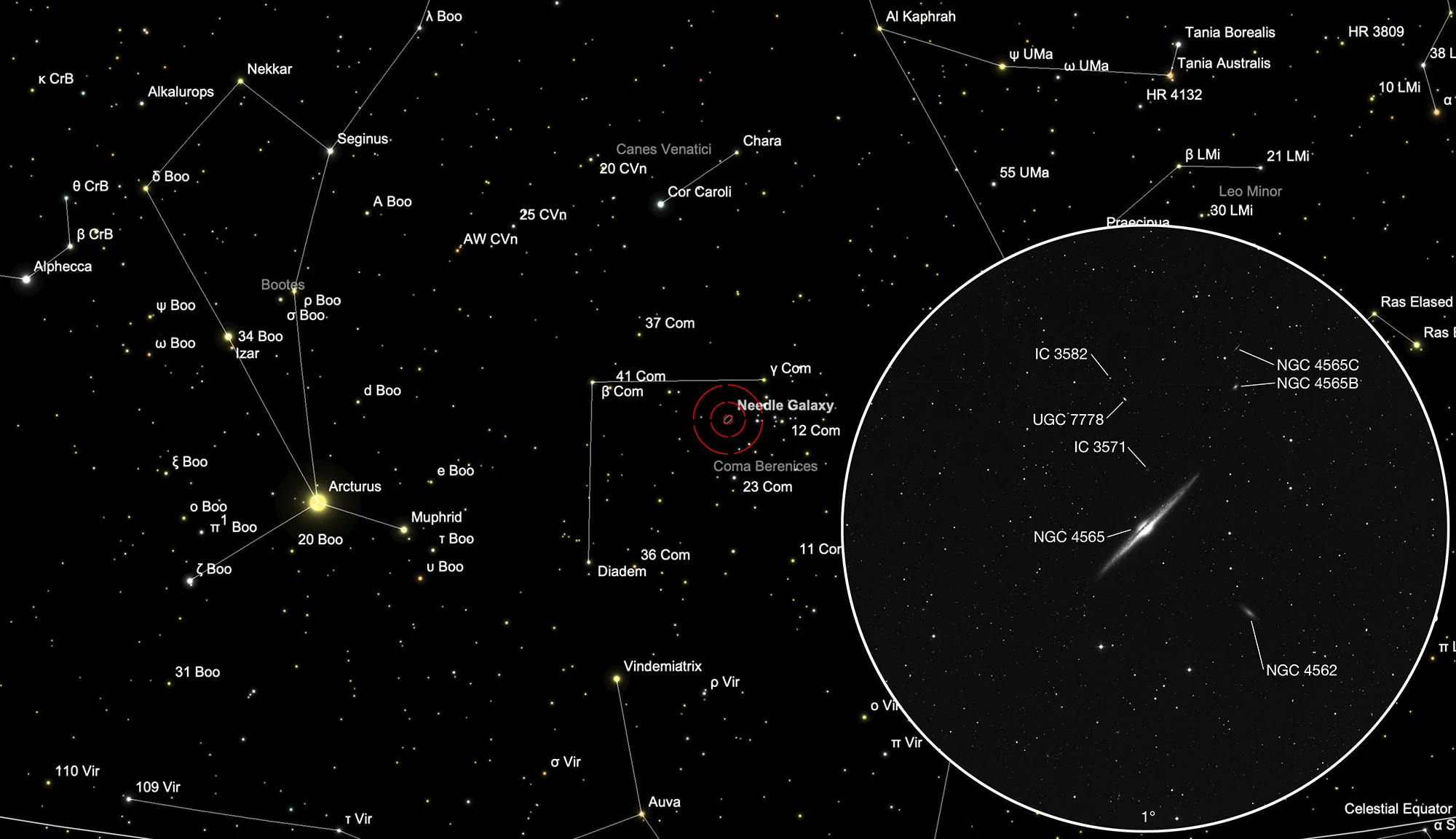
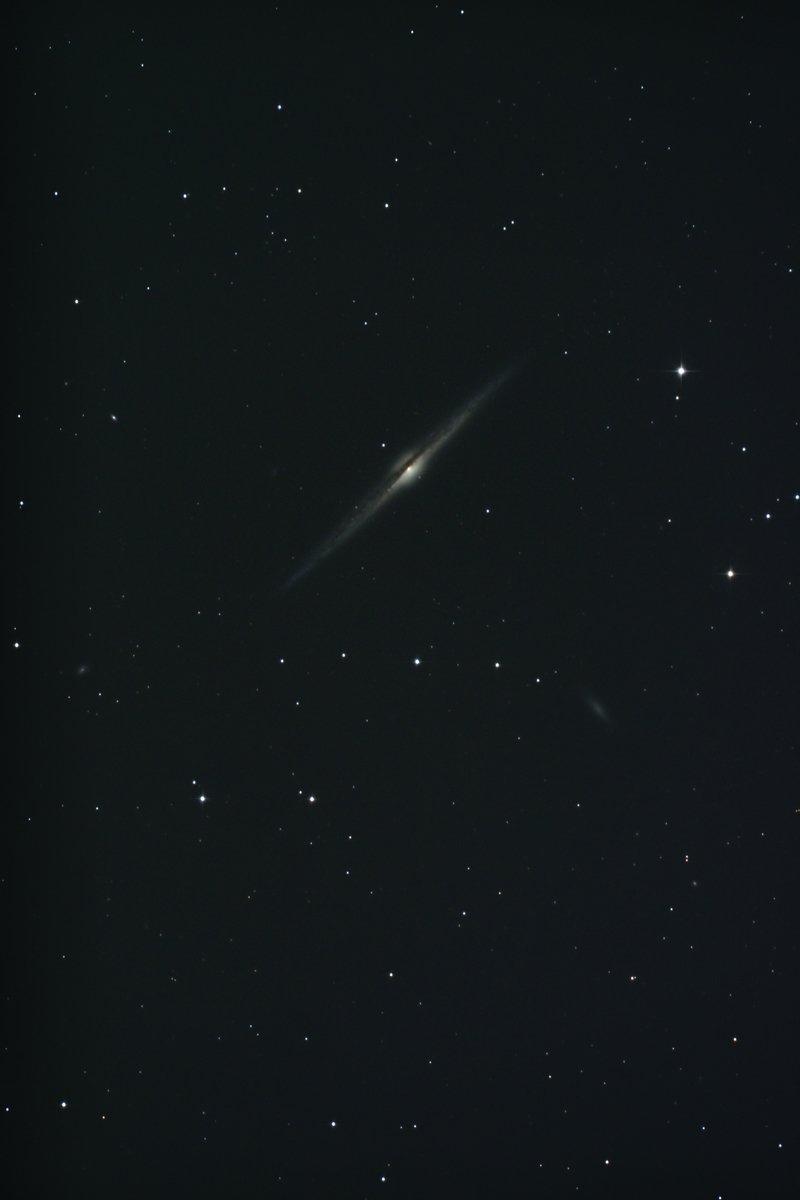
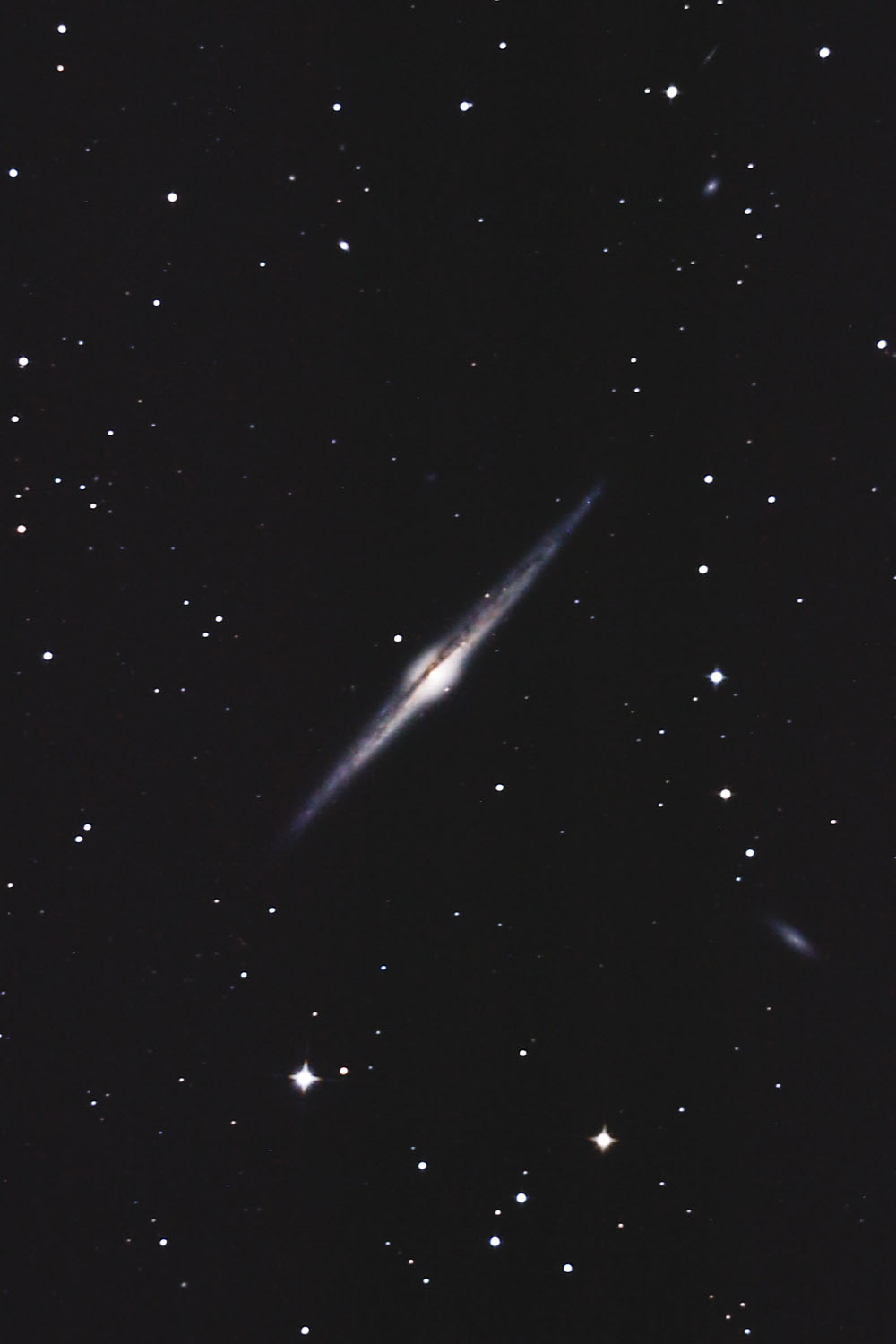
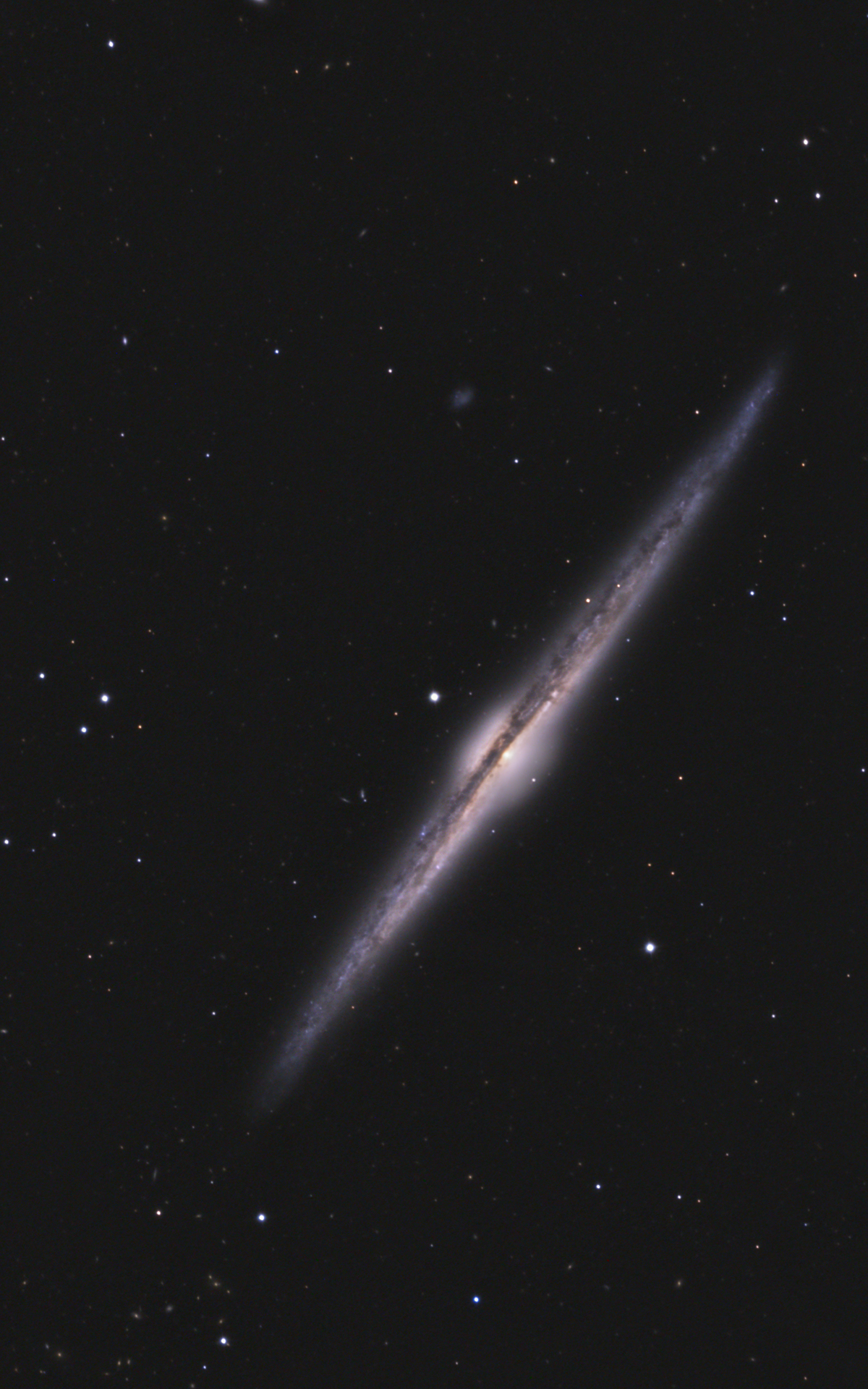
Needle Galaxy (NGC 4565)




History
This galaxy was discovered by William Herschel on 6 April 1785 and cataloged as V 24 (class V = very large nebulae). As for most of his discoveries he was using his 18.7 inch reflecting telescope with 20 feet focal length. He described the galaxy as «a lucid ray 20' long or more, 3 or 4' broad, north preceeding, south following, very bright in the middle, a beautiful appearance». [463]
Physical Properties
NGC 4565 is the largest of the Edge-On galaxies — i. e. a spiral galaxy which we see from its side. It has been nicknamed the «Needle Galaxy» and is of morphological type Sab. It is an outlying and close member of the Virgo cluster, although it lies about 13° north of its main concentration. Radial velocity measurements range from 1178 km/s to 1282 km/s, distance measurements vary from 12 Mpc to 18 Mpc (39 to 58 million light years). [4, 145, 196]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4562 | 12 35 34.5 | +25 50 58 | Gx (SBcd) | 14.1 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 14.0 | 2.4 × 0.7 | 48 | 0.004513 | 19.06 | 12.500 | S, sp V 24 | NGC 4565A; UGC 7758; MCG 4-30-4; CGCG 129-8; KUG 1233+261 |
| NGC 4565 | 12 36 20.5 | +25 59 16 | Gx (Sb) | 10.4 | 9.6 | 0.8 | 13.3 | 15.8 × 2.1 | 136 | 0.004103 | 17.33 | 12.890 | B, eL, eE 135°, vsbMN = * 10·11 | WH V 24; h 1357; GC 3106; UGC 7772; MCG 4-30-6; CGCG 129-10; FGC 1471; KUG 1233+262 |
| NGC 4565 A | 12 35 34.5 | +25 50 58 | dup | 14.1 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 14.0 | 2.4 × 0.7 | 48 | 0.004513 | 19.06 | 12.500 | B, eL, eE 135°, vsbMN = * 10·11 | WH V 24; h 1357; GC 3106; NGC 4562; UGC 7758; MCG 4-30-4; CGCG 129-8; KUG 1233+261 |
| NGC 4565 B | 12 35 41.6 | +26 13 21 | dup | 15.3 | 14.6 | 0.7 | 13.2 | 0.8 × 0.4 | 135 | 0.021465 | 90.67 | B, eL, eE 135°, vsbMN = * 10·11 | WH V 24; h 1357; GC 3106; IC 3546; MCG 4-30-5; CGCG 129-9; CGCG 159-20; KUG 1233+264 | |
| NGC 4565 C | 12 35 41.3 | +26 17 12 | dup | 16.5 | 15.8 | 0.7 | 13.0 | 0.9 × 0.1 | 142 | 0.021398 | 90.38 | B, eL, eE 135°, vsbMN = * 10·11 | WH V 24; h 1357; GC 3106; IC 3543; UGC 7764; FGC 1466; KUG 1233+265 | |
| IC 3571 | 12 36 19.9 | +26 05 03 | Gx (Irr) | 17.5 | 16.9 | 0.6 | 14.1 | 0.3 × 0.3 | 0.004203 | 17.75 | eF, S, iF, others nr | Reiz 2601 | ||
| IC 3582 | 12 36 36.9 | +26 14 05 | Gx (C) | 17.2 | 16.2 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 0.2 × 0.2 | 0.022773 | 96.19 | F, vS, com, bM, others nr |
Finder Chart
The Needle Galaxy is located in the constellation Coma Berenices just 1.7° east of the variable binary star 17 Comae, which at mag 5.25 is still visible to the unaided eye. The galaxy is best observed from December to September.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: In the 21 mm ethos (85x) the galaxy NGC 4565 stands out as a bright, long, thin stripe with a thickened centre. The dust band is well visible here. With increasing magnification, the contrast increases compared to the sky background. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Glaubenberg, SQM 21.34, a bit windy, Sahara dust and hazy und dunstig, 22. 5. 2022, Bernd Nies