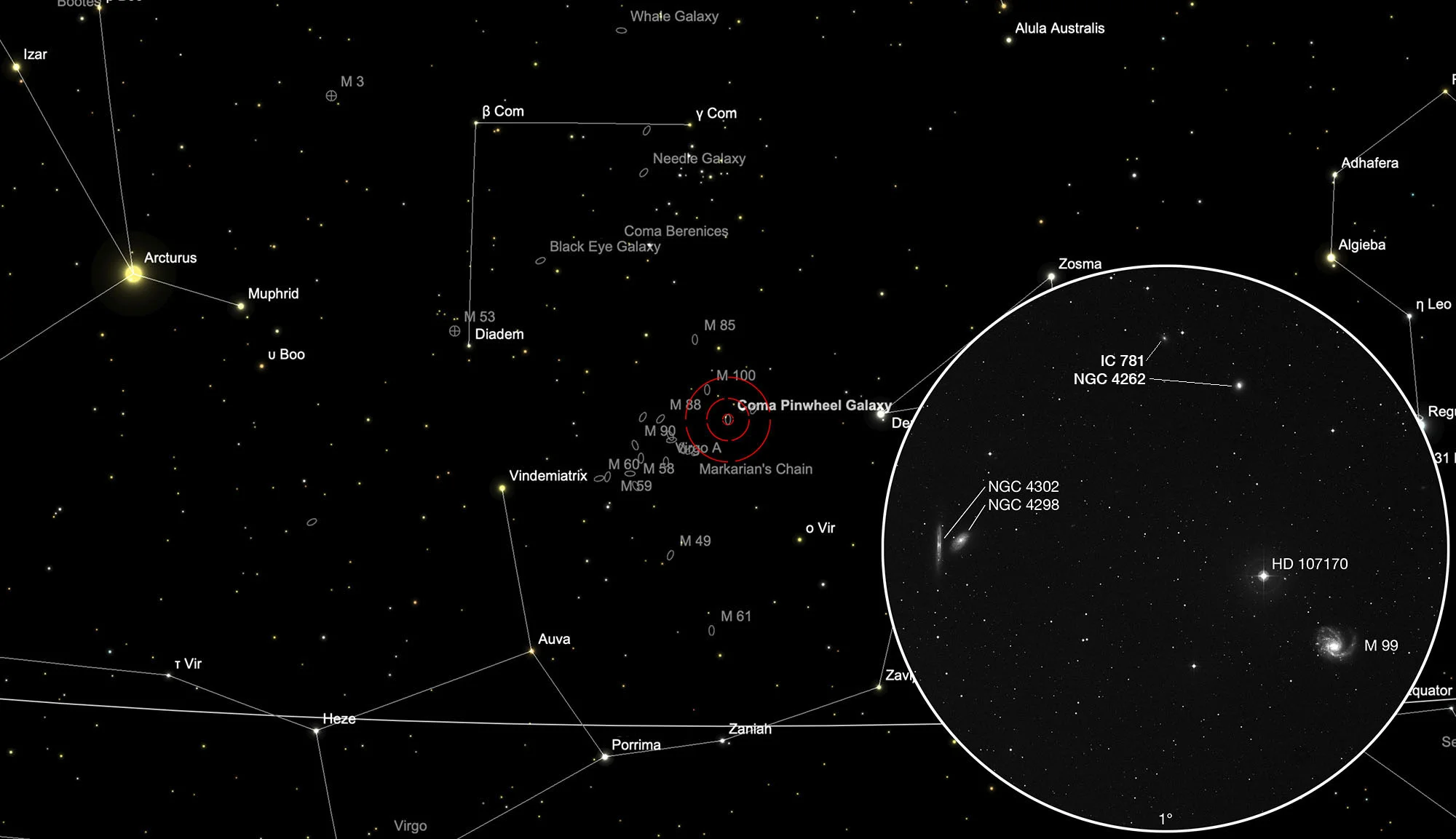
Galaxies Messier 99, NGC 4298, NGC 4302

History
The galaxy M 99 was discovered by Pierre Méchain on 15 March 1781 and cataloged by Charles Messier on April 13. He wrote: «Nebula without a star, of very weak light, but somewhat clearer than the previous one [M 98], above the northern wing of the Virgin and next to the same star No. 6 of Berenice's hair. The nebula lies between two stars of seventh and eighth magnitude. M. Méchain sighted them on 15 March 1781.» [281]
Physical Properties
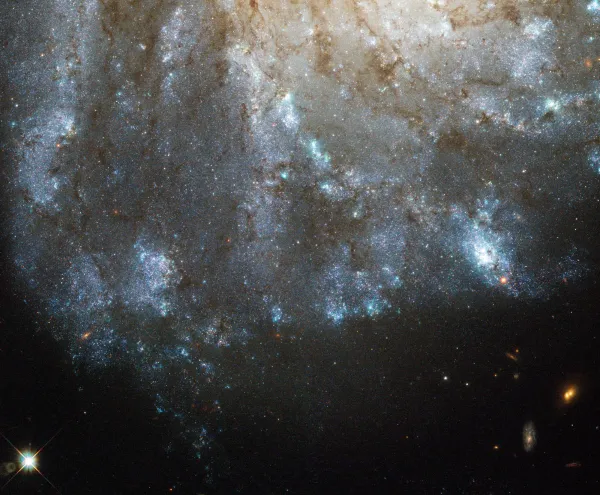

M 99 is a spiral galaxy of the morphological type SA(s)c and the brightness class LC III. It is moving away from us at about 2400 km/s and the distance is about 15 Mpc (49 million light years). [194] It has a somewhat asymmetrical appearance with one normal-looking arm and one elongated, less twisted arm. The reason for this could have been a close and rapid encounter with the galaxy NGC 4262 about 280 million years ago. The distance from M 99 to the centre of the Virgo cluster (M 87) is about 1 Mpc. [293]
| Designation | NGC 4254 |
| Type | Gx (Sc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 12h 18m 49.3s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +14° 25' 03" |
| Diameter | 5.3 × 4.6 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 10.4 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 9.9 mag |
| Surface brightness | 13.3 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 51° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.008029 |
| Distance derived from z | 33.91 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 15.420 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | !! (H, h) B, L, R, gbM, r, (R & L) 3-branched spiral |
| Identification, Remarks | h 1173; GC 2838; M 99; UGC 7345; MCG 3-31-99; CGCG 99-11; CGCG 98-144; VCC 307; IRAS 12162+1441 |
Further Galaxies in that Area
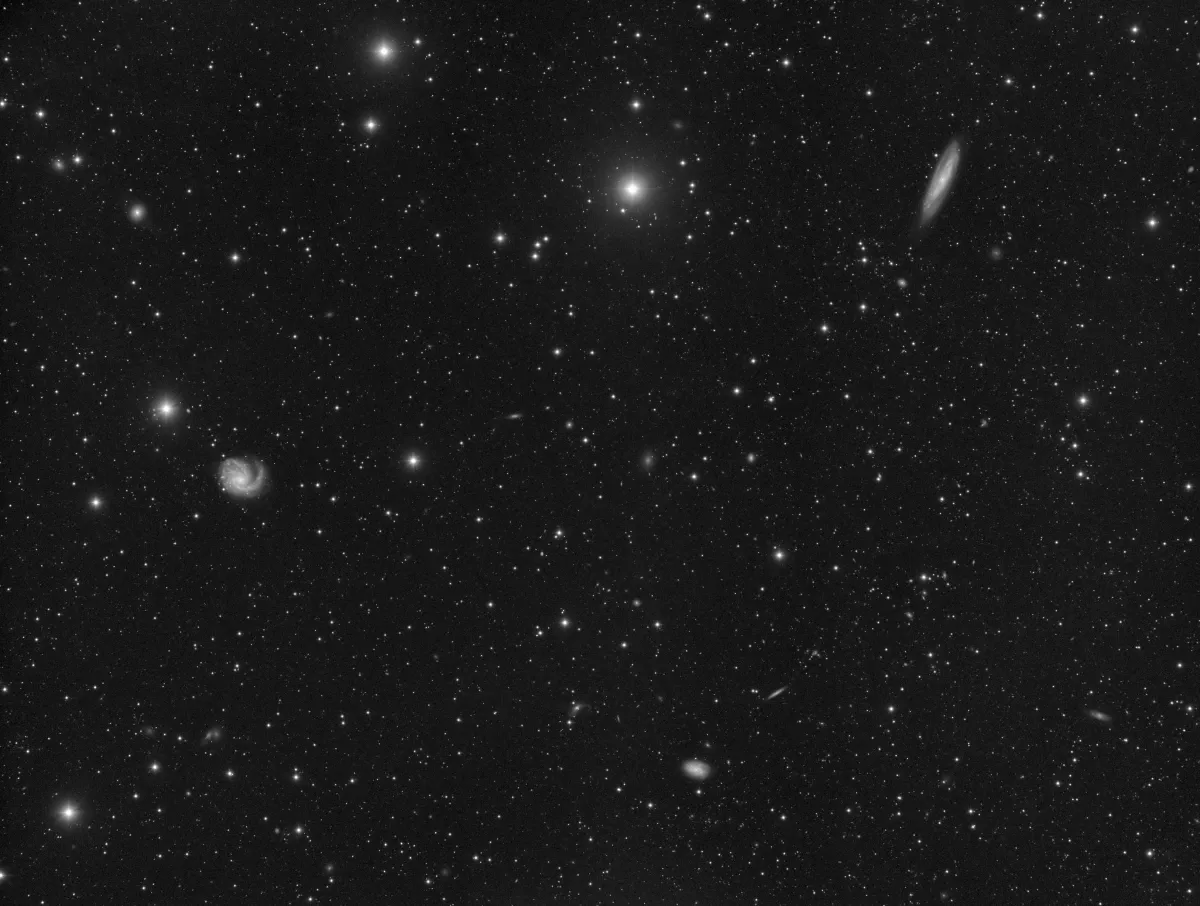
The small galaxy NGC 4262 was discovered by William Herschel on 8 April 1784. A morphological type of SB_a can be found here at Simbad. Measured values from the last 20 years show speeds of 1359 km/s to 1367 km/s and distances of 15.4 Mpc to 19.5. She is member No. VCC 355 of the Virgo Cluster. [145, 196]
The galaxy IC 781 is even more inconspicuous. It was discovered on 10 May 1888 by Guillaume Bigourdan. Morphological type dS0, heliocentric speed 1356 km/s and distance 14 Mpc. Virgo Cluster member number VCC 389. [145, 196]
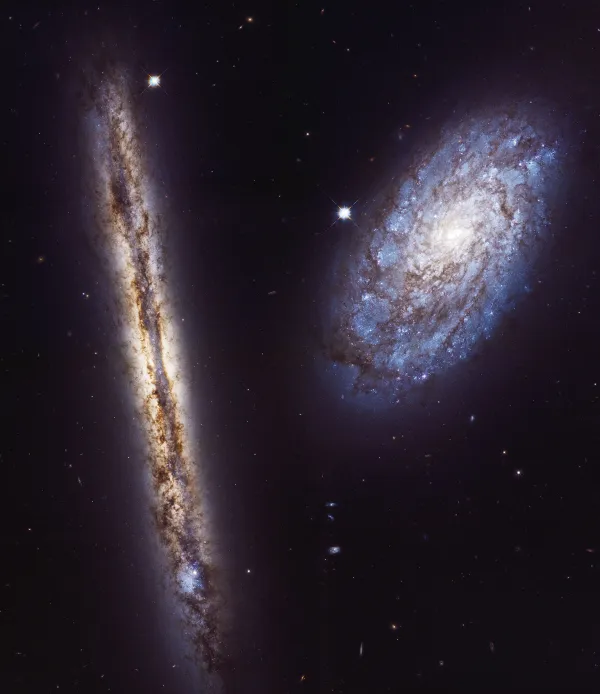

The beautiful galaxy pair NGC 4298 and NGC 4302 was discovered by William Herschel on 8 April 1784. Although they look very different because we look at them from different angles, they are quite similar in structure. Although both galaxies are right next to each other from our perspective, they are far enough apart that no gravitational interaction can be observed between them.
NGC 4298 is of morphological type SA(rs)c and about 16 Mpc (52 million light years) away. We see them at an angle of about 70°. Their size is estimated to be around 45'000 light years, roughly a third of our Milky Way. With 17 billion solar masses, it is less than two percent as heavy as our Milky Way.
Of NGC 4302, which we see directly from the edge, only the central dust band is visible. It is about 20 Mpc (65 million light years) away. A large blue area in the southern area is evidence of recent star formation. Its diameter is estimated to be around 87'000 light years, which is around 60% of that of our Milky Way. It contains about 110 billion solar masses, about a tenth of our Milky Way. [194, 196, 294]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4262 | 12 19 30.6 | +14 52 40 | Gx (E/SB0) | 12.5 | 11.6 | 0.9 | 12.7 | 1.8 × 1.6 | 120 | 0.004533 | 19.15 | 19.210 | B, S, R, r | WH II 110; h 1179; GC 2845; UGC 7365; MCG 3-31-101; CGCG 99-14; VCC 355 |
| NGC 4298 | 12 21 32.9 | +14 36 24 | Gx (Sc) | 12.0 | 11.3 | 0.7 | 13.1 | 3.2 × 1.9 | 140 | 0.003786 | 15.99 | 15.030 | F, L, E, vgbM, p of 2 | WH II 111; h 1198; GC 2874; UGC 7412; MCG 3-32-7; CGCG 99-24; IRAS 12190+1452; VCC 483; KCPG 332A |
| NGC 4302 | 12 21 42.2 | +14 35 54 | Gx (Sc) | 12.5 | 11.6 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 5.3 × 1 | 178 | 0.003833 | 16.19 | 24.880 | L, vmE 177°, f of 2 | WH II 112; h 1199; GC 2877; UGC 7418; MCG 3-32-9; CGCG 99-27; VCC 497; KCPG 332B |
| IC 781 | 12 20 03.4 | +14 57 41 | Gx (S0-a) | 14.2 | 13.3 | 0.9 | 13.0 | 1.1 × 0.9 | 45 | 0.004550 | 19.22 | vF, S, dif | MCG 3-32-2; CGCG 99-17; VCC 389 |
Finder Chart
The galaxies are located in the constellation Coma Berenices between the stars Vindemiatrix (ε Virginis) and Denebola (β Leonis). The best time for observation is November to September.