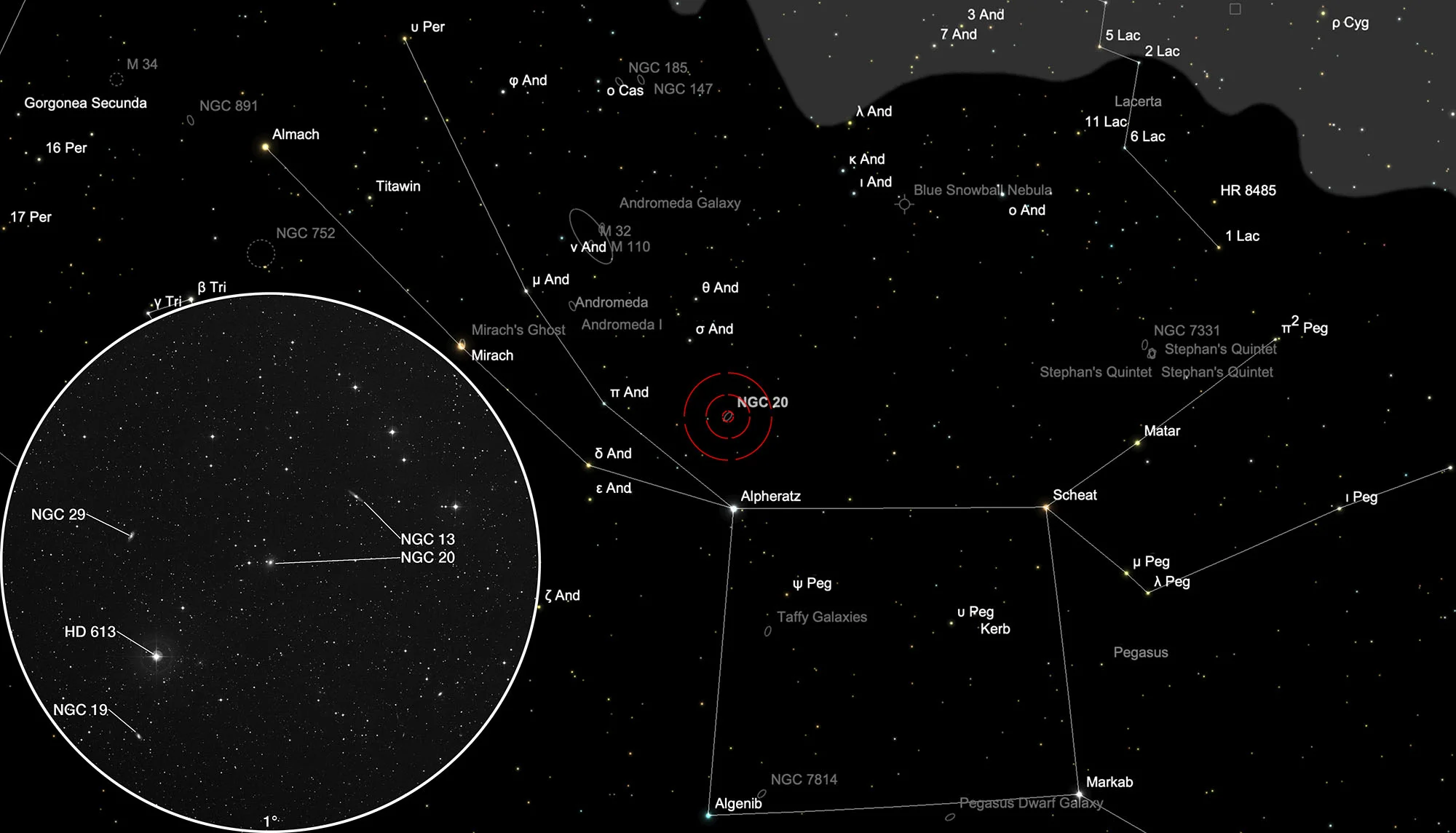
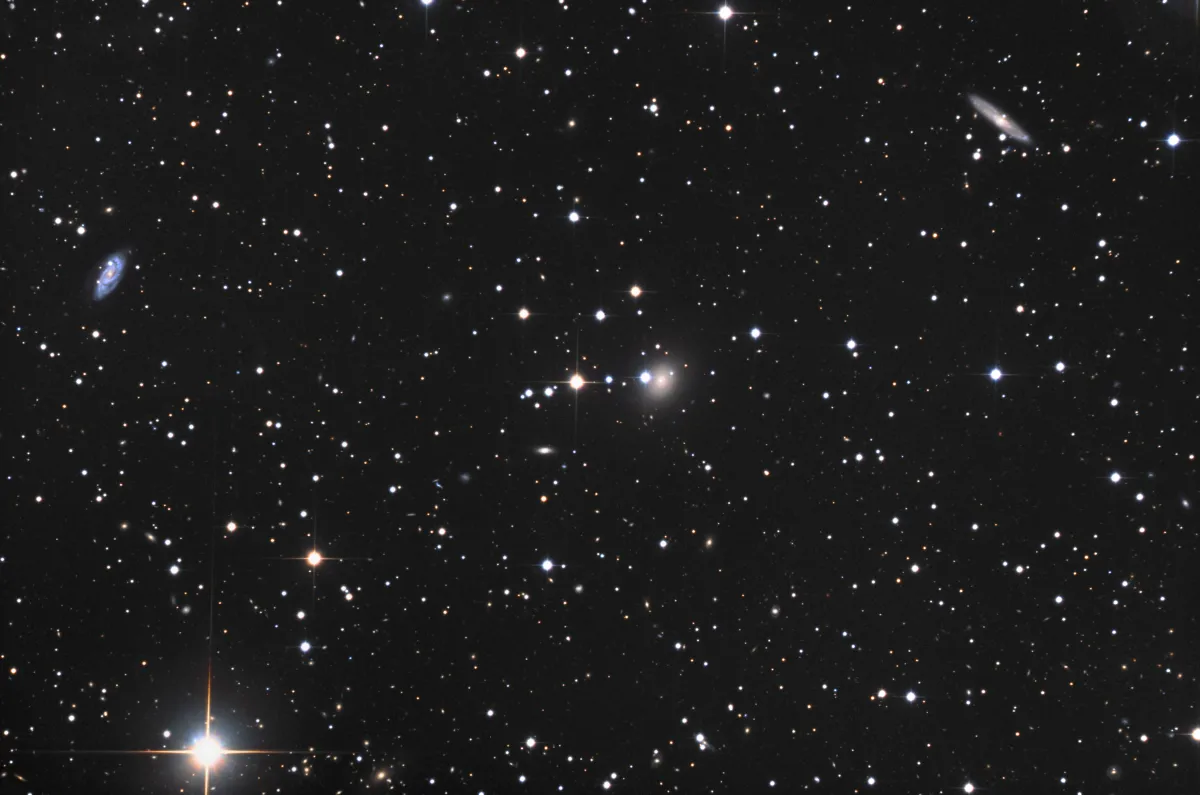
Galaxies NGC 13, NGC 19, NGC 20, NGC 29

History
The first two galaxies of this group were discovered on 26 November 1790 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his self-made 18.7 inch f/12.8 reflector telescope. He logged for III. 866 (NGC 13): «Very faint, very small, the north preceding corner of a square.» And for II. 853 (NGC 29) he wrote: «Faint, small, extended near meridian.» [465]
On the night of 18 September 1857, the Irish astronomer R. J. Mitchell aimed the large 72 inch reflecting telescope of William Parsons, the third Earl of Rosse, on this part of the sky and came across the galaxy NGC 20.
On 20 September 1885, the American astronomer Lewis Swift scoured the same area with the 16 inch refractor of the Warner Observatory in Rochester and recorded three galaxies which were later published by John LE Dreyer in his «New General Catalog of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars» that appeared 1888: NGC 6, NGC 19 and NGC 21. [313] What Dreyer didn't know at the time: Swift's position determinations were flawed. If you take an error of 70 seconds too far west and 8' 12" too far south in all three position determinations then the position of NGC 6 fits to NGC 20 (UGC 84), that of NGC 21 to NGC 29 (UGC 100) and that of NGC 19 to the galaxy UGC 98. [196, 277]
Physical Properties
The redshift of all galaxies is around z ≈ 0.016, which corresponds to an average distance of around 65 Mpc. [145]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 6 | 00 09 32.6 | +33 18 32 | dup | 14.1 | 13.1 | 1.0 | 14.3 | 1.7 × 1.6 | 140 | 0.016581 | 70.04 | eF, vS, cE | NGC 20; UGC 84; MCG 5-1-36; CGCG 498-82; CGCG 499-54 | |
| NGC 13 | 00 08 47.7 | +33 25 59 | Gx (Sab) | 14.0 | 13.2 | 0.8 | 13.5 | 2.3 × 0.6 | 53 | 0.016038 | 67.74 | 61.030 | vF, vS, S st + neb | WH III 866; h 2; GC 5; UGC 77; MCG 5-1-34; CGCG 498-81; CGCG 499-53 |
| NGC 19 | 00 10 40.8 | +32 58 58 | Gx (SBbc) | 14.1 | 13.3 | 0.8 | 12.7 | 1.1 × 0.6 | 42 | 0.015971 | 67.46 | 63.430 | eeF, lE, 3 vF st around | UGC 98; MCG 5-1-46; CGCG 499-65; KAZ 18; IRAS 00080+3242 |
| NGC 20 | 00 09 32.6 | +33 18 32 | Gx (E-S0) | 14.1 | 13.1 | 1.0 | 14.3 | 1.7 × 1.6 | 140 | 0.016581 | 70.04 | F, * 10 att | GC 6=5086; NGC 6; UGC 84; MCG 5-1-36; CGCG 498-82; CGCG 499-54 | |
| NGC 21 | 00 10 47.0 | +33 21 07 | dup | 13.5 | 12.7 | 0.8 | 12.8 | 1.5 × 0.7 | 154 | 0.015911 | 67.21 | 71.680 | eF, S, lE | NGC 29; UGC 100; MCG 5-1-48; IRAS 00082+3304; CGCG 499-66; KAZ 19 |
| NGC 29 | 00 10 47.0 | +33 21 07 | Gx (SBbc) | 13.5 | 12.7 | 0.8 | 12.8 | 1.5 × 0.7 | 154 | 0.015911 | 67.21 | 71.680 | pB, pL, E 0° | WH II 853; h 6; GC 14; NGC 21; UGC 100; MCG 5-1-48; IRAS 00082+3304; CGCG 499-66; KAZ 19 |
Finder Chart
The galaxies are located in the constellation Andromeda, which is best visible from May to February.