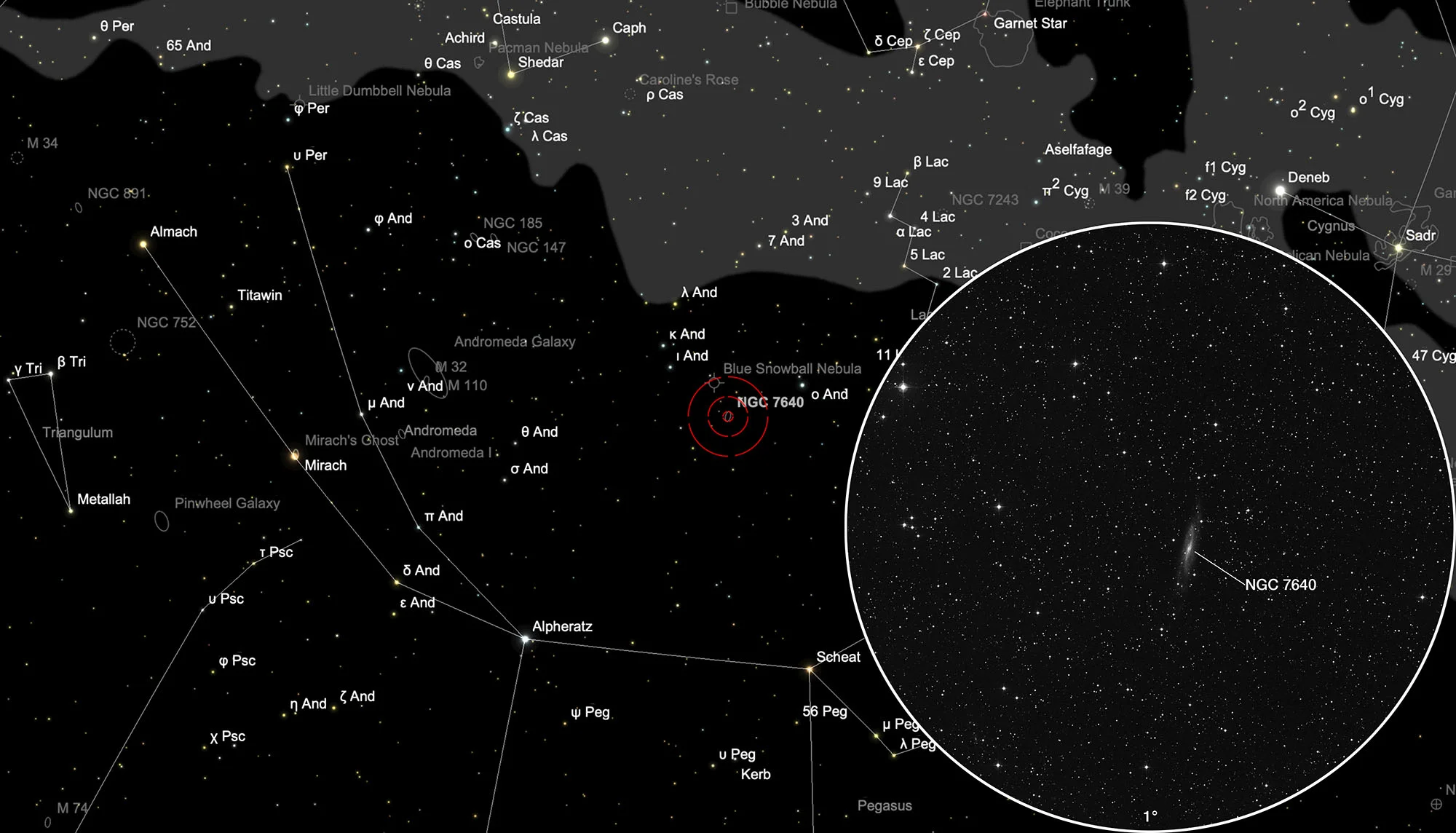
Galaxy NGC 7640

History
The galaxy NGC 7640 was discovered in 1784 with his home-made 18.7 inch f/12.8 reflecting telescope in Slough, England. On 17 October 1786 he cataloged it as II 600. [277, 464]
Physical Properties
Distance measurements of this SBc-type galaxy range from 8.4 Mpc to 11.9 Mpc. [145] There are indications, that the increased star formation is due to a recent interaction with a smaller galaxy. [431]
| Designation | NGC 7640 |
| Type | Gx (SBc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 23h 22m 06.6s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +40° 50' 42" |
| Diameter | 10.5 × 1.8 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 11.9 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 11.3 mag |
| Surface brightness | 14.5 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 167° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.001231 |
| Distance derived from z | 5.20 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 8.510 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | cF, L, mE 164°, vlbM, r |
| Identification, Remarks | WH II 600; h 2236; GC 4950; UGC 12554; MCG 7-48-2; CGCG 532-17; CGCG 533-1; IRAS 23197+4034 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 7640 is located in the constellation Andromeda. On 13 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is May to February, when it is highest at night.