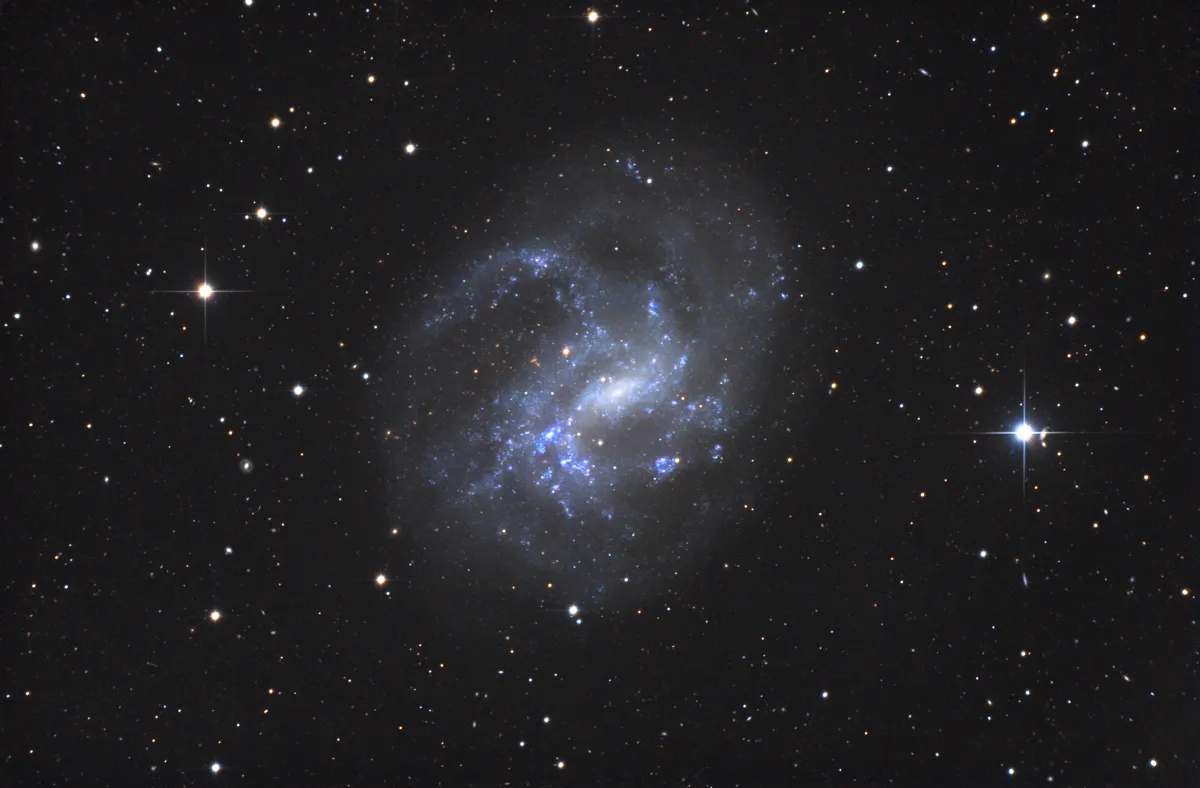
Galaxy NGC 4395

History
The galaxy NGC 4395 was discovered on 2 January 1786 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7 inch reflecting telescope. His son John recorded another nebula with a bright centre on 29th July 1827, southwest of NGC 4395, which was named as NGC 4401. On 13 April 1850, Irish astronomer George Johnstone Stoney, using the 72 inch reflecting telescope owned by William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, discovered two more small nebulae, NGC 4399 and NGC 4400, which formed a trapezium with the previously discovered ones. [196, 277]
In 1920, the American astronomer Francis Gladheim Pease recognized from photographs taken by him in the years 1917 to 1919 with the 60 inch reflecting telescope on Mount Palomar that these four nebulae together with a large number of smaller nebulae formed a large, round spiral nebula. [443] At that time it was still believed that these nebulae were in our Milky Way, which represented the known universe. Some suspected that planetary systems were forming behind them. This was to change in the late 1920s with the discoveries of Edwin Hubble, which revealed the true nature of such spiral nebulae as world islands in their own right at a distance of several million light years.
Physical Properties
NGC 4395 is a galaxy of the morphological type SAB, an intermediate form from a spiral to a barred spiral. It is a Seyfert 2 galaxy with a bright core but low surface brightness. The brightest of the active star-forming regions have their own NGC numbers. Distances range from 3.9 Mpc to 4.7 Mpc (about 12 to 15 million light years). [145]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4395 | 12 25 48.8 | +33 32 48 | Gx (SBm) | 10.6 | 10.2 | 0.4 | 15.4 | 13.2 × 11 | 147 | 0.001064 | 4.49 | 4.490 | eF, vL, np of D neb | WH V 29.1; h 1252; GC 2958; UGC 7524; MCG 6-27-53; CGCG 187-42; KUG 1223+338; IRAS 12233+3348 |
| NGC 4399 | 12 25 42.9 | +33 31 00 | GxyP | 14.0 | 1 | 4.490 | vF, form trapezium with 2958 and 62 | GC 2959; MCG 6-27-53; CGCG 187-42; HII in N 4395 | ||||||
| NGC 4400 | 12 25 55.9 | +33 30 57 | GxyP | 14.5 | 0.3 | 4.490 | vF, form trapezium with 2958 and 62 | GC 2960; MCG 6-27-53; CGCG 187-42; HII in N 4395 | ||||||
| NGC 4401 | 12 25 57.9 | +33 31 38 | GxyP | 14.0 | 0.6 | 4.490 | vF, vL, pslbM, sf of D neb | WH V 29.2; h 1252; GC 2962; MCG 6-27-53; CGCG 187-42; HII in N 4395 |
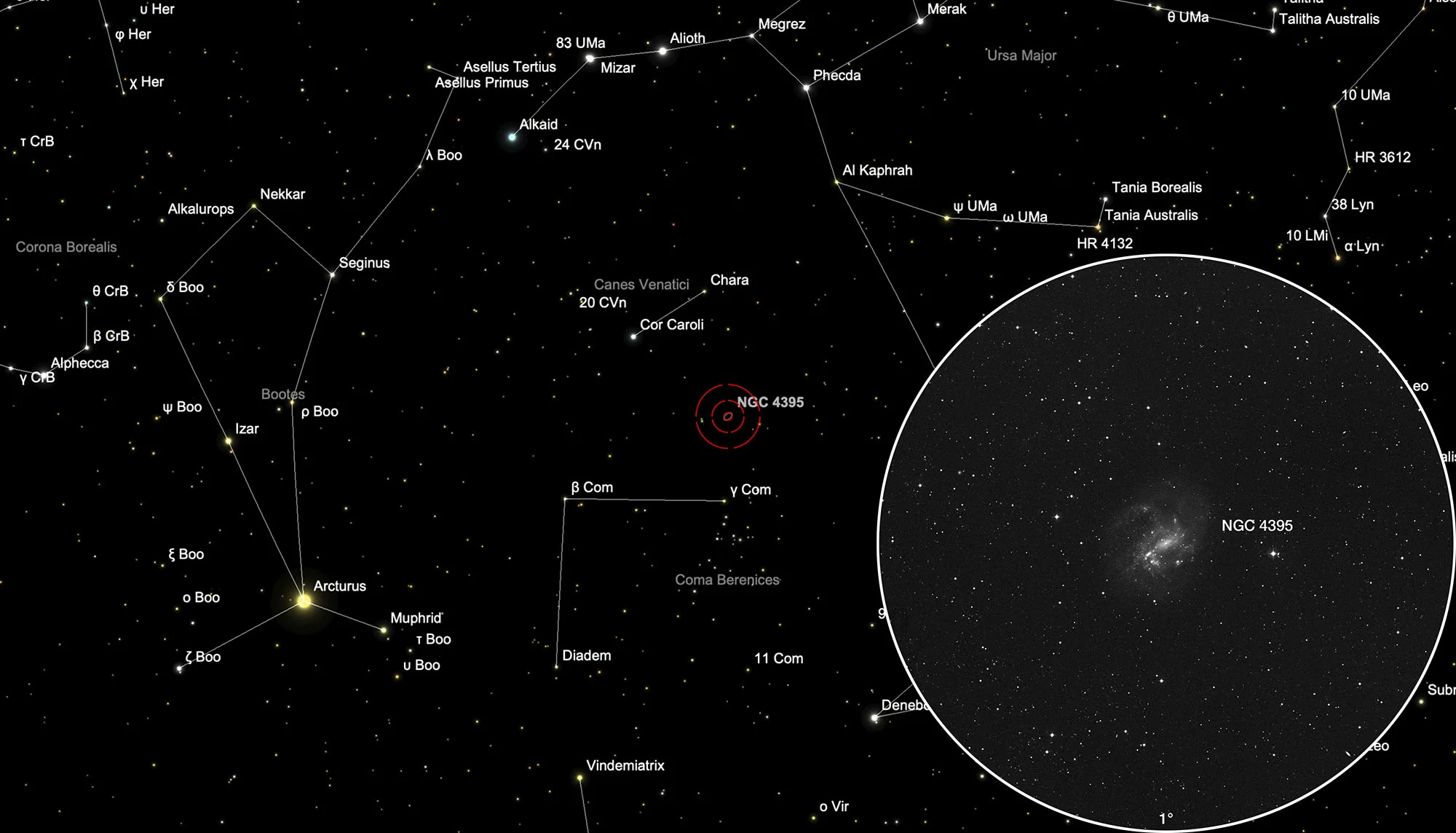
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 4395 is located in the constellation Canes Venatici. The best observation time is December to September, when it is highest at night.