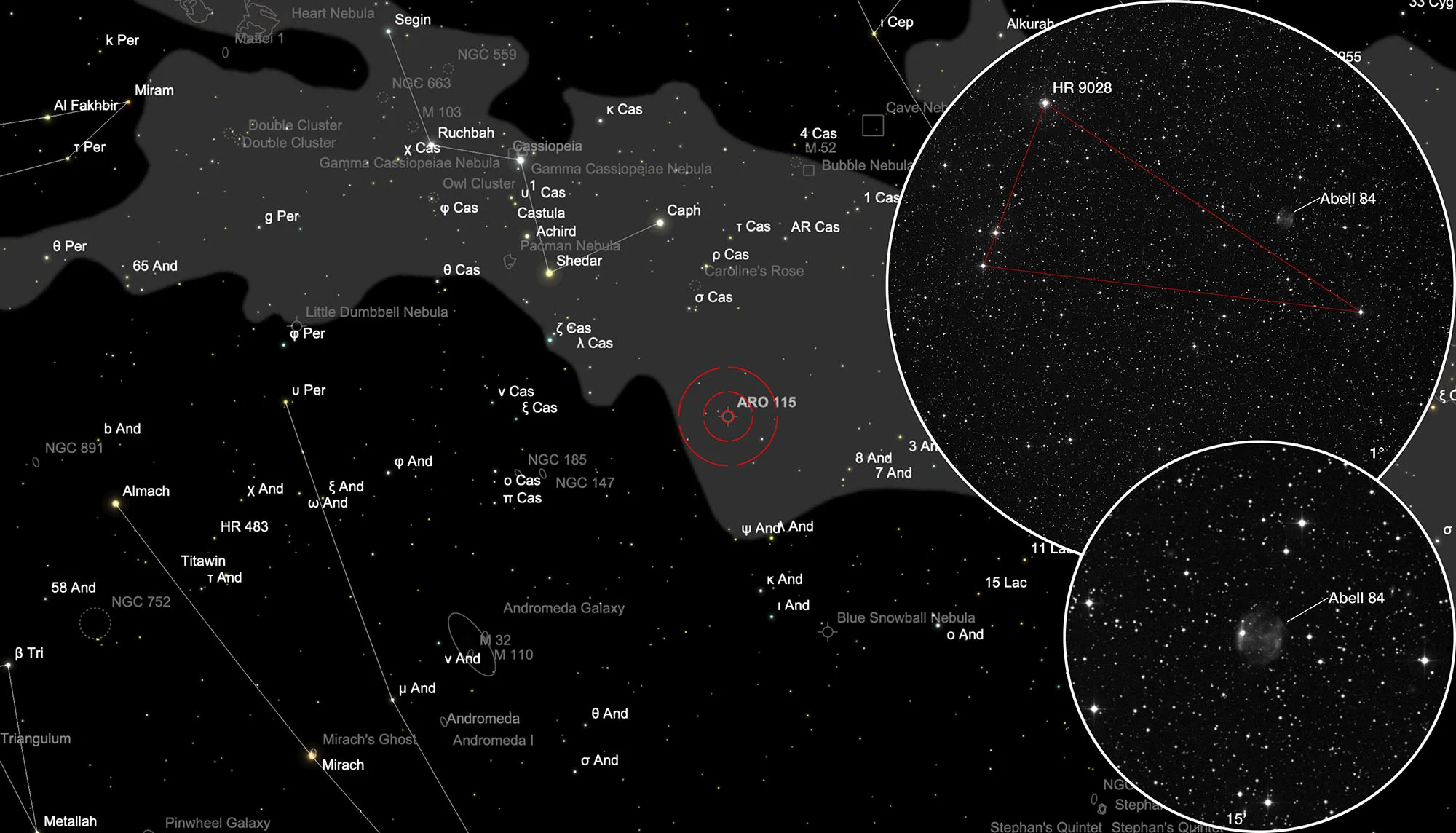
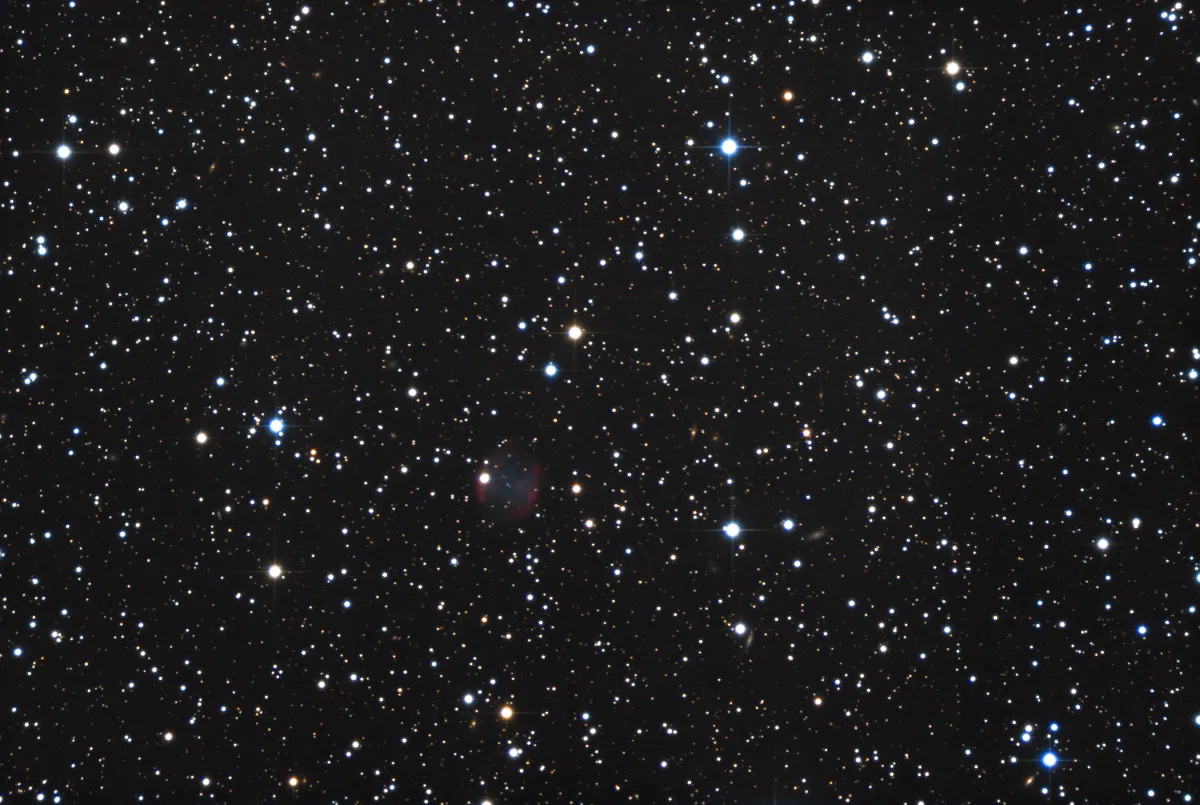
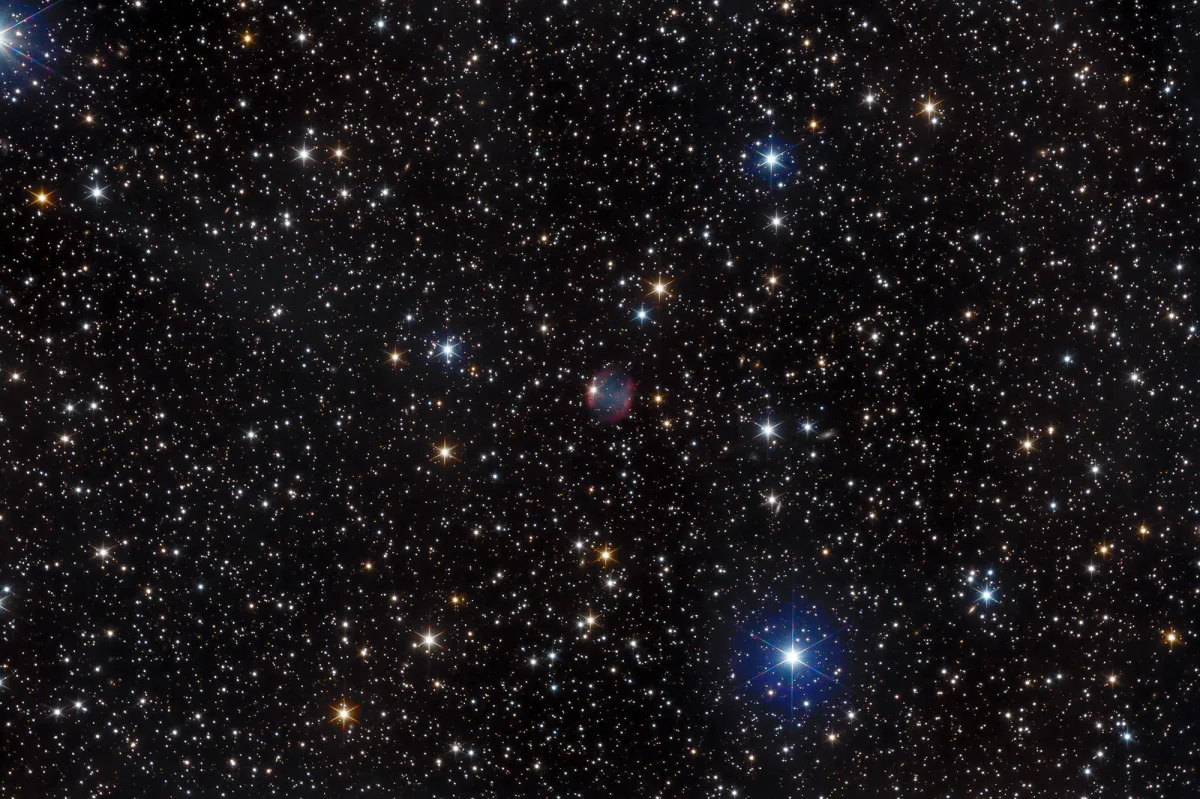
Planetary Nebula Abell 84


History
The planetary nebula Abell 84 (PN A55 70, PN A66 84, PK 112-10.1, PN ARO 115) was discovered in 1955 by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell on the photo plates of the «Palomar Observatory Sky Survey» (POSS ) discovered. Most of these 86 PNs discovered on the POSS photo plates are large and have a low surface brightness, which suggests that their stage of development is advanced. Abell described the PN as an asymmetrical ring with bright spots or regions 147x114" in diameter. [331, 332]
Physical Properties
Distances range from 1579 parsecs. The apparent brightnesses in different filters are: B = 18.4 mag, V = 18.6 mag, R = 18.6 mag, I = 18.7 mag. [145]
| Designations | PN G112.9-10.2: A 84, PK 112-10.1, A55 70, ARO 115, VV' 581 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 23h 47m 45s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +51° 23' 58" |
| Dimensions | 120." (optical) |
| Expansion Velocity | 16. (O-III) 25. (N-II) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 458, CSI +51 -23452, UBV 20433 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 17.67, B: 18.67, V: 18.49 |
| Discoverer | ABELL 1955 |
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Abell 84 is located in the constellation Cassiopeia and is circumpolar for Central Europe. On 20 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time to observe is May to February, when it is highest at night.