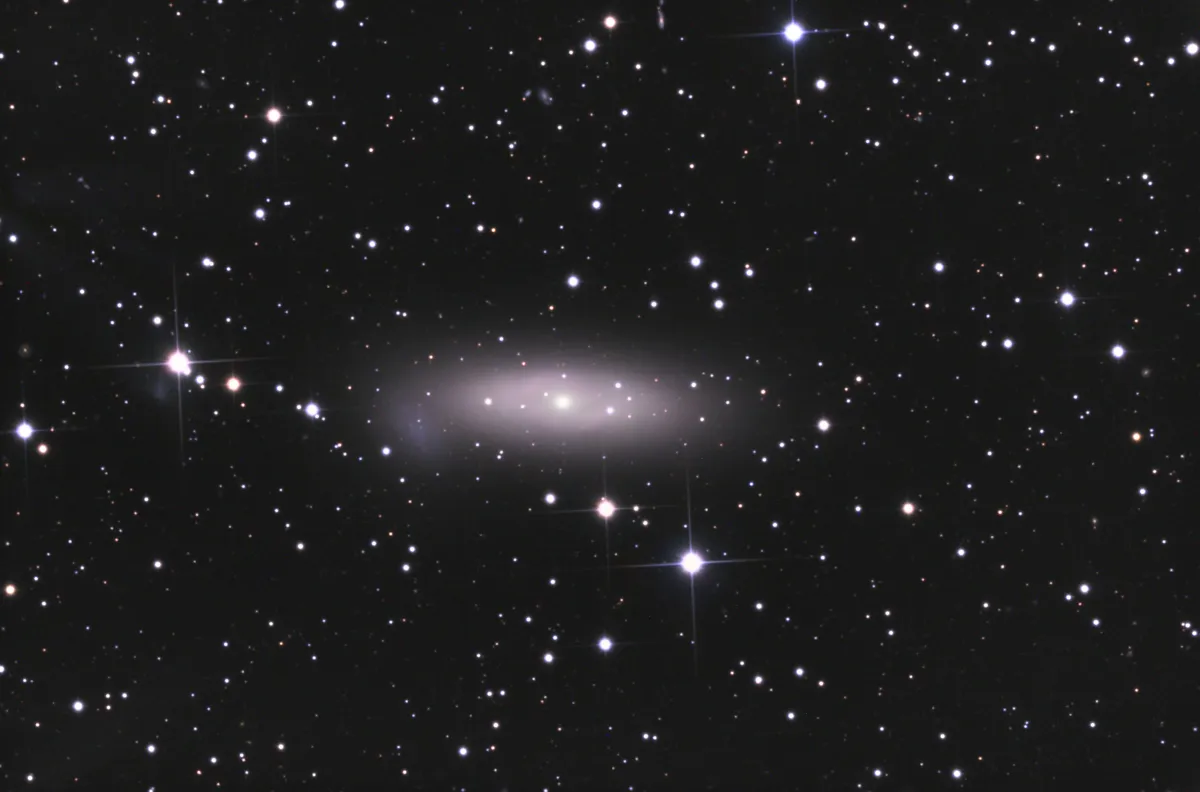
Galaxy NGC 1023

History
The galaxy NGC 1023 was discovered on 18 October 1786 by William Herschel with his 18.7 inch reflecting telescope. [277] Halton Arp listed NGC 1023 and the companion galaxy NGC 1023A in his 1966 «Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies» under the name Arp 135 as one Galaxy with nearby fragments. [199]
Physical Properties
In the centre of this galaxy of morphological type SB(rs)0- is a supermassive black hole with about 40 to 60 million solar masses. The distance from NGC 1023 is approximately 11 Mpc. [428] The galaxy is the brightest member of the LGG 70 galaxy group. The closest companion is the magellanic, irregular dwarf galaxy NGC 1023A about 2.7 arc minutes east of the centre of NGC 1023, which corresponds to a projected distance of about 8 kpc. The two galaxies are connected by a bridge of neutral hydrogen, suggesting an ongoing interaction that began about two billion years ago. [429]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 1023 | 02 40 24.1 | +39 03 48 | Gx (E/SB0) | 10.4 | 9.4 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 7.4 × 2.5 | 87 | 0.002125 | 8.98 | 11.620 | vB, vL, vmE, vvmbM | WH I 156; h 242; GC 575; UGC 2154; MCG 6-6-73; CGCG 523-83; Arp 135 |
| NGC 1023 A | 02 40 36.9 | +39 03 37 | Gx (IBm) | 14.3 | 13.6 | 0.7 | 13.8 | 1.3 × 0.7 | 14 | 0.002478 | 10.47 | vB, vL, vmE, vvmbM | WH I 156; h 242; GC 575; Arp 135 |
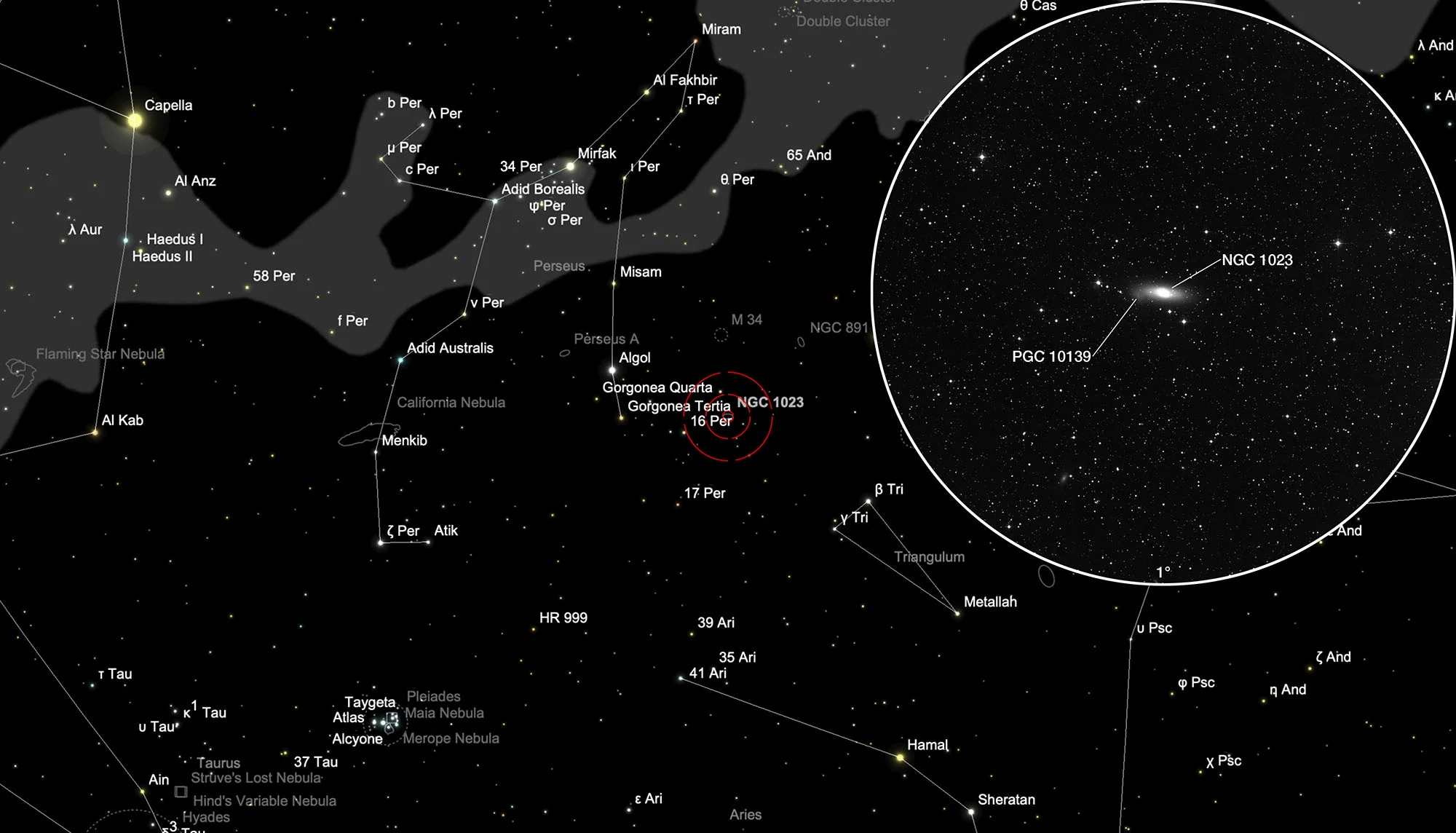
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 1023 is located in the constellation Perseus. The best observation time is July to April.