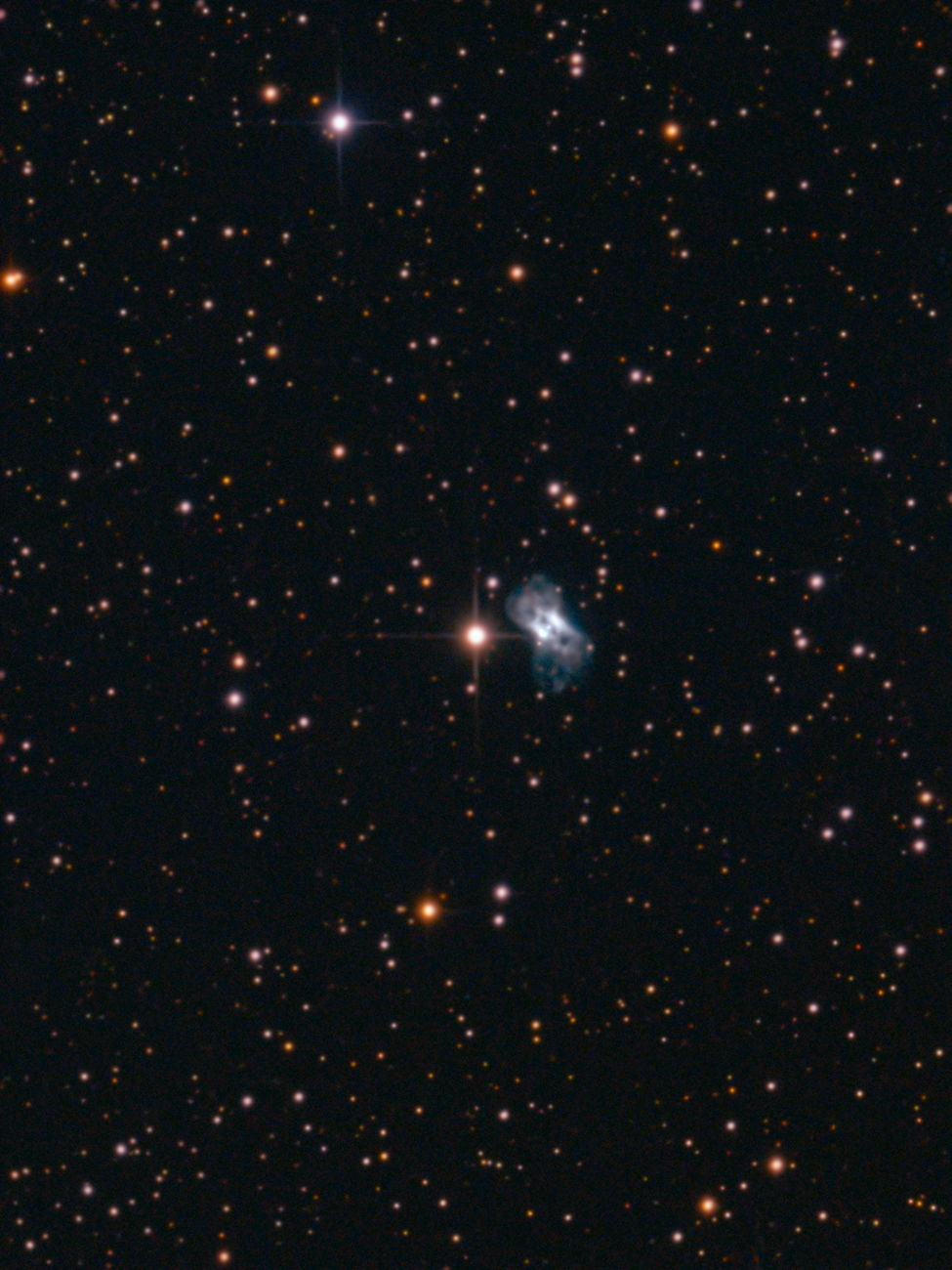
Cheeseburger Nebula (NGC 7026)


History
The planetary nebula NGC 7026 was discovered on July 6, 1873, by the American astronomer Sherbourne Burnham using a 6" Clark refractor. Independently, it was also discovered on November 18, 1880, by the British astronomer Ralph Copeland through visual spectroscopy with a 6.1" refractor at the Dun Echt Observatory in Scotland. J. L. E. Dreyer described the nebula in his 1888 NGC catalog as a "fairly bright planetary nebula with two nuclei." [196, 313]
Physical Properties

NGC 7026 is a complex, bipolar nebula. It consists of three opposite polar pairs of lobes and four sets of nodes, all symmetrical about the core, and a conical outlet. The nebula shows a strongly ionized structure. Investigations with the XMM-Newton telescope showed X-rays emanating from the bipolar lobes, suggesting a temperature of the escaping gas of around 1.1 million Kelvin. At the centre is a hydrogen-poor WC star, a subset of Wolf-Rayet stars. Along the main axis of symmetry, the nebula is expanding at 150 km/s and the equatorial ring is expanding at about 57 km/s. The age of the nebula is estimated at 1500 years. The main axis of the nebula is tilted about 75° in our direction. The distance to NGC 7026 is estimated at 2086 ± 420 pc, about 6800 ± 1300 light years. [344, 345]
| Designations | PN G089.0+00.3: NGC 7026, PK 89+00.1, ARO 59, EM* CDS 1218, VV 260, VV' 542 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 21h 06m 18s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +47° 51' 07" |
| Dimensions | 20." (optical) |
| Distance | 2.5 kpc |
| Radial Velocity | -40.6 ± 0.6 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 38. (O-III) 52.5 (N-II) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 420, CSI +47 -21046, HD 201192, PLX 5080 |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 15.33, V: 14.20 |
| C-Star Spectral Type | O VI, WC 3 |
| Discoverer | COPELAND 1880 |
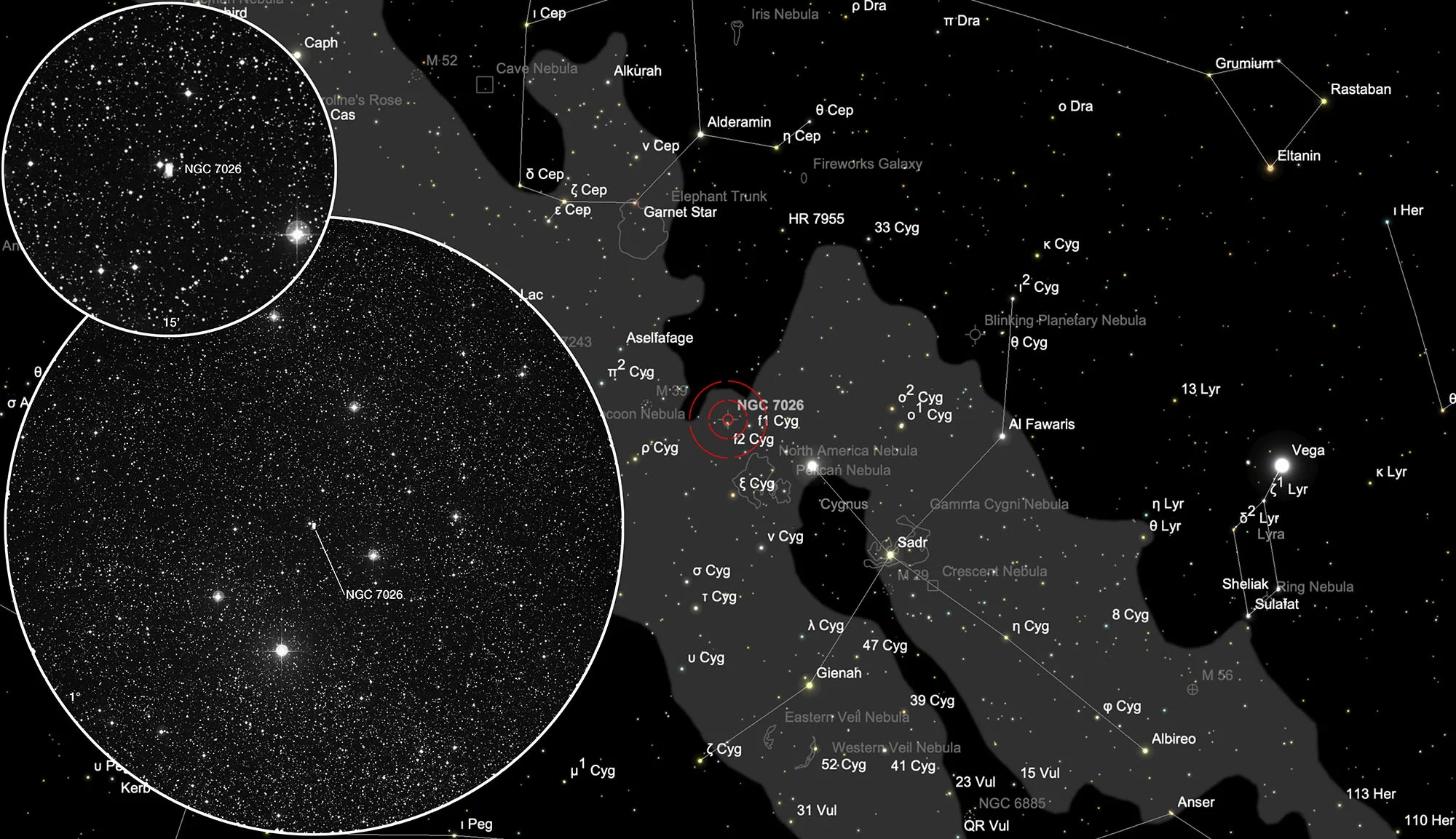
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula NGC 7026 is located in the constellation Cygnus. On 7 August it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observing time is April to January, when the PN is highest in the night sky.
Visual Observation
762 mm Aperture: In the Cheeseburger Nebula NGC 7026, two blurred stars appear at medium magnification. At high magnification, the two stars each become an elongated line or the two pieces of bread on the cheeseburger. A broad black dividing line appears between them. — 30" f/3.3 SlipStream Dobsonian, Hasliberg, 20. 06. 2025, SQM-L 21.27, Eduard von Bergen