Planetary Nebula NGC 7048

History
The planetary nebula NGC 7048 was discovered by French astronomer Édouard Stephan on 19 October 1878. [196]
Physical Properties
Visual brightness is given as 11 or 12 magnitudes. The nebula has an ellipsoidal shape, which is slightly brighter on the western and eastern edges. Infrared images suggest that the nebula has a bi-polar shape similar to a butterfly, tilted about 60° in the line of sight. Due to the nebula's low surface brightness, it is believed to be well advanced in its evolution. The angular diameter is about one arc minute and the distance 1613 pc (about 5200 light years). The white dwarf star in the centre has a brightness of about 19 mag. [145, 196, 322]
| Designations | PN G088.7-01.6: NGC 7048, PK 88-01.1, ARO 41, Hb 9, VV 262, VV' 545 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 21h 14m 15s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +46° 17' 19" |
| Dimensions | 61." (optical), 70." (radio) |
| Distance | 1.3 - 2.5 kpc |
| Radial Velocity | -50.2 ± 8.1 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 15. (O-III) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 424 |
| C-Star Magnitude | V: 19.12 |
| Discoverer | CURTIS 1919 |
Finder Chart
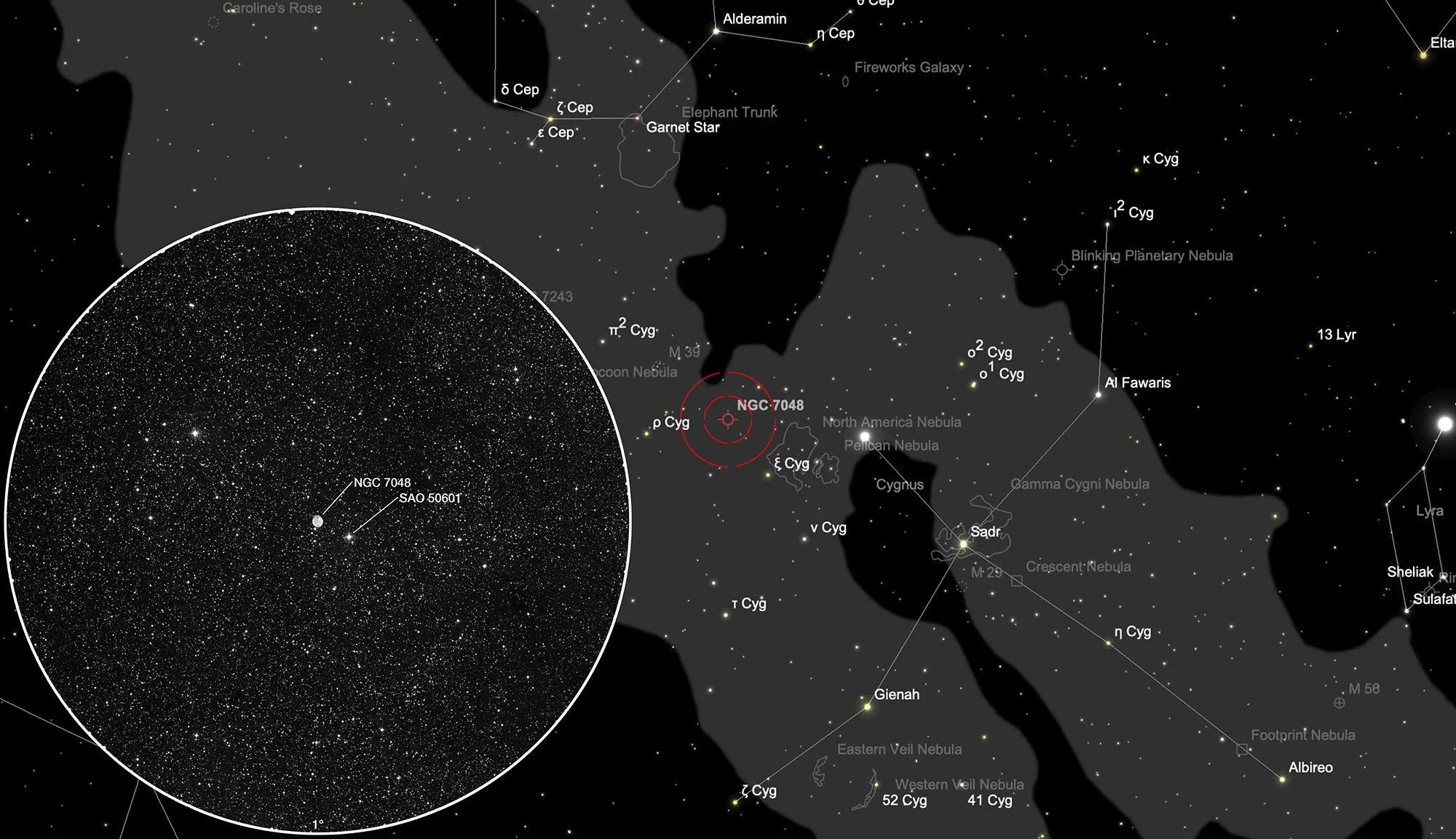
The planetary nebula NGC 7048 is located in the constellation Cygnus, roughly between the two stars Deneb (α Cygni) and ρ Cygni, one third closer to ρ Cygni. Only 3' 20" away is the 8.2 mag bright star SAO 50601. On 9 August it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is from April to January.