Soul Nebula (IC 1848)
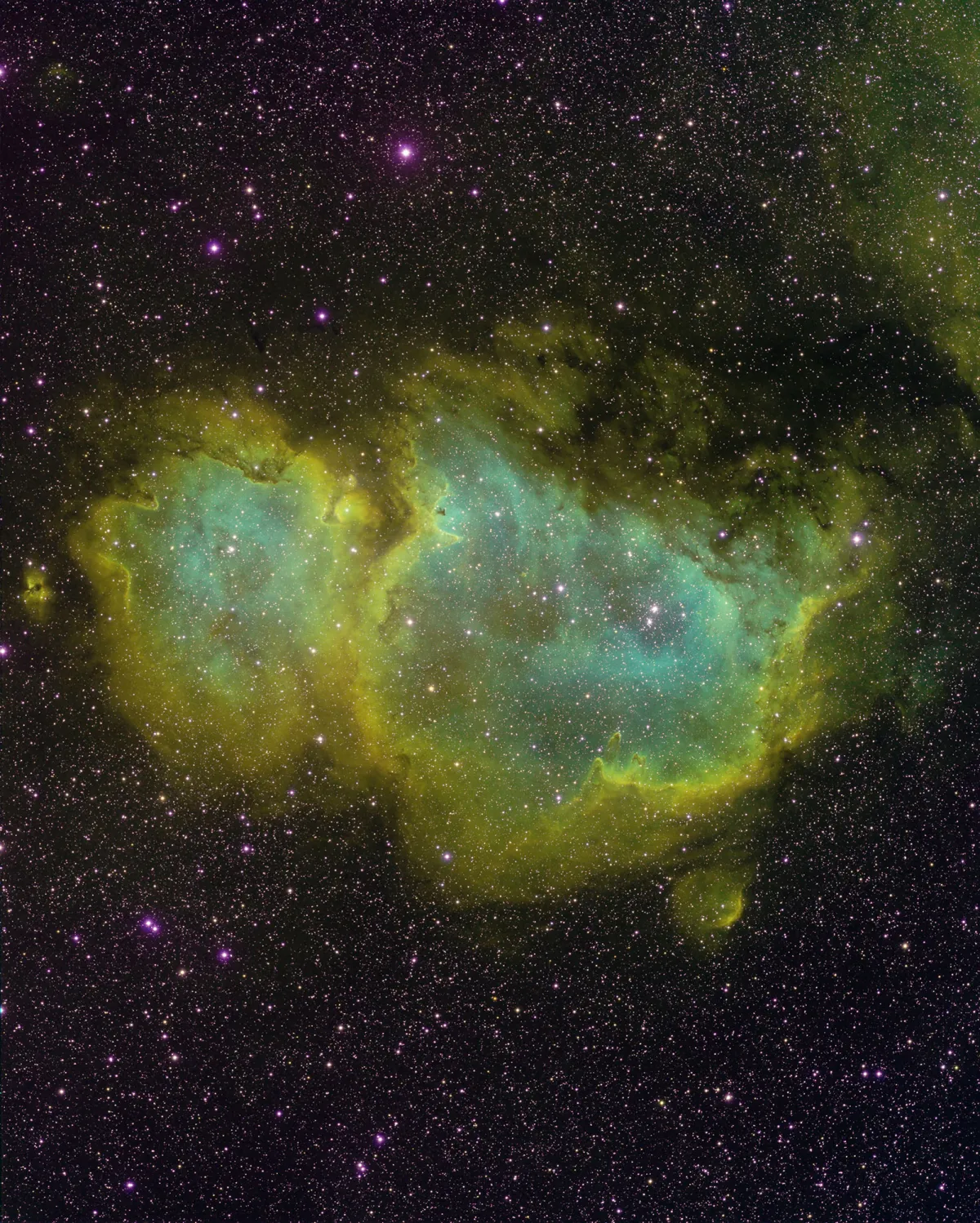
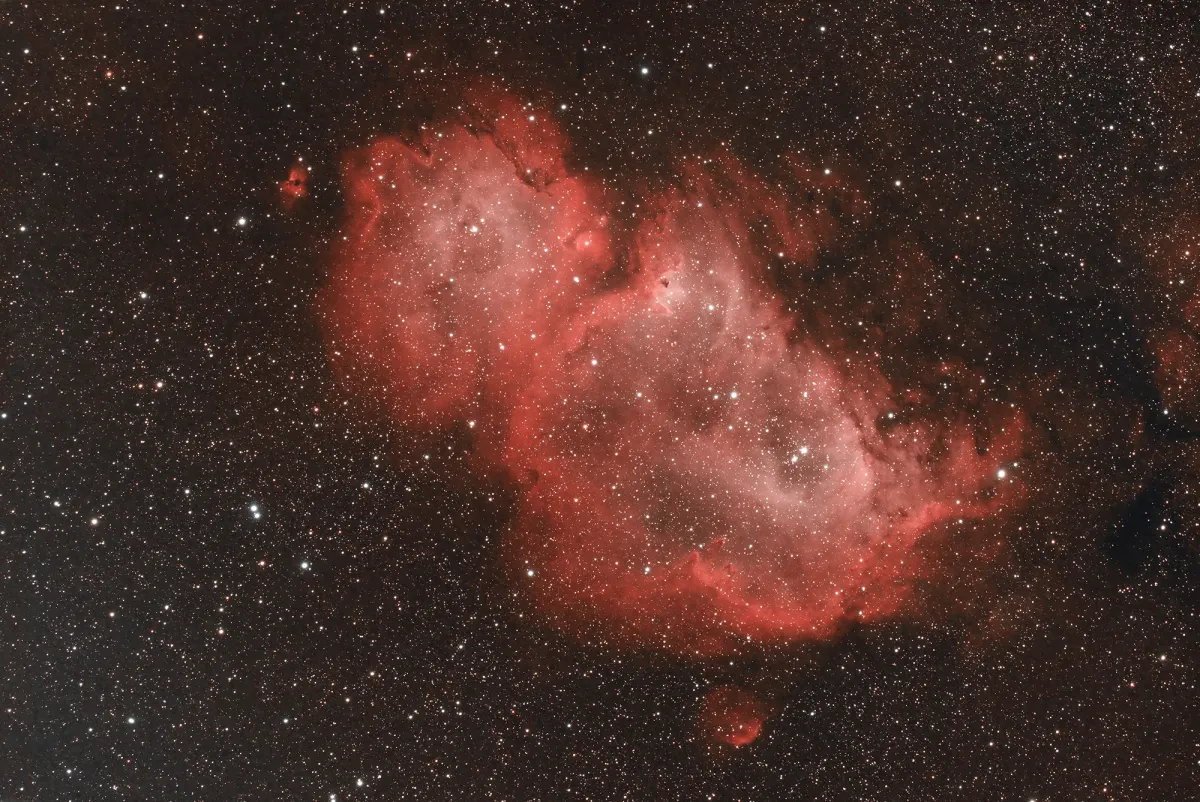


History
American astronomer Edward Emerson Barnard discovered this nebula photographically and notified Dreyer directly, which included it as IC 1848 in his «Second Index Catalogue» published in 1910. The IC description reads: «Cluster, faint stars, extends 8' following, in faint nebulosity.» [315, 364]
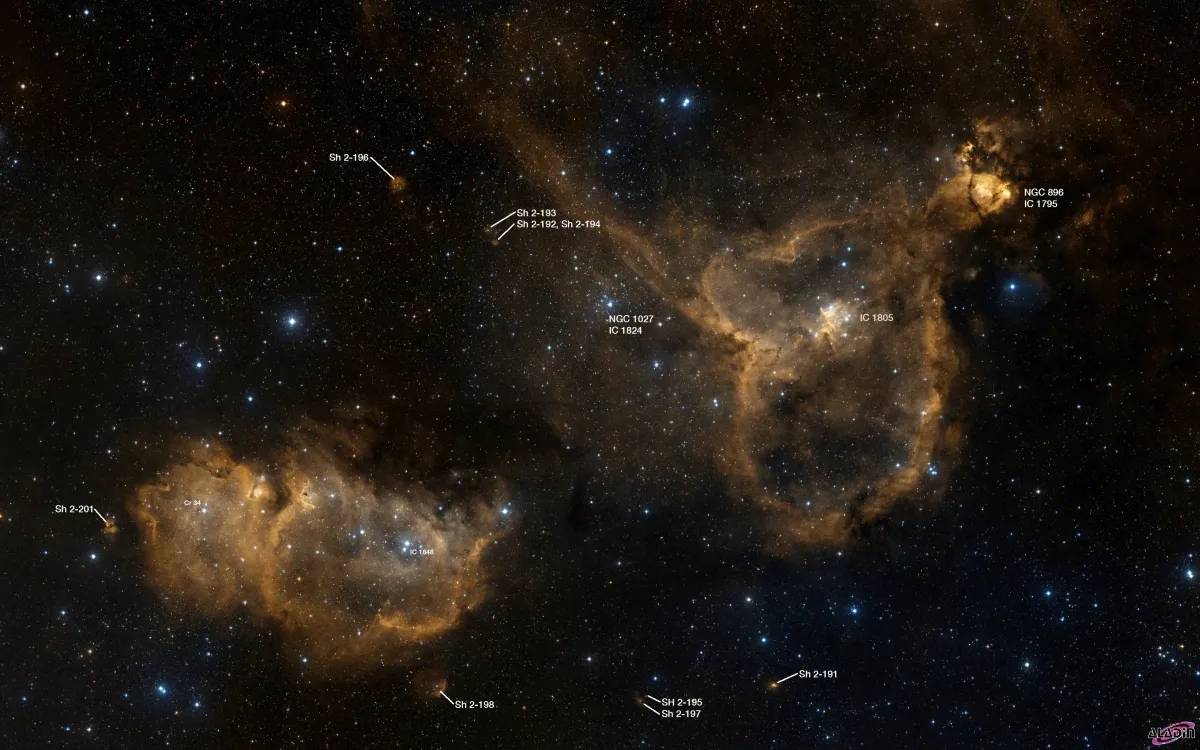
Stewart Sharpless searched in the 1950-ies the photo plates of the «Palomar Observatory Sky Survey» made with the 48 inch Schmidt telescope and published it in 1959 a catalogue of 313 H-II regions. There he identified IC 1848 with Sh 2-199 and some further small patches of nebula as numbers 196, 197, 198, 201. [310]
IC 1848 was nicknamed the «Soul Nebula» because of the neighbouring nebula IC 1805. Both are often referred to as the «Heart and Soul Nebula» when depicted in wide-field images. Another common nickname is «Baby Nebula», as it resembles a baby in shape.
Physical Properties
The Heart (IC 1805) and Soul (IC 1848) nebulae are part of the Cas OB6 Association, a sprawling complex of gas, dust and massive O- and B-class stars in the Perseus Arm. [364] Simbad lists distances ranging from ~1.7 kpc to ~6.1 kpc. [145]
| Name | Type | RA (J2000.0) | Dec (J2000.0) | PM [mas/y] | Parall. [mas] | Rvel [km/s] | z | M Type | Size ['] | Magnitudes | Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC 1848 | OpC | 02h 51m 19s | +60° 25' 32" | -0.372 | 0.415 | -57.452 | -0.000192 | 24 × 24 | B 6.87; V 6.5 | C 0247+602; CTB 11; Cl Bica 225; Cl Collinder 32; DA 84; GCRV 53465; IC 1848; LBN 137.24+00.77; LBN 667; LISC 0863; OCISM 93; OCl 364; OCl 364.0; SH 2-199; VRO 60.02.01; W 5; [HXW2022] OC-0255; [KPR2004b] 38; [KPS2012] MWSC 0236 | |
| IC 1871 | HII | 03h 03m 00s | +60° 24' 00" | IC 1871; LBN 138.50+01.59; LBN 675 | |||||||
| Sh 2-196 | HII | 02h 51m 34s | +62° 12' 42" | 87GB 024732.3+620028; BWE 0247+6200; CGPSE 135; F3R 4009; GB6 B0247+6200; LBN 136.40+02.50; LBN 664; SH 2-196; WB 0247+6200; WN B0247.5+6200; [PBD2003] G136.4+02.5 | |||||||
| Sh 2-197 | GiG | 02h 41m 55s | +59° 36' 15" | 14 | 0.000047 | Sbc | B 16; J 6.91; H 5.742; K 5.215 | 2MASX J02415509+5936147; AKARI-FIS-V1 J0241537+593632; AKARI-IRC-V1 J0241548+593615; Anon 0238+59; Dwingeloo 136.5-00.3; LEDA 10217; MSX6C G136.4978-00.3252; Maffei 2; SH 2-197; SPB 35; UGCA 39; WISE J024155.07+593616.4; WISEA J024155.05+593616.1; Weinberger 21; ZOAG G136.50+00.33; ZOAG G136.50-00.33; ZOAG G136.51-00.33; [CHM2007] HDC 173 J024155.09+5936147; [CHM2007] LDC 264 J024155.09+5936147; [KSP2003] G136.4978-00.3253; [KSP2003] J024154.84+593616.6; [M98c] 023807.9+592324; [VDD93] 20 | |||
| Sh 2-198 | HII | 02h 50m 02s | +59° 42' 00" | SH 2-198 | |||||||
| Sh 2-201 | HII | 03h 03m 18s | +60° 27' 53" | GAL 138.50+01.64; IRAS 02593+6016; IRCO 3963; RAFGL 416; SH 2-201; WB89 465; [BNM96] 138.498+1.641; [L89b] 138.486+01.635; [LG97] B02593+6016 |
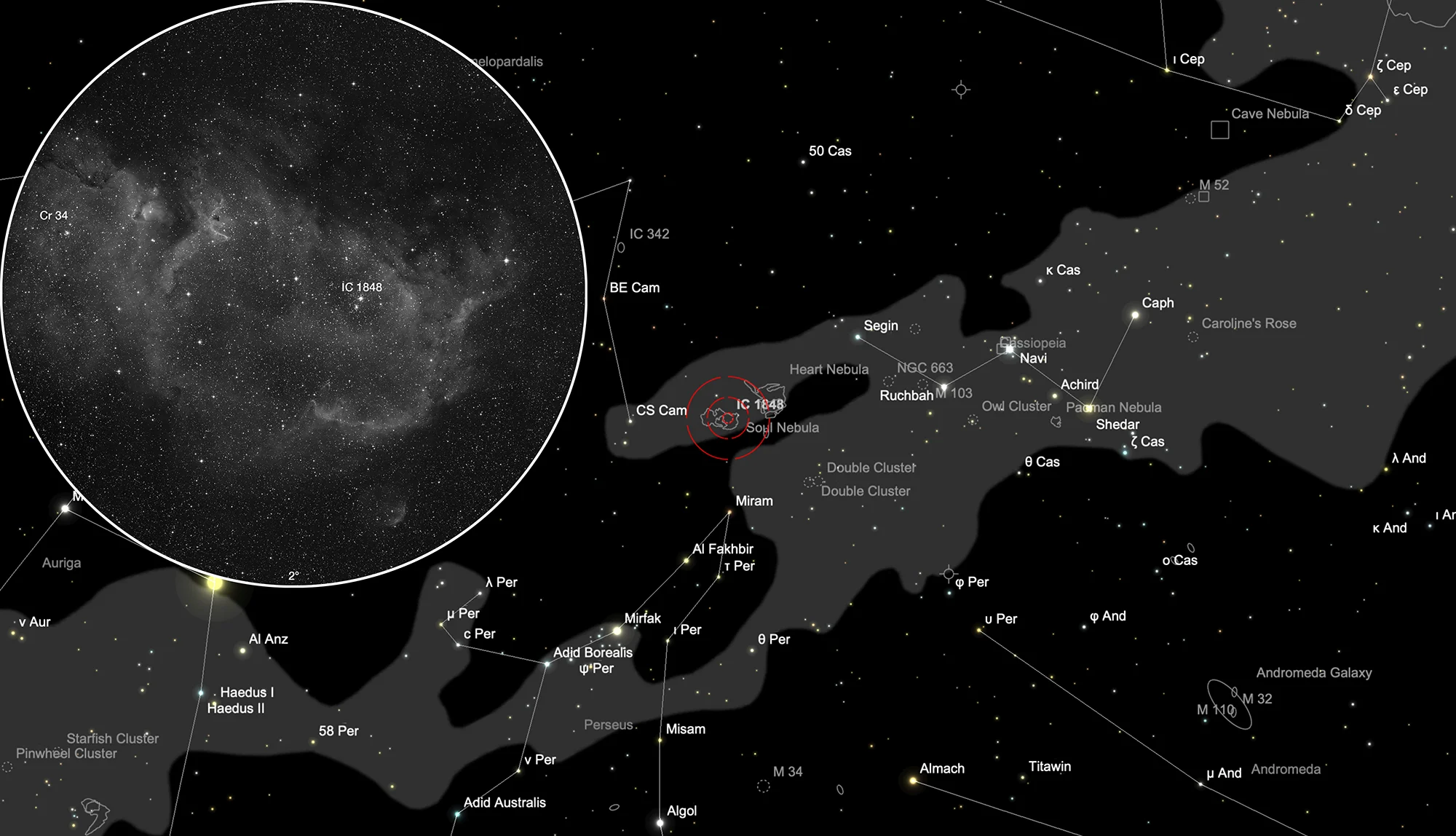
Finder Chart
The Soul Nebula is located in the constellation Cassiopeia. In Central Europe it is circumpolar. The best time to observe, however, is July to April, when the constellation is highest at night. About 2.5 degrees further west is the Heart Nebula (Sh 2-199 with cluster IC 1805).