Quasar 3C 273

Object Description
3C 273 is the brightest known example of a «quasi-stellar radio source» or in short: Quasar. It is a strong radio source that looks like a faint star in the telescope. The spectrum shows an enormous redshift of z = 0.158, which indicates that this object is moving away from us at around 47'400 km/s or 15.8% of the speed of light. With a Hubble constant of 75 km/s/Mpc, the quasar is about two billion light years away from us.
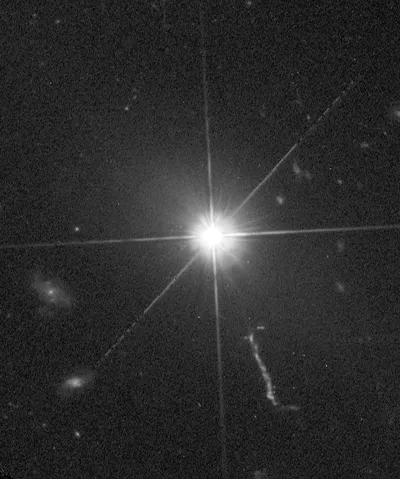

In 1963 3C 273 was covered by the moon. Since then it has been known that this is a dual radio source and that the two radio components can be identified with optically visible details. The star-like component is the main component, but about 90% of the radio energy comes from the foggy streak or «jet» southwest of the object. The jet starts about 11" from the bright centre and continues about another 10" and is about 1" to 2" wide. If the distance from the quasar is correct, then this jet is about 300'000 light years long.
The stellar component of 3C 273 has a radio core about 0.5" in diameter and is surrounded by a 3" halo. Assuming the distance is correct, the diameter of the radio core should be around 7'500 light years. The enormous energy output of such a relatively small object is difficult to explain. But a new problem arises: The stellar component shows fluctuations in brightness of around 0.5 magnitudes with half a period of around 13 years, but also sudden increases for a week or so. It is difficult to understand how an object of galactic dimensions can exhibit such rapid changes in brightness when it takes centuries for light to cross the object. This suggests that the true source must have a diameter of a few light months. [70, 90, 92, 95, 106, 111, 124]
The term «3C» refers to the number in the Third Cambridge Catalog of Radio Sources, published in 1959 by the Royal Astronomical Society in London. The quasar is also listed under the designation PGC 41121 in the «Principal Galaxies Catalog».
| Name | 3C 273 |
| Object Type | BL Lac |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 12h 29m 07s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +02° 03' 09" |
| Parallaxes | 0.0108 mas |
| Radial velocity | 43555 km/s |
| Redshift z | 0.15756751 |
| Morphological type | E3 |
| Magnitudes | B 13.05; V 14.83; G 12.84409; R 14.11; J 11.692; H 10.953; K 9.937; u 13.859; g 12.99; r 12.871; i 12.63; z 13.242 |
| Identifiers | 0FGL J1229.1+0202; 1AGL J1228+0142; 1CG 291+65; 1ES 1226+02.3; 1FGL J1229.1+0203; 1FLE J1227+0218; 1H 1226+022; 1Jy 1226+02; 1Jy 1226+023; 1RXS J122906.5+020311; 2A 1225+022; 2AGL J1228+0154; 2CG 289+64; 2E 1226.5+0219; 2E 2729; 2EG J1229+0206; 2EUVE J1229+02.0; 2FGL J1229.1+0202; 2MASS J12290669+0203085; 2MASX J12290674+0203083; 2U 1224+02; 2XMM J122906.6+020308; 2XMMi J122906.6+020308; 3A 1226+023; 3C 273; 3C 273.0; 3C 273B; 3C 273C; 3CR 273; 3EG J1229+0210; 3FGL J1229.1+0202; 3FHL J1229.2+0201; 3U 1224+02; 4C 02.32; 4FGL J1229.0+0202; 4FGL J1229.1+0202; 4U 1226+02; 87GB 122633.1+021928; 9Y-MST J1229+0200; AAVSO 1224+02; AKARI-FIS-V1 J1229071+020309; Balloon 110607001; CGRaBS J1229+0203; CTA 53; CWISE J122906.70+020308.6; CWISEP J122906.70+020308.6; DA 324; EGR J1229+0203; EPIC 229151988; EUVE J1229+02.0; FL8Y J1229.0+0202; GB6 B1226+0219; GB6 J1229+0202; GLEAM J122906+020251; GRA B1226+02; GSC 00282-00202; Gaia DR1 3700386901308864384; Gaia DR2 3700386905605055360; Gaia DR3 3700386905605055360; H 1226+023; HE 1226+0219; HIC 60936; HIP 60936; ICRF J122906.6+020308; IERS B1226+023; IGR J12291+0203; INTREF 500; IRAS 12265+0219; IRAS F12265+0219; JCMTSE J122906.7+020308; JCMTSF J122906.7+020308; JVAS B1226+023; JVAS J1229+0203; LAMOST J122906.41+020305.1; LAMOST J122906.69+020308.6; LAMOST J122906.70+020308.6; LAMOST J122906.96+020307.60; LEDA 41121; MRC 1226+023; MSH 12+0-08; NEWPS5 J1229+0203; NRAO 400; NVSS J122906+020305; NVSS J122906+020308; OHIO N 044; PBC J1229.1+0202; PCCS2 143 G289.94+64.36; PG 1226+02; PG 1226+023; PKS 1226+02; PKS 1226+023; PKS J1229+0203; PLCKERC -857 G289.96+64.35; PLX 2877.01; PMN J1229+0203; PSCz Q12265+0219; QSO B1226+0219; QSO B1226+023; QSO J1229+0203; RBS 1114; RGB J1229.1+0203; RORF 1226+023; RX J1229.1+0203; RX J122906+02031; SDSS J122906.69+020308.5; SDSS J122906.69+020308.6; SIM 1226+02.0; SRGA J122906.1+020316; SWIFT J1229.1+0202; SWIFT J1229.1+0203; TYC 282-202-1; USNO 731; UVQS J122906.69+020308.6; VSOP J1229+0202; VSOP J1229+0203; WB 1226+0219; WISE J122906.69+020308.6; WISE J122906.70+020308.6; WISEA J122906.69+020308.6; WMAP 170; WMAP J1229+0202; WMAP J1229+0203; WMAP J1229+0204; XSS J12288+0200; [BAG2012] 187.2817+02.04932; [BDW2002] q1226+0219; [CGL99] 11; [CMG2008] 188.75+3.14; [DGT2001] B1226+023; [DGW65] 56; [DML87] 295; [GGR94] 1226+023; [GR92] 1226+023; [GW2008] CoNFIG 137; [HB93] 1226+023; [HSN2016] J187.27+02.05; [IN88] 1226+023; [KRL2007b] 118; [MGL2009] BZQ J1229+0203; [MML2015] 5BZQ J1229+0203; [POS96] 8; [PUC81] 3C 273 B; [PUC81] 3C 273 C; [S77] 207; [VV2000] J122906.7+020308; [VV2003] J122906.7+020308; [VV2006] J122906.7+020308; [VV2010] J122906.7+020308; [VV96] J122906.7+020308; [VV98] J122906.7+020308; [VYP98] 1226+023; [WCO2009] J122908+020306; [WTW94] 1226+023; [WZX98] 12265+0219; [ZEH2003] RX J1229.1+0203 1 |
Finder Chart
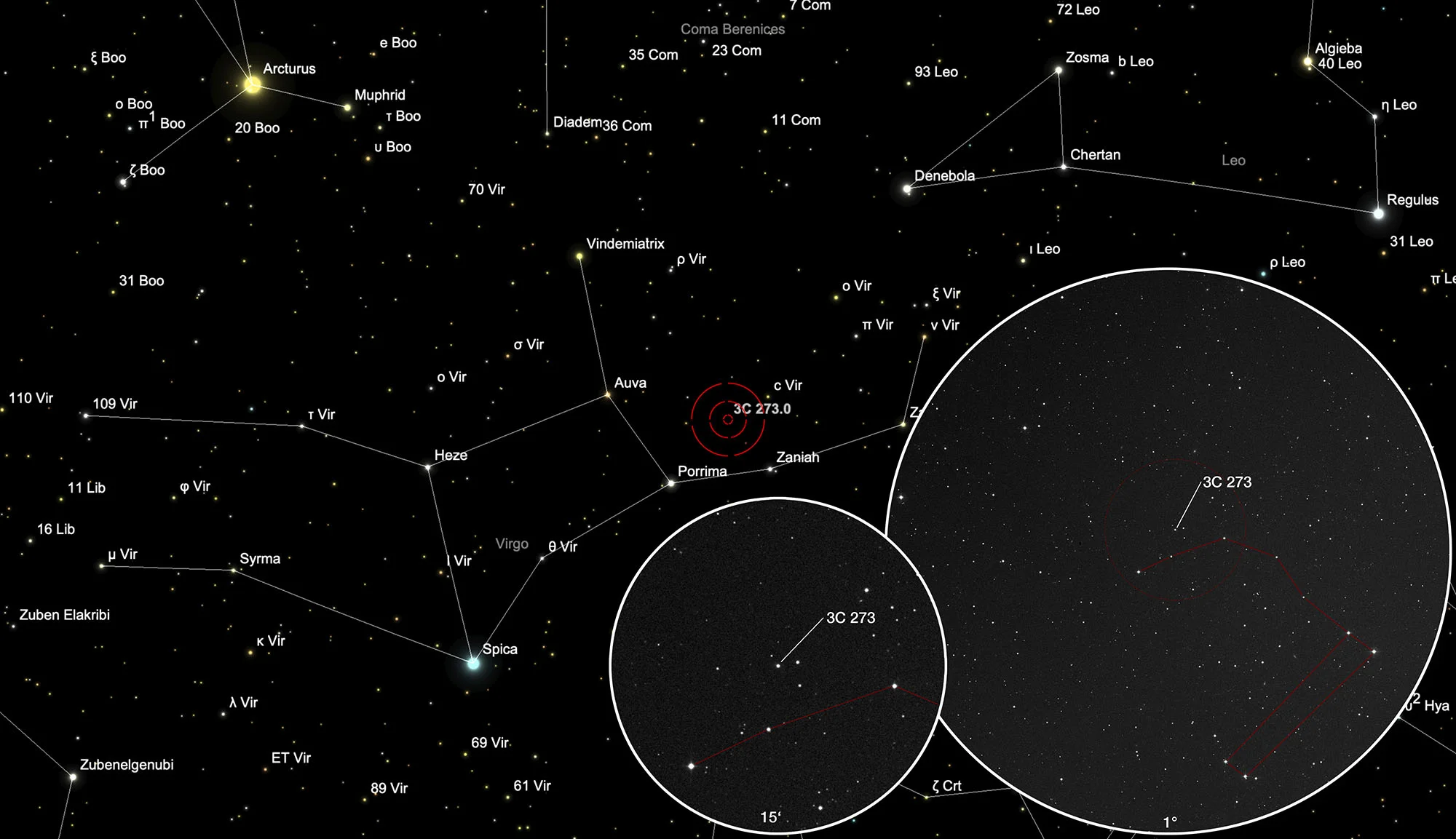
The map below shows the position of quasar 3C 273 in the constellation Virgo. Once you are in the correct section of the sky, the 1° and 15' excerpts from the STScI Digitized Sky Survey help with the precise identification of the quasar, as it does not differ visually from the surrounding stars. On 29 March the quasar is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight.
Visual Observation
300 mm Aperture: This really extremely exotic deep-sky object is much easier to track down and view than it appears at first glance - the sight of a 12.3 to 12.8 bright little star is all the more frustrating, which is why no sketch was made. Nothing can be recognized from the said jet, which seems to be asking a lot. The quasar is very clearly visible with an aperture of 300 mm, probably even down to an aperture of 150 mm. — 1996, Bernd Nies