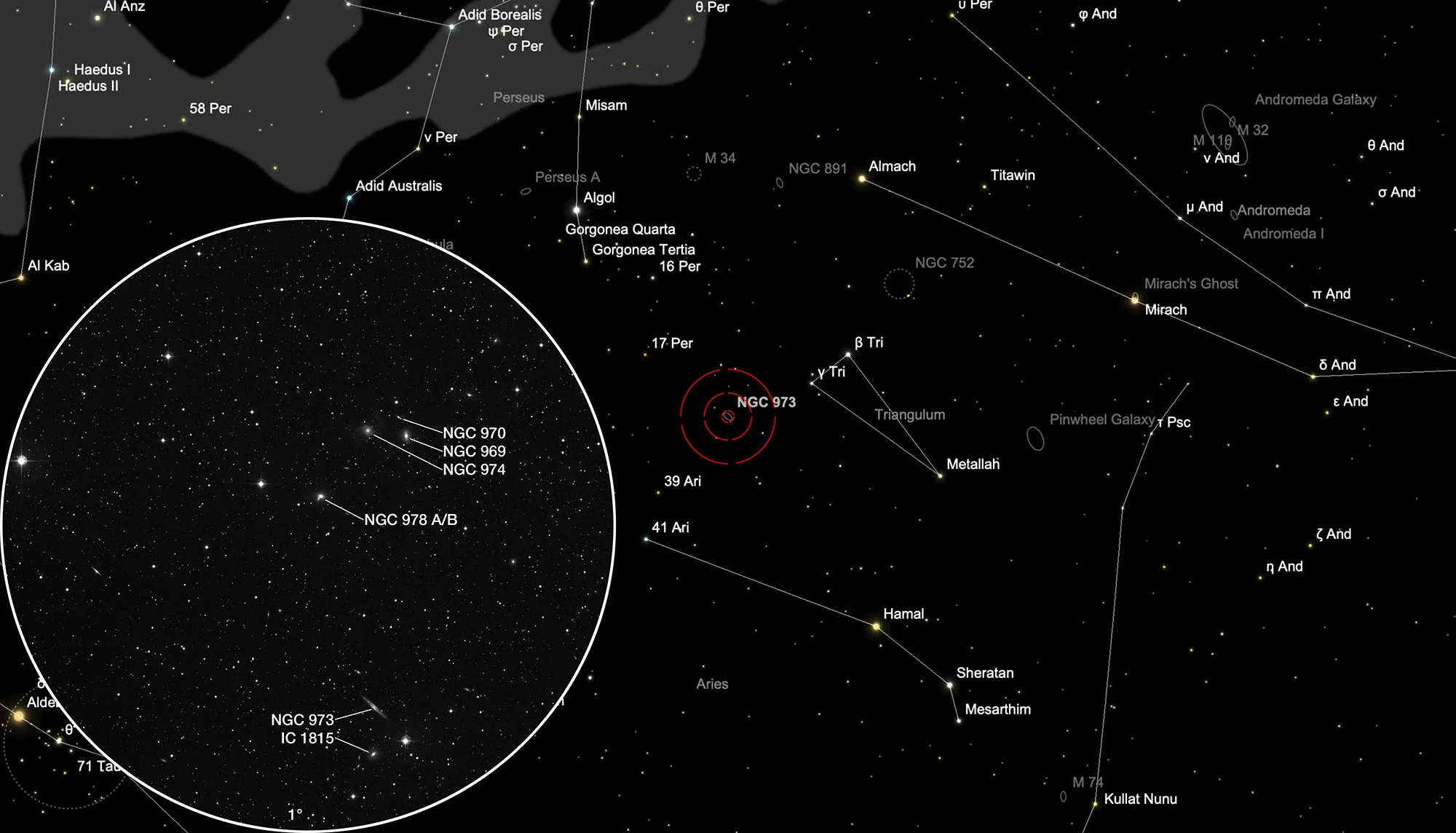
NGC 973 Galaxy Group


History
The galaxies NGC 969, NGC 974 and NGC 978 were discovered on 22 November 1827 by John Herschel with his 18.3 inch reflecting telescope in Slough, England. On 14 September 1850, the engineer Bindon Stoney set up the 72 inch «Leviathan» reflecting telescope in Birr Castle, Ireland. His employer William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, on this spot and discovered the galaxy NGC 970. NGC 973 was discovered on 30 October 1885 by the American astronomer Lewis Swift with a 16 inch reflecting telescope. IC 1815 was discovered on 20 January 1898 discovered by the French astronomer Stephane Javelle with the 76 cm lens telescope of the Observatoire de Nice.[196, 277]
Physical Properties
The galaxies NGC 969, NGC 973, NGC 974, NGC 978 and IC 1815 show similar redshifts in the range z ≈ 0.015 and belong to the NGC 973 galaxy group, which is located at a distance of about 61 Mpc to 69 Mpc. NGC 973 is a Seyfert 2 galaxy that we are looking directly at the edge. NGC 970 is a redshift of z ≈ 0.033 much further away and does not belong to the group. [145]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 969 | 02 34 08.0 | +32 56 47 | Gx (S0) | 13.3 | 12.3 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 1.7 × 1 | 3 | 0.015037 | 63.52 | S, R, psbM, 1st of 5 | h 231; GC 557; UGC 2039; MCG 5-7-8; CGCG 505-10 | |
| NGC 970 | 02 34 11.7 | +32 58 35 | Gx (S) | 15.6 | 14.8 | 0.8 | 12.5 | 0.7 × 0.2 | 55 | 0.032673 | 138.0 | vF, vS, R, 2nd of 5 | GC 558; MCG 5-7-9; CGCG 505-11 | |
| NGC 973 | 02 34 20.1 | +32 30 20 | Gx (Sb) | 13.6 | 12.8 | 0.8 | 13.3 | 3.7 × 0.5 | 48 | 0.016195 | 68.41 | 62.630 | eeF, S, mE, pB * nr sp | UGC 2048; MCG 5-7-13; CGCG 505-14; IRAS 02313+3217; FGC 314; KUG 0231+322 |
| NGC 974 | 02 34 25.7 | +32 57 18 | Gx (Sb) | 13.6 | 12.8 | 0.8 | 13.4 | 1.7 × 1.2 | 63 | 0.015010 | 63.40 | vF, R, bM, 4th of 5 | h 233; GC 561; UGC 2049; MCG 5-7-12; CGCG 505-15; NPM1G +32.0104; IRAS 02314+3243 | |
| NGC 978 | 02 34 47.0 | +32 50 42 | Gx (E-S0) | 13.2 | 12.2 | 1.0 | 12.6 | 1.3 × 1 | 62 | 0.015831 | 66.87 | pB, R, 5th of 5 | h 234; GC 563; NGC 978A; UGC 2057; MCG 5-7-16; CGCG 505-18; KCPG 71A | |
| NGC 978 A | 02 34 47.0 | +32 50 42 | dup | 13.2 | 12.2 | 1.0 | 12.6 | 1.3 × 1 | 62 | 0.015831 | 66.87 | pB, R, 5th of 5 | h 234; GC 563; NGC 978; UGC 2057; MCG 5-7-16; CGCG 505-18; KCPG 71A | |
| NGC 978 B | 02 34 48.1 | +32 50 33 | Gx (S0) | 15.5 | 14.5 | 1.0 | 11.6 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 166 | 0.014462 | 61.09 | pB, R, 5th of 5 | h 234; GC 563; MCG 5-7-17; KCPG 71B | |
| IC 1815 | 02 34 19.9 | +32 25 48 | Gx (SB0) | 14.3 | 13.3 | 1.0 | 13.6 | 1.4 × 1.1 | 141 | 0.015684 | 66.25 | F, S, R, gbMN | UGC 2047; MCG 5-7-14; CGCG 505-13; NPM1G +32.0103 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy is located in the constellation Triangulum. On 4 November it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time to observe is July to April, when it is highest at night.