Galaxy Messier 49

History
The galaxy was discovered by Charles Messier on 19 February 1771. He described it as «difficult to see in a 3.5 foot [focal length] telescope». It was the first and largest galaxy in the Virgo Cluster that he had discovered. [4, 196]
Physical Properties
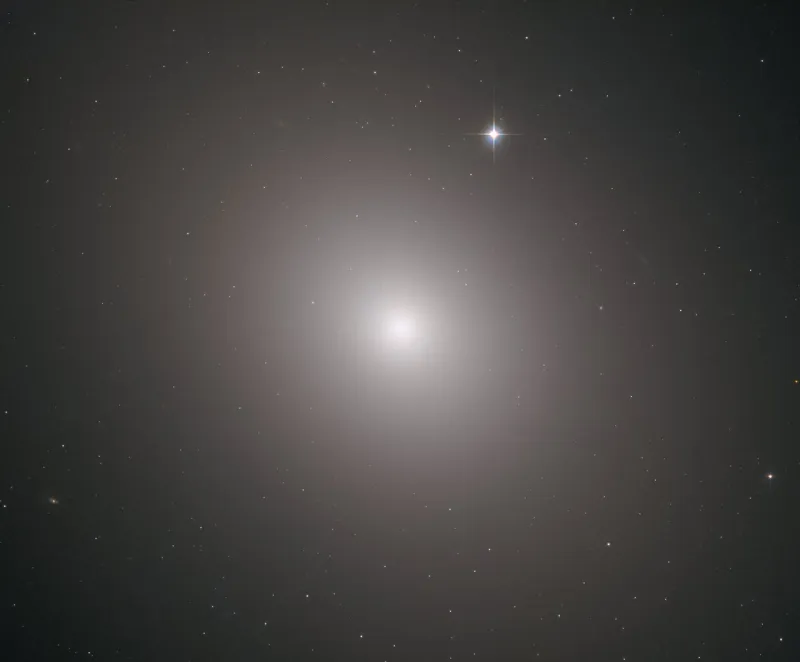
M 49 is an elliptical Seyfert 2 galaxy of the morphological type E2, contains around 200 billion mostly old stars. The last stars formed here about six billion years ago - before the birth of our sun. The diameter is 157'000 light years. The measured distances range from 16.8 Mpc to 19.28 Mpc (approximately 55 to 63 million light years). A supermassive black hole with about 500 million solar masses is up to mischief in the extremely active core and is a powerful source of X-rays. M 49 is also rich in globular clusters. About 6000 were counted here. The Milky Way has just 150 of them. The average age of globular clusters is around 10 billion years. [145, 273]
| Designation | NGC 4472 |
| Type | Gx (E2) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 12h 29m 46.7s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +08° 00' 00" |
| Diameter | 10.2 × 8.3 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 9.4 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 8.4 mag |
| Surface brightness | 13.2 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 155° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.003326 |
| Distance derived from z | 14.05 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 16.000 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | vB, L, R, mbM, r |
| Identification, Remarks | WH I 7; h 1294; GC 3021; M 49; UGC 7629; MCG 1-32-83; Arp 134; VCC 1226; CGCG 42-134 |
Further Galaxies Nearby
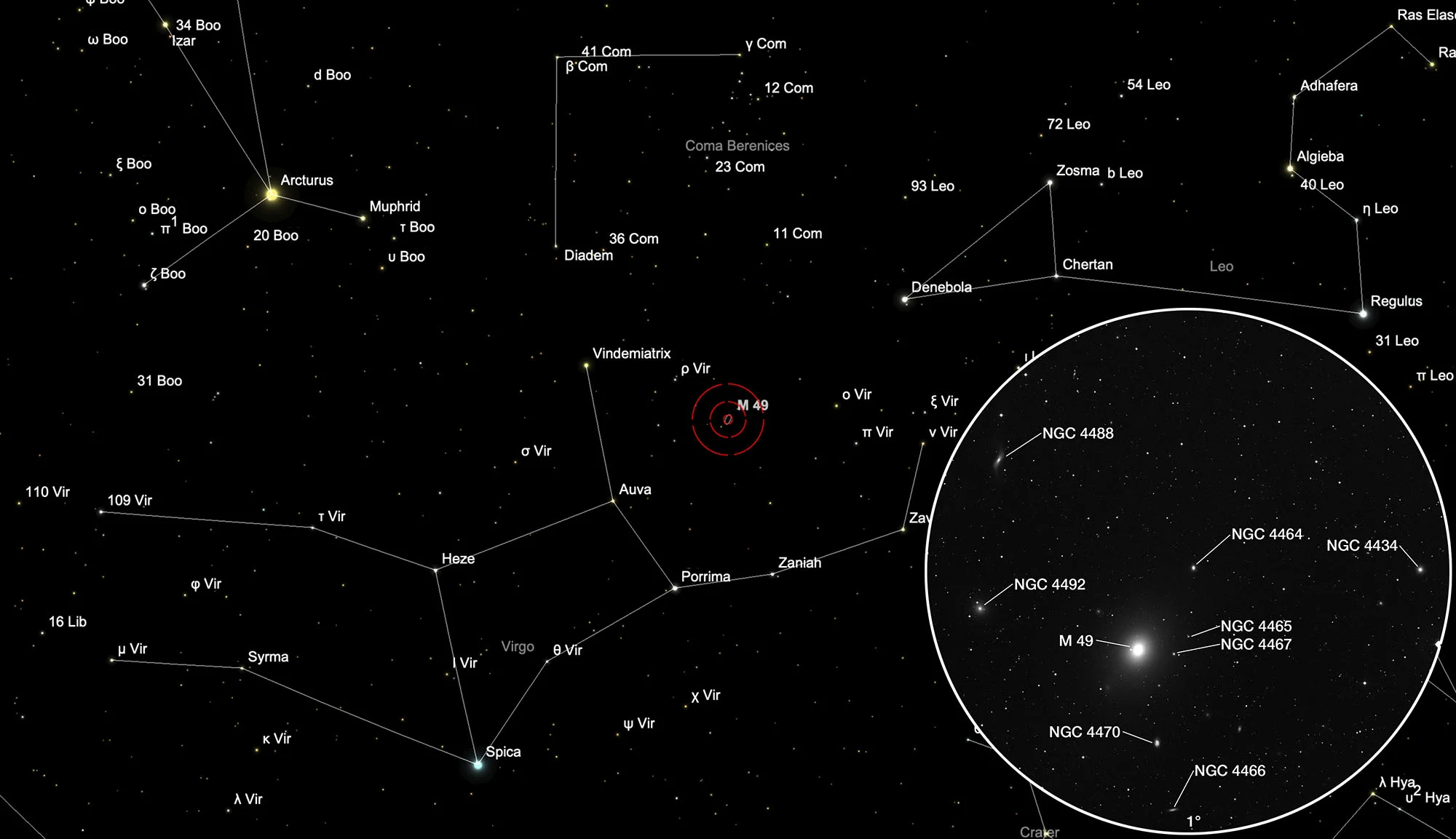
Looking in the direction of M 49 there are other much smaller and fainter galaxies, which are listed here in tabular form only for the sake of shape.
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4434 | 12 27 36.6 | +08 09 16 | Gx (E0) | 13.0 | 12.2 | 0.8 | 12.8 | 1.4 × 1.4 | 0.003572 | 15.09 | 21.990 | pF, vS | WH II 497; GC 2989; UGC 7571; MCG 1-32-69; CGCG 42-115; VCC 1025 | |
| NGC 4464 | 12 29 21.2 | +08 09 25 | Gx (E) | 13.5 | 12.5 | 1.0 | 12.2 | 0.9 × 0.7 | 171 | 0.004146 | 17.51 | 15.350 | F, vS, R, pgbM | WH III 483; h 1292; GC 3018; UGC 7619; MCG 1-32-78; CGCG 42-128; VCC 1178 |
| NGC 4465 | 12 29 23.5 | +08 01 34 | Gx (Sc) | 15.2 | 14.5 | 0.7 | 12.3 | 0.5 × 0.3 | 95 | 0.024634 | 104.0 | vF, v dif | CGCG 42-127; VCC 1182 | |
| NGC 4466 | 12 29 30.6 | +07 41 49 | Gx (Sab) | 14.4 | 13.5 | 0.9 | 12.2 | 1.1 × 0.3 | 101 | 0.002512 | 10.61 | 29.700 | vF, pS, iR | WH [II 18]; GC 5653; UGC 7626; MCG 1-32-81; CGCG 42-131; VCC 1193 |
| NGC 4467 | 12 29 30.3 | +07 59 34 | Gx (E2) | 14.8 | 13.8 | 1.0 | 13.9 | 0.4 × 0.3 | 45 | 0.004747 | 20.05 | 16.370 | vF, vS, lE | WH II 18; GC 3020=5654; MCG 1-32-80; CGCG 42-130; ARAK 369; VCC 1192 |
| NGC 4470 | 12 29 37.9 | +07 49 26 | Gx (Sa) | 13.1 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 12.1 | 1.3 × 0.9 | 0 | 0.007809 | 32.98 | 15.830 | F, pL, iR, bM | WH II 19, III 498; h 1247; GC 3020; UGC 7627; MCG 1-32-82; IRAS 12270+0806; VCC 1205; CGCG 42-132 |
| NGC 4471 | 12 29 42.0 | +07 53 46 | * | 14.4 | vF, vS (not found by d'A) | GC 5655 | ||||||||
| NGC 4488 | 12 30 51.3 | +08 21 35 | Gx (SB0-a) | 13.1 | 12.2 | 0.9 | 13.9 | 4.1 × 1.7 | 176 | 0.003242 | 13.69 | vF, vS, lE | WH III 484; h 1302; GC 3037; UGC 7653; MCG 2-32-104; CGCG 70-137; VCC 1318 | |
| NGC 4492 | 12 30 59.7 | +08 04 41 | Gx (Sa) | 13.2 | 12.6 | 0.6 | 13.5 | 1.7 × 1.6 | 90 | 0.005804 | 24.52 | 16.800 | pF, pL, vglbM, 2 st nr | WH II 499; h 1305; GC 3040; IC 3438; UGC 7656; MCG 1-32-89; CGCG 42-141; VCC 1330 |
Finder Chart
M 49 is located in the constellation Virgo about halfway between the stars Vindemiatrix (π Virginis) and ν Virginis. The best way to see the galaxy is from December to September.