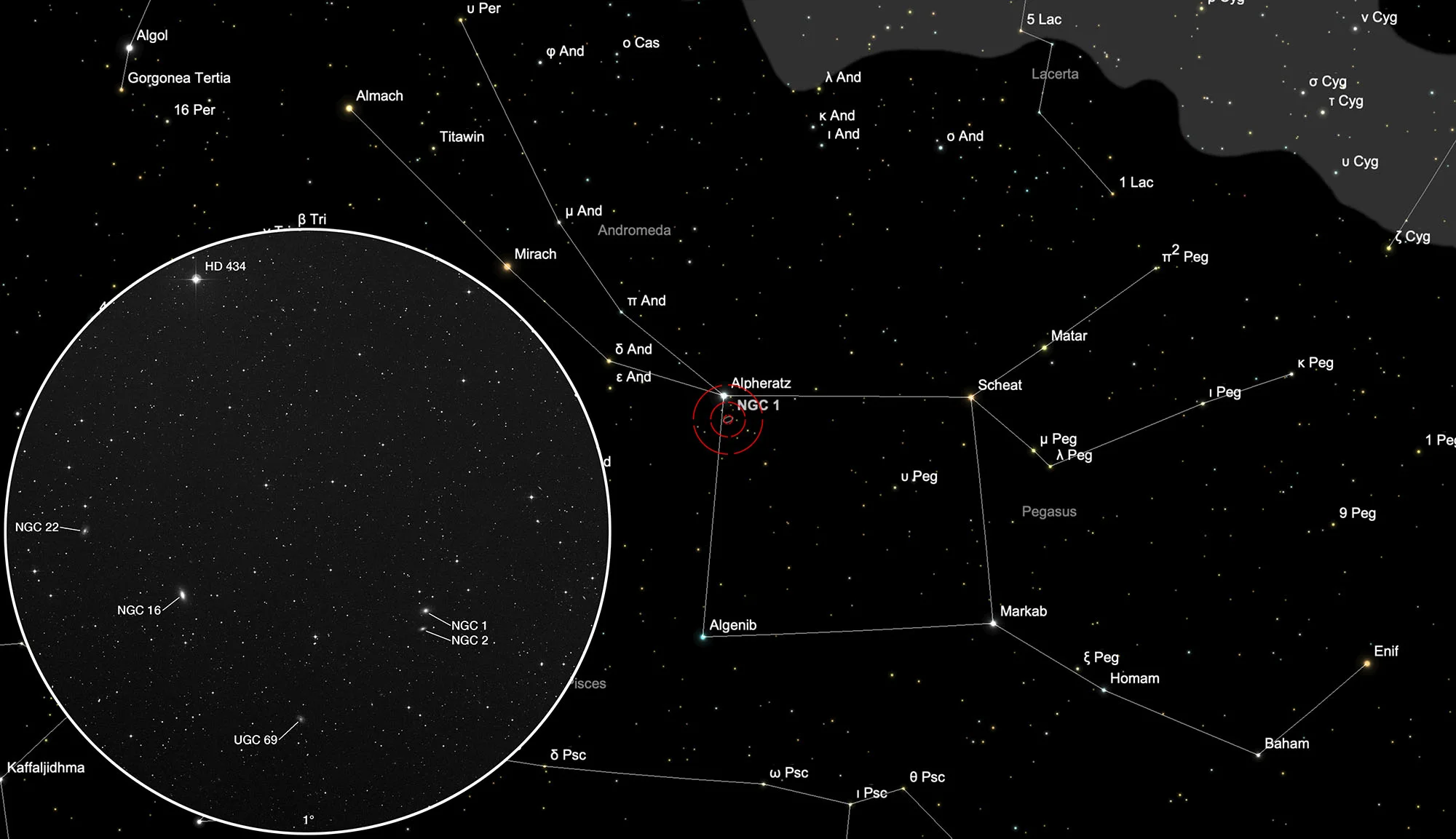
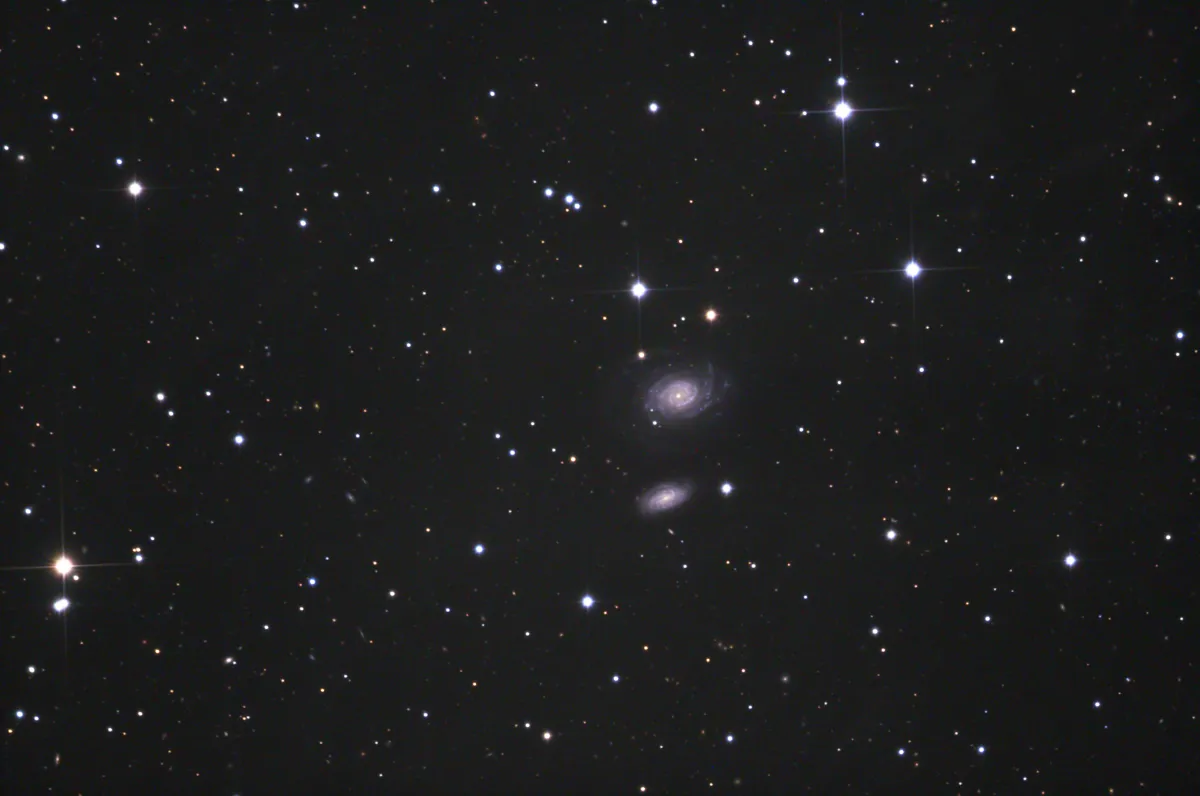
Galaxies NGC 1, NGC 2

History
The galaxy NGC 1 was discovered on 30 September 1861 by the German astronomer Heinrich Louis d'Arrest using the 11-inch f/17.5 Merz refractor of the Copenhagen Observatory. His descriptions (combination of 4 observations) read «faint, small, round, 20", no concentration. In a straight line connecting two stars 11 and 14 mag.» He missed the fainter galaxy NGC 2 just south of it. Herman Schultz observed NGC 1 three times in 1866 and 1868 with a 9.6-inch refractor at Uppsala Observatory. He also missed fainter NGC 2. [364]
NGC 2 was discovered on 20 August 1873 by Lawrence Parsons, the 4th Earl of Rosse. He recorded a «very faint companion [to NGC 1] south». Dreyer confirmed the observation on 29 October 1877 and noted, «Nova 2' ssf easily seen, vF, eS stellar.» Yann Pothier credits Auguste Voigt with the original discovery on 14 Sep 1865 with the 31-inch Foucault reflector at the Marseilles Observatory. [364]
Physical Properties
NGC 1 is a spiral galaxy of the morphological type SAbc. The escape speeds measured since the year 2000 are in the range of 4550 km/s to 4620 km/s, the resulting distances from 64 Mpc to 74 Mpc (209 to 241 million light years). For the galaxy NGC 2, the measured escape speeds are in the range of 7547 km/s to 7559 km/s, i.e. much higher. In fact, this galaxy is much farther away: 88 Mpc to 103 Mpc (287 to 336 million light years). The two galaxies have nothing to do with each other and are just coincidentally close to each other. [145]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 1 | 00 07 15.9 | +27 42 32 | Gx (Sb) | 13.7 | 12.9 | 0.8 | 13.5 | 1.7 × 1.2 | 120 | 0.015177 | 64.11 | 63.200 | F, S, R, bet * 11 and * 14 | GC 1; UGC 57; MCG 4-1-25; CGCG 477-54; IRAS 00047+2725; KCPG 2A; CGCG 478-26 |
| NGC 2 | 00 07 17.1 | +27 40 43 | Gx (Sab) | 15.0 | 14.2 | 0.8 | 13.6 | 1 × 0.6 | 112 | 0.025214 | 106.5 | 93.190 | vF, S, s of G.C. 1 | GC 6246; UGC 59; MCG 4-1-26; CGCG 477-55; CGCG 478-27; KCPG 2B |
| NGC 16 | 00 09 04.2 | +27 43 48 | Gx (E/SB0) | 13.0 | 12.0 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 1.8 × 1 | 16 | 0.010340 | 43.68 | pB, S, R, bM | h 4; GC 8; UGC 80; MCG 4-1-32; CGCG 477-61; CGCG 478-33 | |
| NGC 22 | 00 09 48.2 | +27 49 58 | Gx (Sb) | 14.4 | 13.6 | 0.8 | 13.8 | 1.3 × 1 | 160 | 0.027726 | 117.1 | 108.50 | vF, pS, R, lbM, r | WH IV 15; h 5?; GC 12?; UGC 86; MCG 5-1-39; CGCG 499-55 |
Finder Chart
The first two entries in Dreyer's «New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars» are in the constellation Pegasus, about 1.5° south of the star Alpheratz (α Andromedae). The best observation time is May to February.