Galaxy Messier 85

Object Description
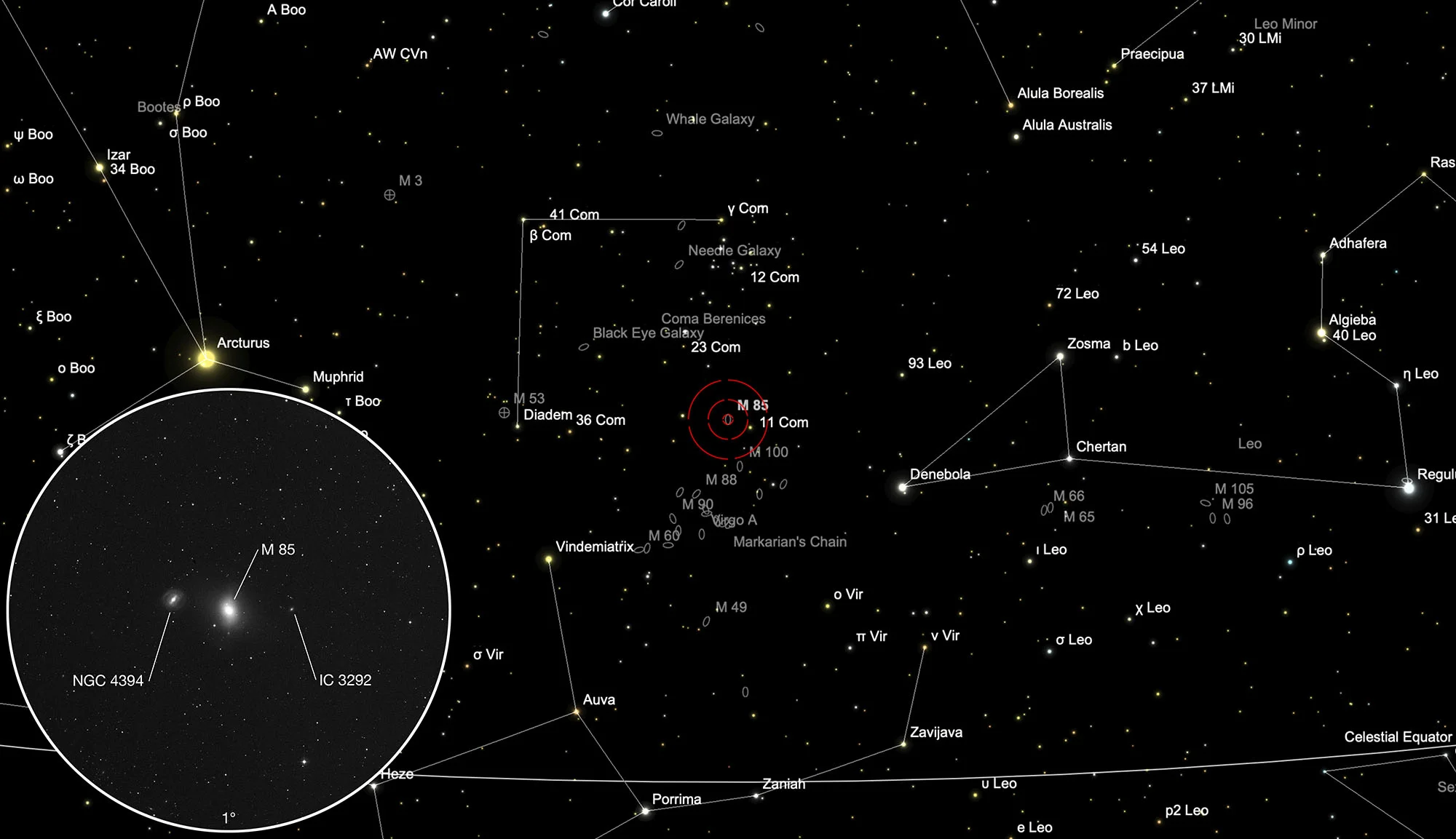
The galaxy M 85 was discovered by Pierre Méchain on 4 March 1781 and visited by Charles Messier on March 18. Messier wrote about M 85: «Nebula without a star, below and next to the ear of the Virgin, between the two stars 11 and 14 of the hair of Berenice, according to the catalog of Flamsteed: This nebula is very faint. M. Méchain had determined his position on 4 March 1781.» Here Messier apparently made a mistake and meant the star 24 Comae Berenices instead of 14 or it was a misprint in the «La Connoissance» of 1784. In the same night he came across numerous other «nebulae without a star» in the Virgo cluster: M 84, M 86, M 87, M 88, M 89, M 90 and M 91. [281]
Physical Properties
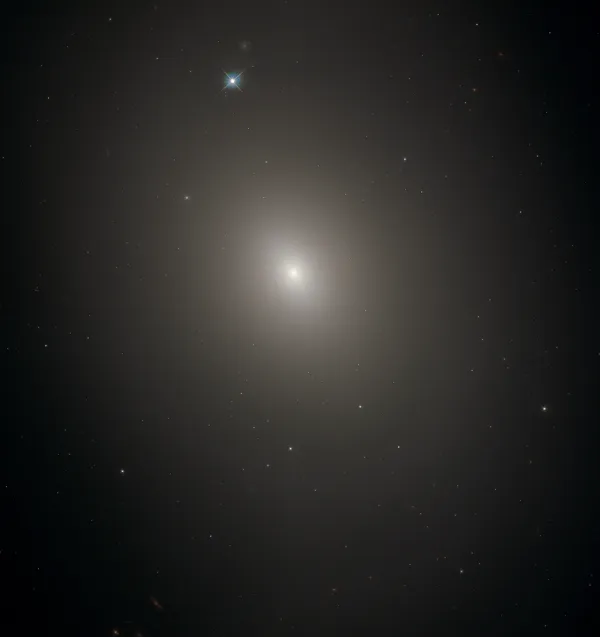

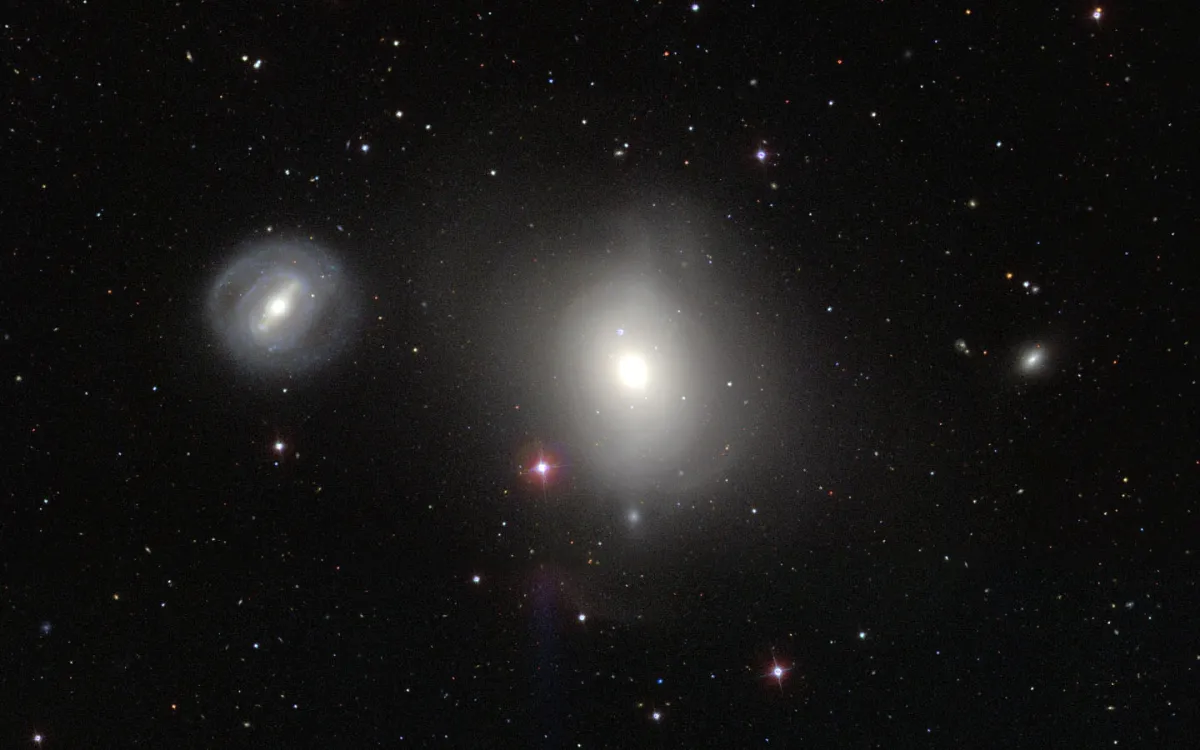
In the case of M 85, there is still no full agreement as to whether it is an elliptical or a lenticular galaxy. Lenticular galaxies have properties of both elliptical and spiral galaxies and are sometimes called «armless spiral galaxies». M 85 interacts with two neighboring galaxies: spiral galaxy NGC 4394 and elliptical galaxy MCG 3-32-28 (not MCG 3-32-38 as in the ESA/Hubble Press Release). The galaxies are members of the Virgo Galaxy Cluster and are about 60 million light years away from Earth.
About four to seven billion years ago, M 85 appears to have merged with another galaxy. M 85 contains about 400 billion stars, most of which are very old. In the central region, however, there are predominantly young stars, less than three billion years old. These could have come from a recent outbreak of star formation. There is a supermassive black hole in the core of M 85. In 2006 a supernova occurred northeast of the core. [215]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4382 | 12 25 23.9 | +18 11 27 | Gx (S0-a) | 10.0 | 9.1 | 0.9 | 12.9 | 7.1 × 5.5 | 5 | 0.002432 | 10.27 | 17.080 | vB, pL, R, bM, * np | h 1242; GC 2946; M 85; UGC 7508; MCG 3-32-29; KCPG 334A; CGCG 99-45; VCC 798 |
| NGC 4394 | 12 25 55.6 | +18 12 51 | Gx (SBb) | 11.7 | 10.9 | 0.8 | 13.4 | 3.4 × 3.2 | 141 | 0.003075 | 12.99 | 16.800 | pB, lE, bM | WH II 55; h 1251; GC 2957; UGC 7523; MCG 3-32-35; CGCG 99-47; IRAS 12234+1829; VCC 857; KCPG 334B |
| IC 3292 | 12 24 48.3 | +18 11 44 | Gx (S0-a) | 15.7 | 14.8 | 0.9 | 12.9 | 0.5 × 0.4 | 0.002325 | 9.82 | 15.580 | F, vS, R, bM | CGCG 99-39; VCC 751; NPM1G +18.0327 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy M 85 is located in the constellation Coma Berenices (Hair of Berenices) between the stars 24 Comae Berenices and 11 Comae Berenices, about 1 ° 10 'east of 11 Comae Berenices.