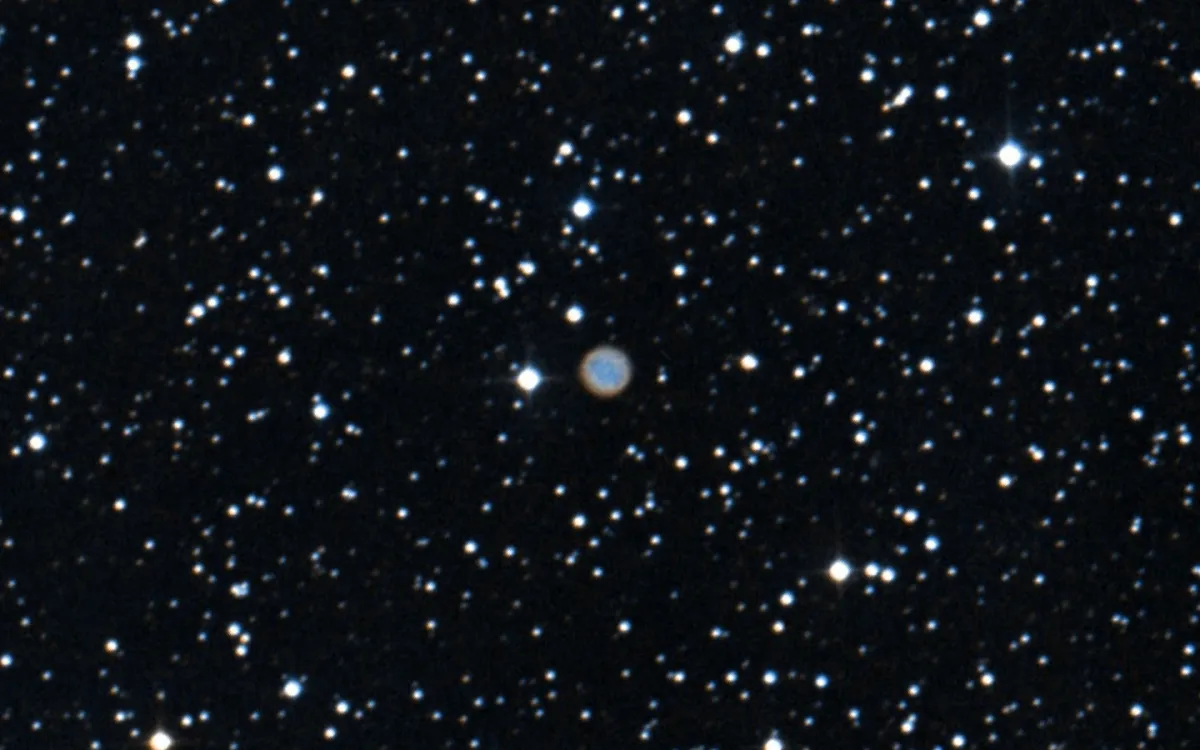
Planetary Nebula BV 5-3

History
In 1956 the German-American astronomer Erika Böhm-Vitense discovered three new planetary nebulae during a study of extragalactic nebulae at Lick Observatory. This nebula here was the third listed in table V of her publication, hence the designations Böhm Vitense 5-3, BV 5-3, or also sometimes just BV 3. The other ones on this list were BV 5-1 and BV 5-2. [548]
Physical Properties
According to Simbad the magnitudes measured in different bands are: B 10.3, V 10.3. [145]
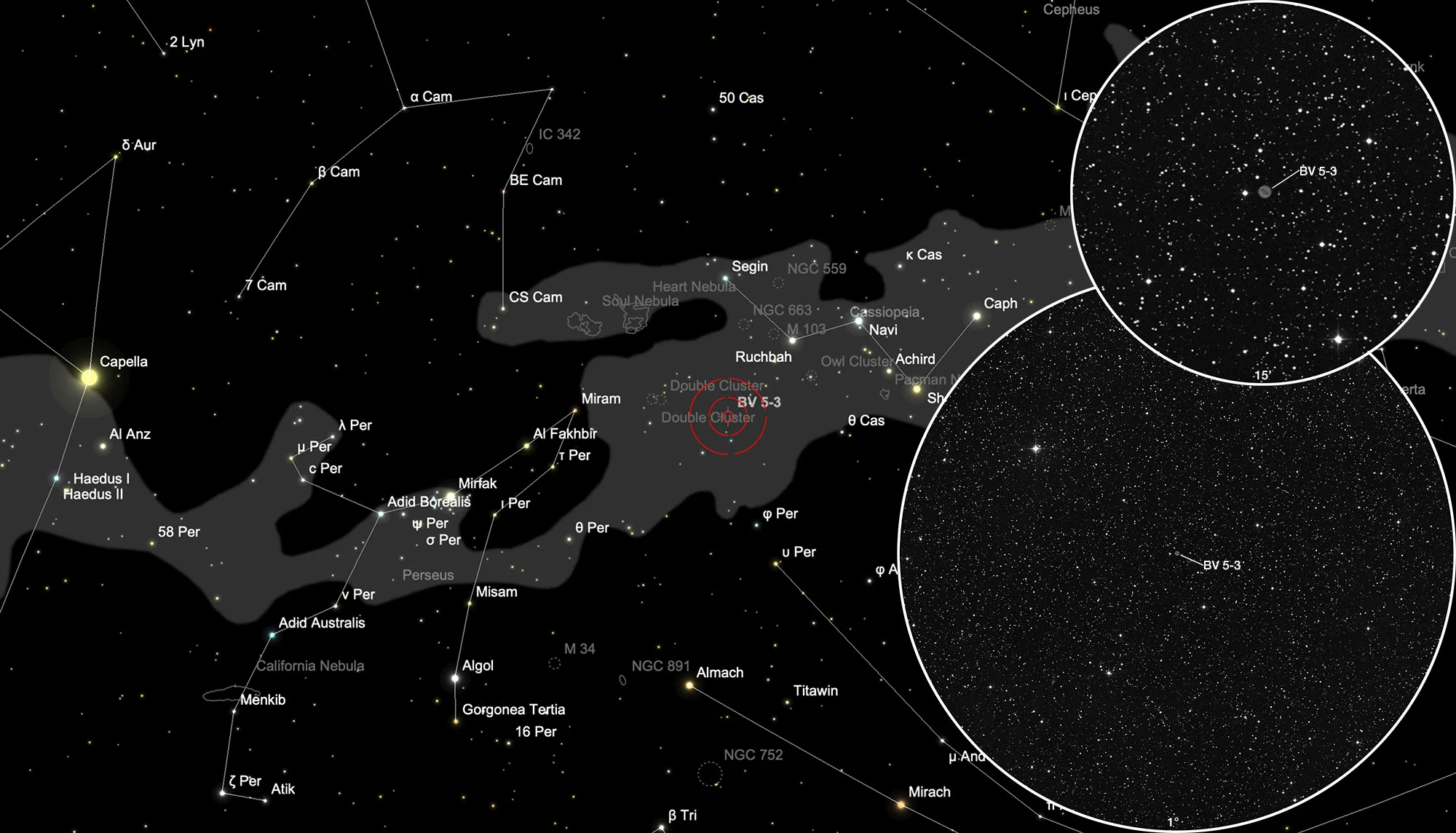
| Designations | PN G131.4-05.4: BV 5-3, PK 131-05.1, ARO 203 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 01h 53m 02s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +56° 24' 22" |
| Dimensions | 24." : (optical) |
| Radial Velocity | -59.0 ± 25.0 km/s |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 18. |
| Discoverer | BOHM-VITENSE 1956 |
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Böhm-Vitense 5-3 can be found in the constellation Perseus. On 24 October it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The object is circumpolar, but from June to March it is highest in the sky and best for observing.
Visual Observation
300 mm Aperture: It took quite a while to clearly determine the position of planetary nebula BV 5-3, as there are no distinctive star patterns in the surrounding area. Unfortunately, attempts to observe the nebula in the 21 mm and 13 mm Ethos, both with and without an OIII filter, were unsuccessful. This may also have been due to suboptimal observation conditions with light cirrus clouds. — 300 mm f/4 Popp-Newton, Hasliberg, SQM 20.9, 18. 10. 2025, Bernd Nies