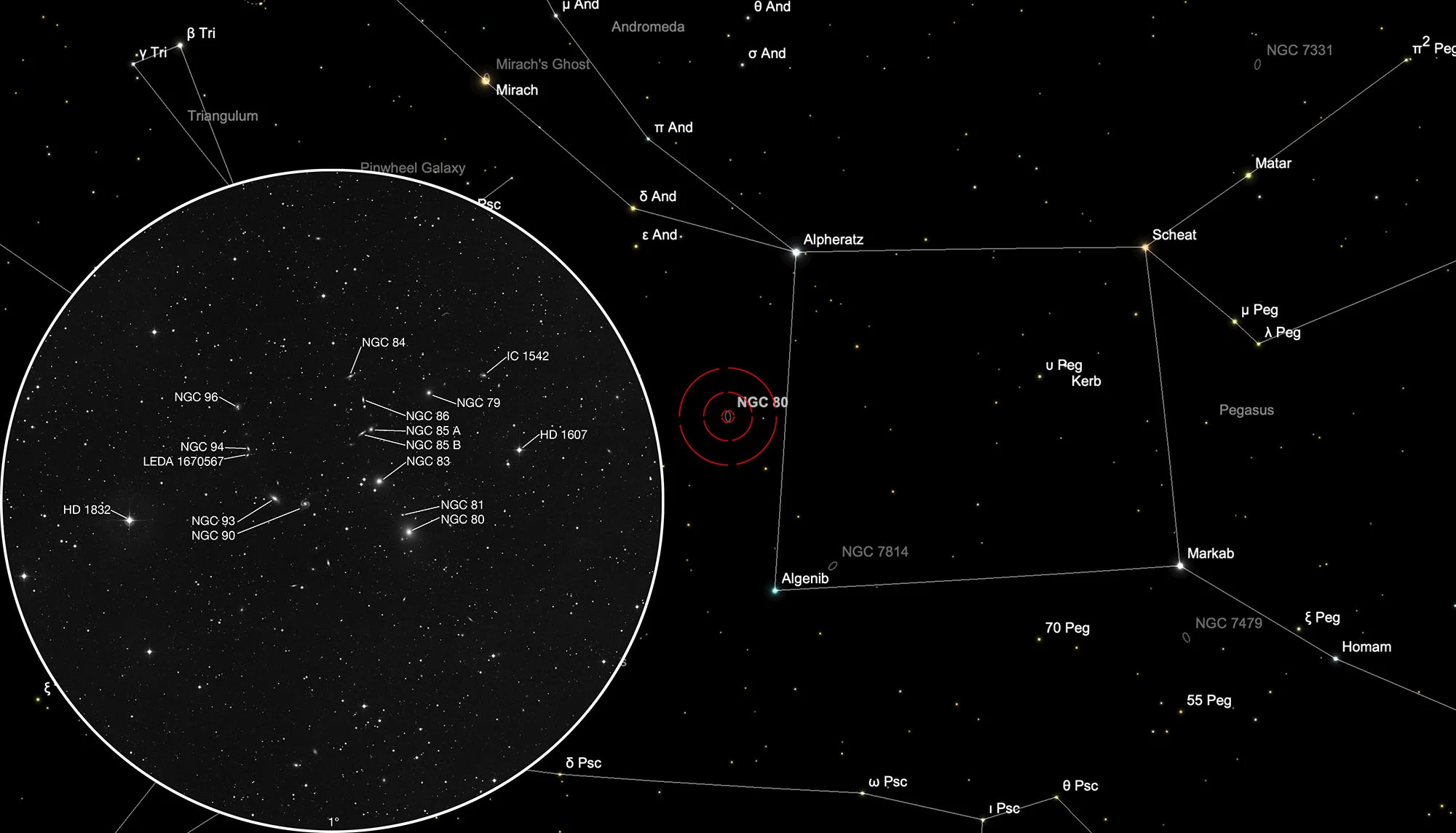
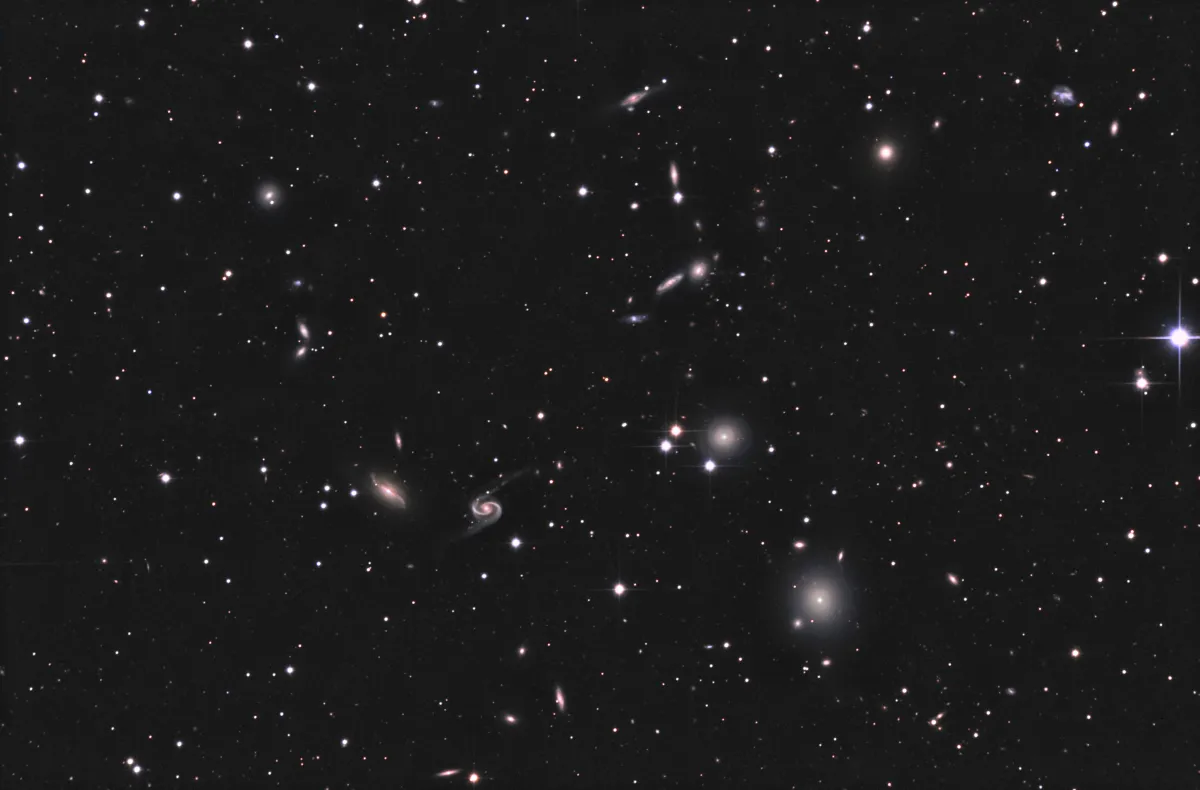
NGC 80 Galaxy Group & Arp 65

History
The brightest two galaxies in this group were discovered by John Herschel on 17 August 1828 using his 18.25 inch reflecting telescope at Slough, England. He cataloged his discoveries as h 16 and h 17. For h 16 (NGC 80) he noted: «faint; small; round; pretty suddenly brighter in the middle; 15" [diameter] .» For h 17 (NGC 83) he noted: «elliptical; perhaps bicentral; makes trapezium with three bright stars.» [466]
The galaxies NGC 90 and NGC 93 were discovered on 26 October 1854 by R. J. Mitchell. NGC 81 and NGC 85 were discovered on 15 November 1873 by Ralph Copeland. Both were using the giant 72 inch reflector from William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, at Birr Castle. The remaining galaxies of this group were discovered by the French astronomer Guillaume Bigourdan in October/November 1884. He was using the 12.4 inch refractor at Paris Observatory. IC 1542 was discovered on 20 November 1897 by the French astronomer Stephane Javelle. He was using the 30 inch refractor at the Nice Observatory [196, 277]
In Halton Arp's «Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies» from 1966 the two galaxies NGC 90 and NGC 93 are listed as Arp 65. He noted: «Position of open spiral. Components lie off projected ends of both spiral arms.» [199]
Physical Properties
According to HyperLeda the NGC 80 galaxy group counts 13 members which are gravitationally bound and have a mean heliocentric radial velocity of 5942 km/s. [134] At Simbad one finds for NGC 80 distances ranging from 73 Mpc to 76 Mpc. NGC 83 seems to be a bit further away with distances ranging from 80 Mpc to 84 Mpc. [145]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 79 | 00 21 02.8 | +22 34 02 | Gx (E-S0) | 15.0 | 14.0 | 1.0 | 13.0 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.018296 | 77.28 | vF, S, vlbM | MCG 4-2-3; CGCG 479-3; NPM1G +22.0015 | ||
| NGC 80 | 00 21 10.9 | +22 21 28 | Gx (E-S0) | 13.1 | 12.1 | 1.0 | 13.2 | 1.6 × 1.6 | 0.019006 | 80.28 | 94.300 | F, S, R, psbM | h 16; GC 38; UGC 203; MCG 4-2-4; CGCG 479-6 | |
| NGC 81 | 00 21 13.2 | +22 23 00 | Gx (S) | 16.5 | 15.7 | 0.8 | 11.3 | 0.2 × 0.1 | 84 | 0.020447 | 86.37 | eeF, sp h 17 | NPM1G +22.0016 | |
| NGC 83 | 00 21 22.6 | +22 26 03 | Gx (E0) | 13.6 | 12.5 | 1.1 | 13.3 | 1.5 × 1.5 | 0.020771 | 87.74 | 94.300 | E, biN, 3 B st nr | h 17; GC 39; UGC 206; MCG 4-2-5; CGCG 479-8 | |
| NGC 84 | 00 21 21.2 | +22 37 09 | * | eF, st & neb | ||||||||||
| NGC 85 | 00 21 25.5 | +22 30 44 | Gx (S0) | 15.8 | 14.8 | 1.0 | 13.5 | 0.7 × 0.5 | 146 | 0.020694 | 87.41 | eeF, cL, R | GC 5095; NGC 85A; MCG 4-2-7; CGCG 479-9; NPM1G +22.0017 | |
| NGC 85 A | 00 21 25.5 | +22 30 44 | dup | 15.8 | 14.8 | 1.0 | 13.5 | 0.7 × 0.5 | 146 | 0.020694 | 87.41 | eeF, cL, R | GC 5095; NGC 85; MCG 4-2-7; CGCG 479-9; NPM1G +22.0017 | |
| NGC 85 B | 00 21 29.1 | +22 30 23 | dup | 15.5 | 14.7 | 0.8 | 13.1 | 0.9 × 0.3 | 129 | 0.019413 | 82.00 | 83.670 | eeF, cL, R | GC 5095; IC 1546; MCG 4-2-8; CGCG 479-10 |
| NGC 86 | 00 21 28.6 | +22 33 23 | Gx (S?) | 15.7 | 14.8 | 0.9 | 13.0 | 0.7 × 0.3 | 9 | 0.018650 | 78.78 | 88.830 | eF, vS, lbM | MCG 4-2-9; CGCG 479-11 |
| NGC 90 | 00 21 51.6 | +22 24 02 | Gx (SBc) | 14.5 | 13.7 | 0.8 | 14.0 | 1.9 × 0.8 | 132 | 0.017856 | 75.42 | vF, lE | GC 40=5096; UGC 208; MCG 4-2-11; CGCG 479-13; Arp 65 | |
| NGC 93 | 00 22 03.4 | +22 24 32 | Gx (Sb) | 14.3 | 13.2 | 1.1 | 12.8 | 1.4 × 0.6 | 48 | 0.017946 | 75.80 | 91.120 | vF, vS | GC 42=5098; UGC 209; MCG 4-2-12; CGCG 479-15; Arp 65 |
| NGC 94 1 | 00 22 13.6 | +22 29 00 | Gx (S0) | 15.6 | 14.6 | 1.0 | 11.7 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 30 | 0.019604 | 82.81 | eF, vS | CGCG 479-17 | |
| NGC 94 2 | 00 22 13.8 | +22 28 26 | Gx (S0) | 16.5 | 15.5 | 1.0 | 12.6 | 0.4 × 0.2 | 150 | 0.019523 | 82.46 | eF, vS | NPM1G +22.0020 | |
| NGC 96 | 00 22 17.8 | +22 32 48 | Gx (S0) | 15.6 | 14.6 | 1.0 | 13.4 | 0.6 × 0.6 | 0.020631 | 87.14 | vF, S, vlbM | MCG 4-2-14 | ||
| IC 1542 | 00 20 41.4 | +22 35 34 | Gx (S) | 14.9 | 14.1 | 0.8 | 12.8 | 0.7 × 0.5 | 78 | 0.024524 | 103.5 | F, dif, gbM | MCG 4-2-1; CGCG 479-1 |
Finder Chart
The NGC 80 galaxy group is located in the constellation Andromeda on the eastern side of the rectangle of Pegasus. On 29 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight.