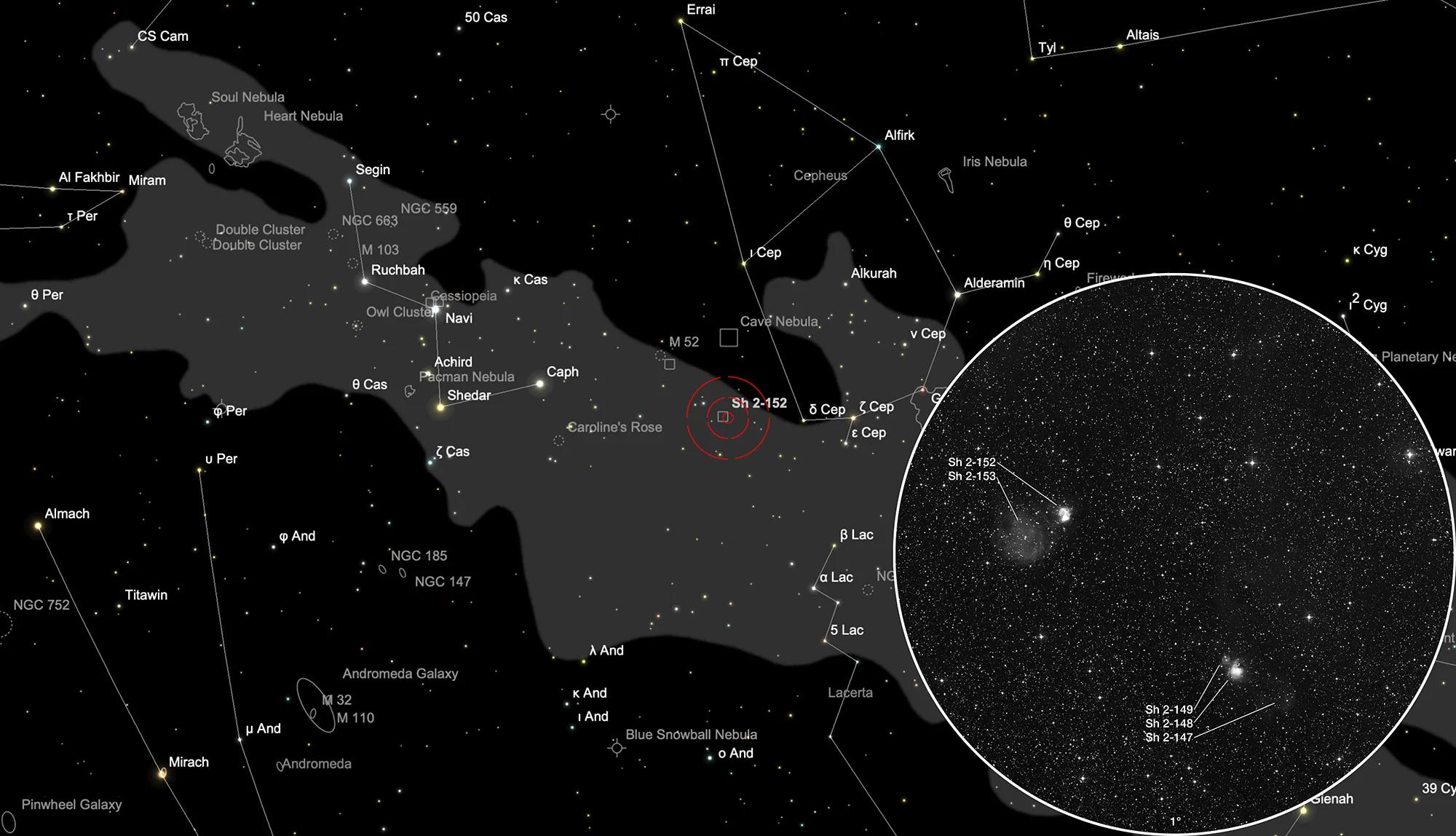
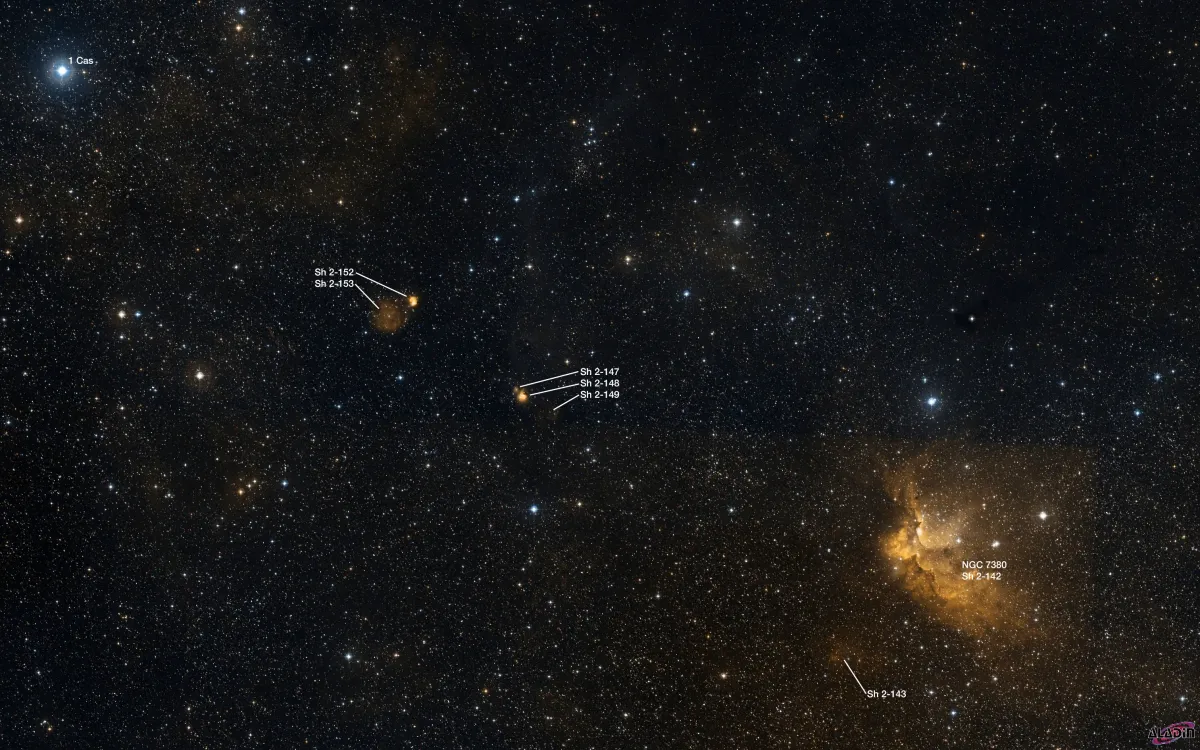
H-II Regions Sh 2-147/148/149/152/153

History
In the 1950-ies the American astronomer Stewart Sharpless did a survey for H II regions on the photo plates of «Palomar Observatory Sky Survey» made with the 48-inch Schmidt telescope. In his first publication the nebulae were listed as number 100, 101, 102, 104 and 105. [309] In 1959 he published a revised and extended version of his survey and listed the western nebulae as Sh 2-147, Sh 2-148, Sh 2-149 and the eastern nebulae as Sh 2-152 and Sh 2-153. [310]
In Beverly Lynds «Catalogue of Bright Nebulae», which was published in 1965. Three of Sharpless nebulae were there listed as LBN 108.33-01.05, LBN 108.80-00.98 and LBN 108.78-01.01. [270]
Physical Properties
| Name | Type | RA (J2000.0) | Dec (J2000.0) | PM [mas/y] | Parall. [mas] | Size ['] | Magnitudes | Identifiers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sh 2-147 | HII | 22h 55m 42s | +58° 28' 00" | SH 2-147 | ||||
| Sh 2-148 | HII | 22h 56m 18s | +58° 31' 00" | 3.02 × 1.58 | SH 2-148; [AAL2018] G108.375-01.056; [ABB2014] WISE G108.375-01.056 | |||
| Sh 2-149 | HII | 22h 56m 17s | +58° 31' 23" | 87GB 225414.0+581521; BWE 2254+5815; F3R 3354; GB6 B2254+5815; GRS G108.20 -01.10; KR 62; LBN 108.33-01.05; LBN 516; NVSS J225617+583117; RRF 1044; SH 2-149; WN B2254.2+5815 | ||||
| Sh 2-152 | HII | 22h 58m 41s | +58° 46' 59" | -3.634 | 0.2889 | 1.047 × 0.9 | G 12.197392; J 8.784; H 8.054; K 7.233 | 2MASX J22584086+5846592; 87GB 225636.5+583050; BWE 2256+5830; F3R 3367; GAL 108.76-00.95; GB6 B2256+5830; Gaia DR3 2013435038638650240; KR 67; LBN 108.80-00.98; LBN 519; NVSS J225840+584702; RRF 1052; SH 2-152; TXS 2256+585; WN B2256.6+5831; [KC97c] G108.8-01.0; [L89b] 108.760-00.952; [PBD2003] G108.8-01.0; [WWB83] G108.76-0.95 |
| Sh 2-153 | HII | 22h 58m 37s | +58° 46' 48" | LBN 108.78-01.01; LBN 518; SH 2-153 |
Finder Chart
The H-II regions Sh 2-147 through Sh 2-153 are located in the constellation Cassiopeia near Cepheus. Roughly 2° towards West there is the Wizard Nebula NGC 7380. These nebulae are circumpolar for Central Europe. On 6 September it is in opposition to the Sun and culminates at local midnight. The best time to observe is May to February, when the constellation is highest at night.