Galaxy Messier 100


History
M 100 was discovered by Pierre Méchain on 15 March 1781 and cataloged by Charles Messier on April 13 of the same year. He wrote: «Nebula without a star, of the same light as the previous one [M 99], placed in the ear of the Virgin. Seen by M. Messier on 15 March 1781. The three nebulae nos. 98, 99 and 100 are very difficult to see because of their low brightness: You can only see them in good weather when they pass the meridian.» [281]
Physical Properties
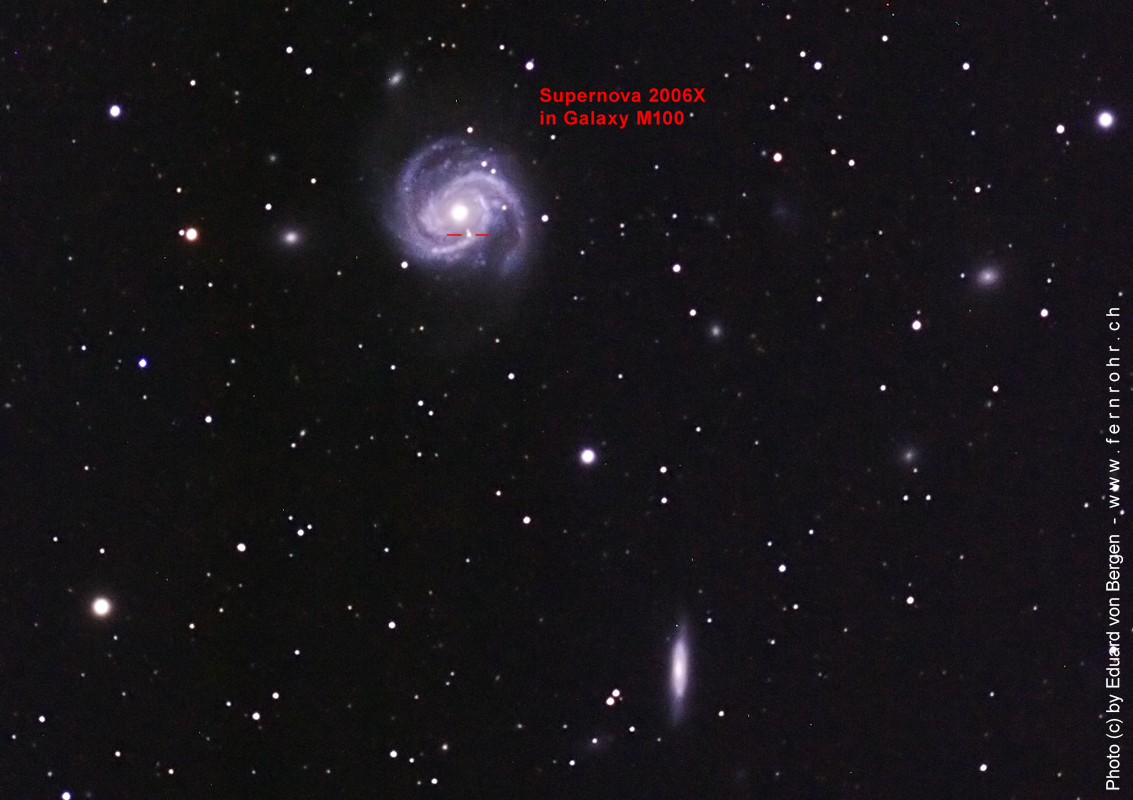
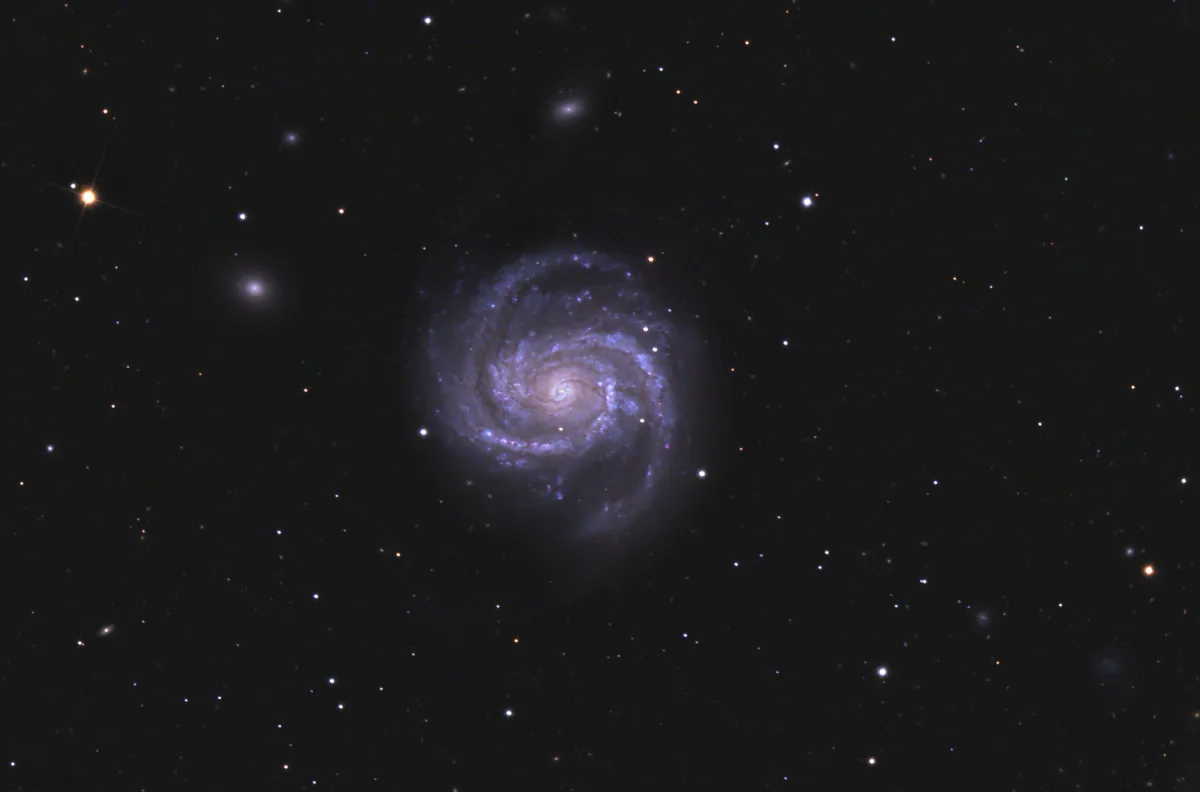
This is a galaxy of the morphological type SAB(s)bc, an intermediate form of spiral galaxy and bar spiral, according to the extended Hubble classification scheme according to de Vaucouleur. Distance measurements with different methods vary from 11.0 Mpc to 27.6 Mpc with a mean value of 16.2 Mpc (52.8 million light years). M 100 has an active core, a bright region in the centre, caused by a supermassive black hole that engulfs matter. There are also smaller black holes in the spiral arms, including the remains of five supernovae observed since 1900. The last one was SN 2006X, a Type Ia supernova. [145, 194, 215]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4312 | 12 22 31.4 | +15 32 17 | Gx (Sab) | 12.5 | 11.7 | 0.8 | 13.3 | 4.6 × 1.1 | 170 | 0.000510 | 2.15 | 10.930 | pB, cL, E, gbM | WH II 628; h 1209; GC 2886; UGC 7442; MCG 3-32-14; CGCG 99-29; VCC 559; IRAS 12199+1548 |
| NGC 4321 | 12 22 54.9 | +15 49 22 | Gx (SBbc) | 10.1 | 9.4 | 0.7 | 13.4 | 7.5 × 6.1 | 30 | 0.005240 | 22.13 | 15.940 | !! pF, vL, R, vg, psbMrN (L) 2-branched spiral | h 1211; GC 2890; M 100; UGC 7450; MCG 3-32-15; IRAS 12204+1605; CGCG 99-30; VCC 596; KUG 1220+160 |
| NGC 4322 | 12 23 01.7 | +15 54 19 | Gx (SB0) | 14.8 | 13.9 | 0.9 | 13.6 | 1.1 × 0.8 | 100 | 0.006182 | 26.11 | 2, vF, n of M 100 | MCG 3-32-16; CGCG 99-31; VCC 608 | |
| NGC 4323 | 12 23 16.0 | +15 54 07 | NF | 2, vF, n of M 100 | ||||||||||
| NGC 4328 | 12 23 20.0 | +15 49 13 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.0 | 13.0 | 1.0 | 13.1 | 1.3 × 0.9 | 90 | 0.001598 | 6.75 | F, S, R, r | WH II 84; GC 2894; MCG 3-32-19; CGCG 99-34; VCC 634 | |
| IC 783 | 12 21 38.8 | +15 44 41 | Gx (SB0-a) | 14.7 | 13.8 | 0.9 | 13.6 | 1.2 × 0.8 | 141 | 0.004226 | 17.85 | 18.300 | eF, S, R | UGC 7415; MCG 3-32-8; CGCG 99-25; VCC 490 |
| IC 783 A | 12 22 19.6 | +15 44 00 | Gx (SB0) | 15.5 | 14.5 | 1.0 | 12.8 | 0.5 × 0.5 | 0.004026 | 17.01 | eF, S, R | MCG 3-32-13; VCC 545 |
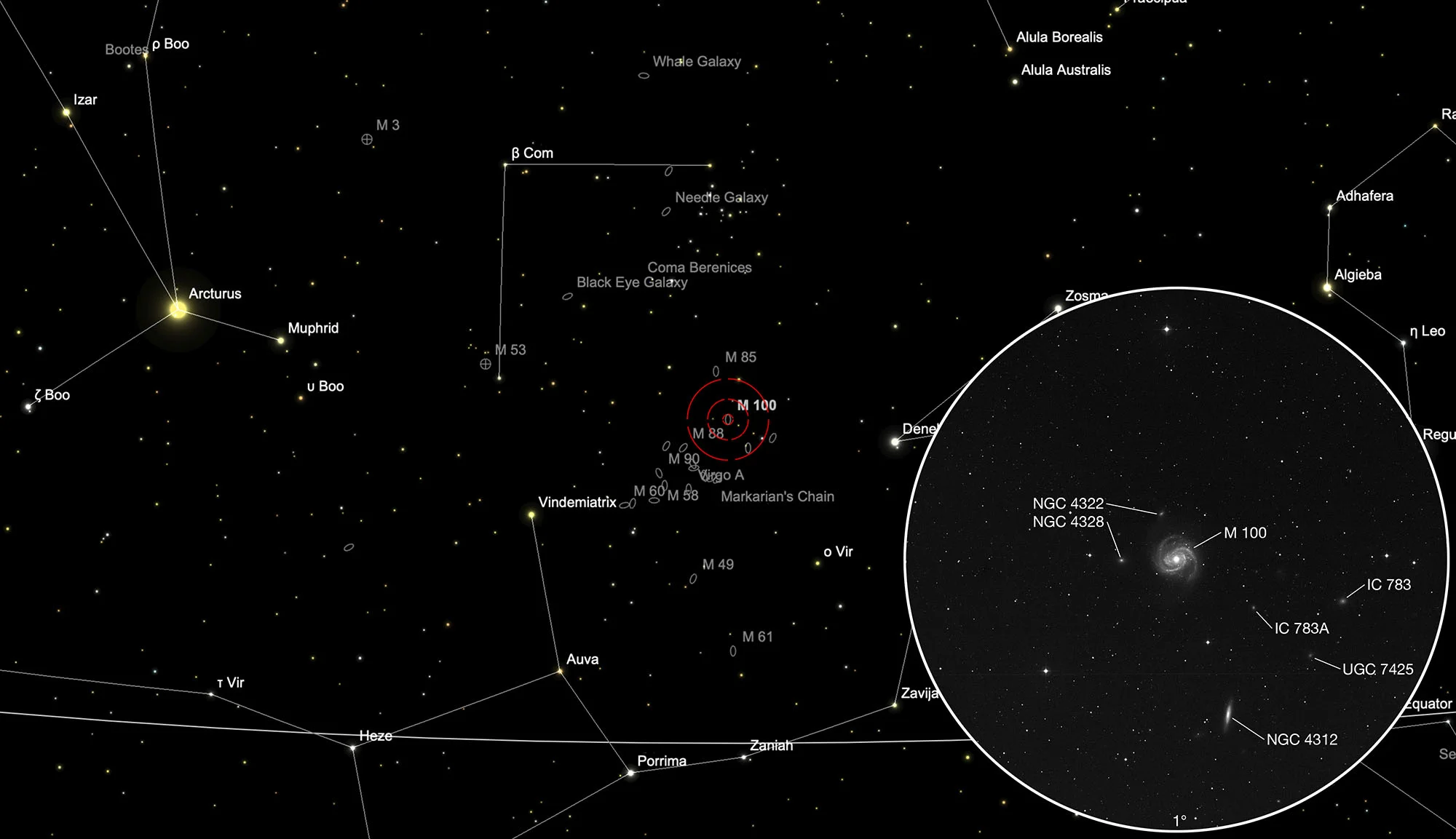
Finder Chart
The galaxy M 100 is located in the constellation Coma Berenices between the stars Vindemiatrix (ε Virginis) and Denebola (β Leonis). The best time for observation is December to September.