2.876 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | Cl, pL, Ri, C, iR, st 12…15 |
| Identification, Remarks | WH VI 25; h 290; GC 658; OCL 389 |
Finder Chart
The open star cluster NGC 1245 is located in the constellation Perseus. The best observation time is July to April.