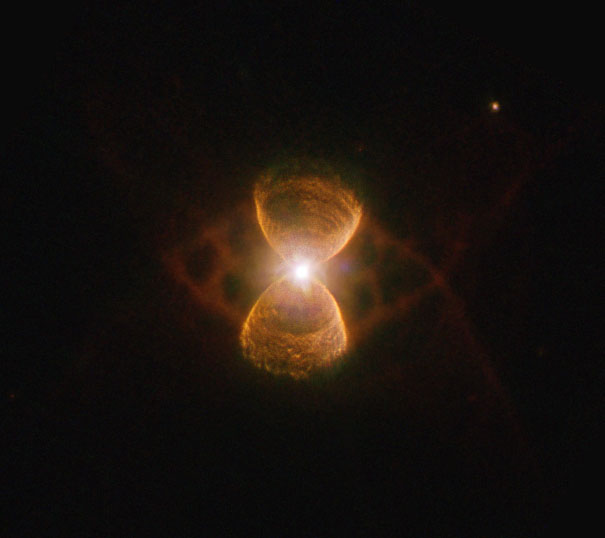
Planetary Nebula Hubble 12

History
This planetary nebula was discovered by the famous astronomer Edwin Hubble in 1921 on photo plates taken with a 10-inch Cooke Astrographic Lens, 45-inch focus, with objective prisms attached, and have been checked by observations with the large reflectors on Mount Wilson Observatory. [416]
Physical Properties
Hubble 12 (Hb 12; PN G111.8-02.8) is a young planetary nebula with a high surface brightness. It shows three pairs of bipolar structures and an arc-shaped filament near the western waist. Together with the presence of H2 knots it suggests that these structures originated from several mass-ejection events during the pre-PN phase. The central star is a binary. The kinematic age of the nebula ranges from about 300 yr for the innermost structure to 1120 yr for entire object. The determined distances of the PN vary between 2.24 kpc and 14.25 kpc. [619] Apparent magnitudes with different filters: B 13.51; V 11.49; R 12.44; J 10.23; H 9.82; K 8.81 [145]
| Designations | PN G111.8-02.8: Hb 12, PK 111-02.1, ARO 381, VV 286, VV'576 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 23h 26m 15s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +58° 10' 55" |
| Dimensions | 1." (optical), 0.7" (radio) |
| Radial Velocity | -5.0 ± 2.3 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 14. (O-III) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 452 |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 14.5, V: 13.8 |
| C-Star Spectral Type | WN 7? |
| Discoverer | HUBBLE 1921 |
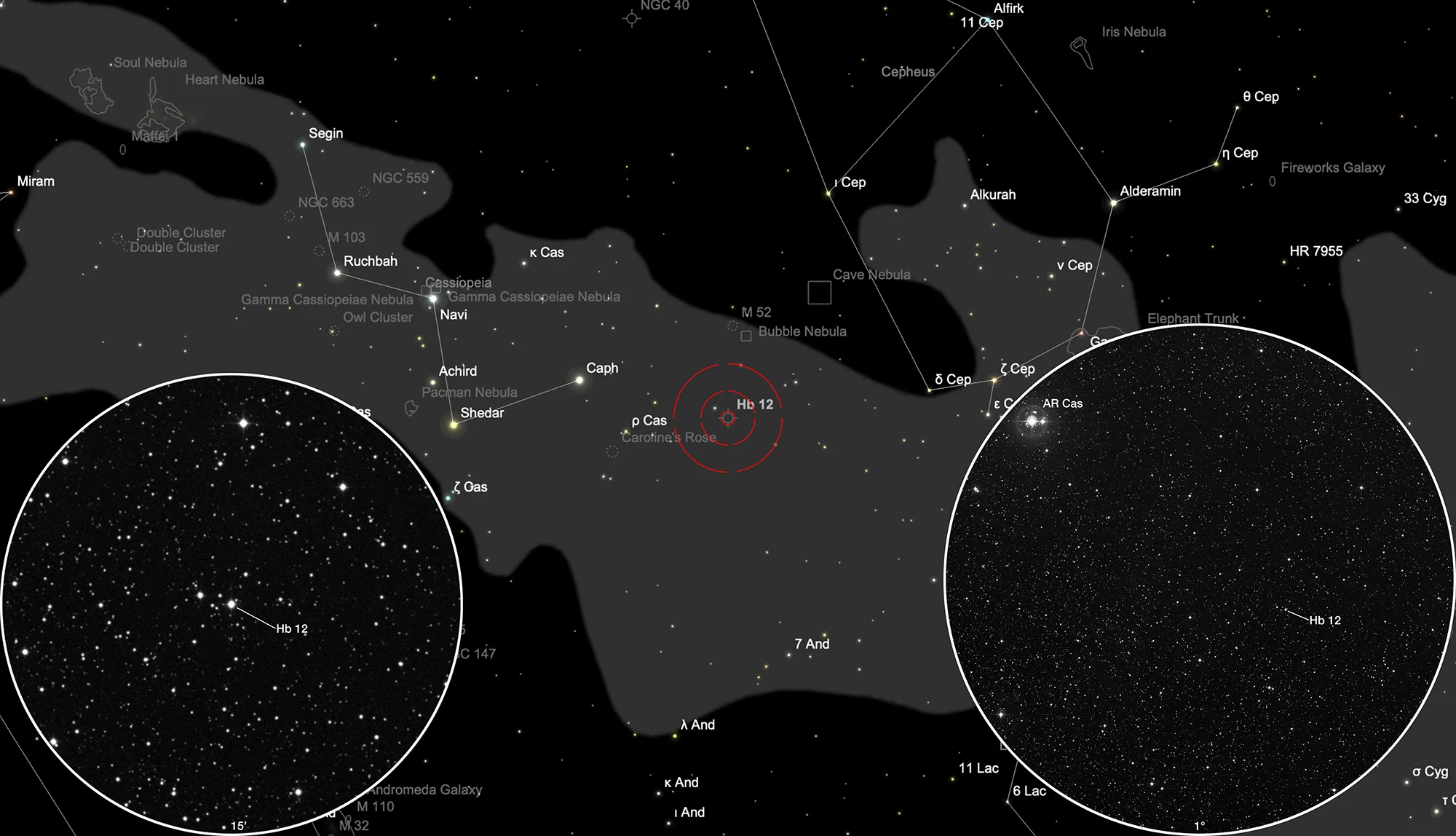
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Hubble 12 is located between the constellations Cassiopeia and Cepheus. On 14 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. It is circumpolar in Central Europe, but the best observation time is May to February, when it is highest at night.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: The position of the planetary nebula Hubble 12 can be clearly determined based on AR Cassiopeiae and a distinctive pair of curved stars. The planetary nebula itself is bright, but even at high magnification, it is only recognizable as a slightly larger spot than a star. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Hasliberg, 16. 12. 2023, SQM 21.2, Bernd Nies