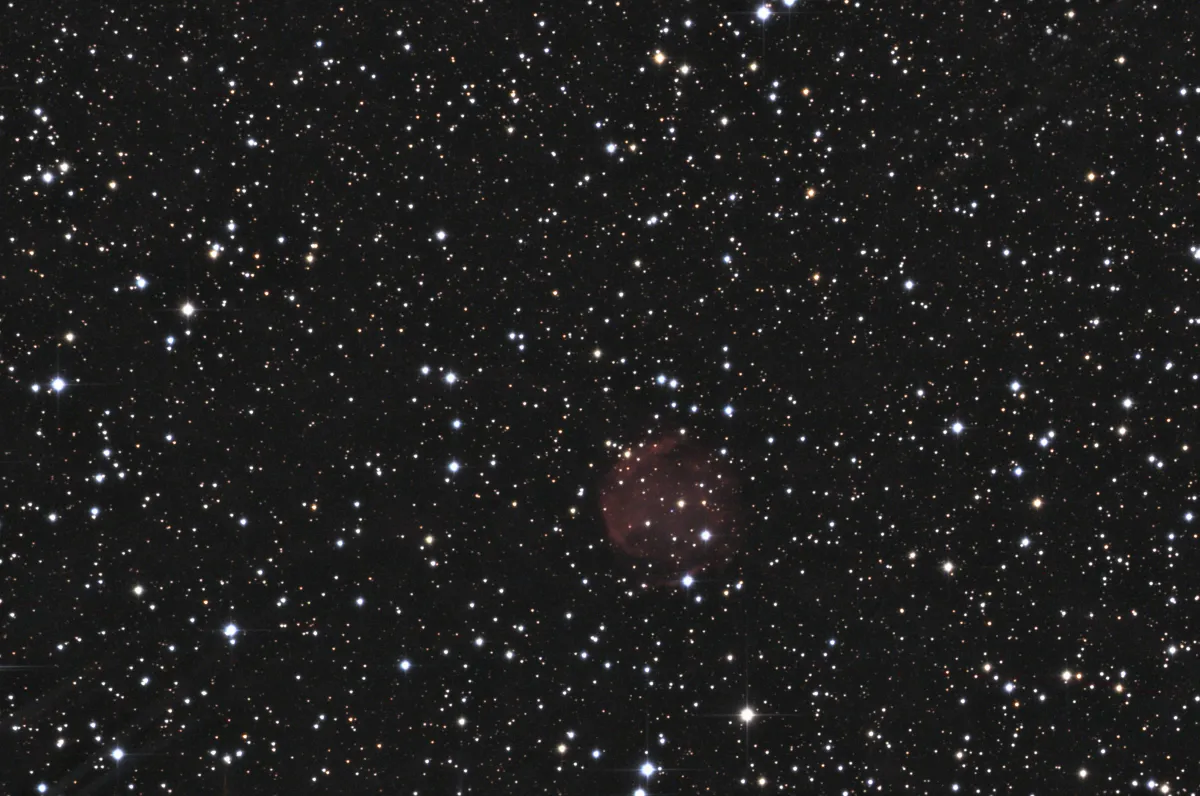
Planetary Nebula Abell 71

History
The planetary nebula Abell 71 (PK 85+4.1) was discovered in 1955 by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell on the photo plates of the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS). In 1955 he published a first list of 13 globular clusters and the positions of 73 planetary nebulae. The PN had the number 58 (A55 58). Stewart Sharpless added the nebula to his catalog of H-II regions as Sh2-116 in 1959. Due to its size and low brightness, it probably did not recognize it as a planetary nebula. In 1966 Abell published a complete list including the size and description of the 86 planetary nebulae discovered on the POSS photo plates. The designation PK 85+4.1 originates from the two Czechoslovak astronomers Luboš Perek and Luboš Kohoutek, who in 1967 compiled a catalog of all the planetary nebulae of the Milky Way known at the time. [331, 332]
Physical Properties
Abell 79 is very large with an angular diameter of around 2.6 arc minutes, but has a very low surface brightness with 19 magnitudes. This suggests an advanced age. The distance was determined to be 729 parsecs (around 2400 light years) in 2008. [145]
| Designations | PN G084.9+04.4: A 71, PK 85+04.1, A55 58, ARO 352, Sh 2-116, VV' 537 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 20h 32m 23s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +47° 21' 04" |
| Dimensions | 157." (optical) |
| Expansion Velocity | 10. (O-III) 20. (N-II) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 412, CSI +47 -20308, UBV 17830 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 18.66, B: 19.32, V: 18.95 |
| Discoverer | ABELL 1955 |
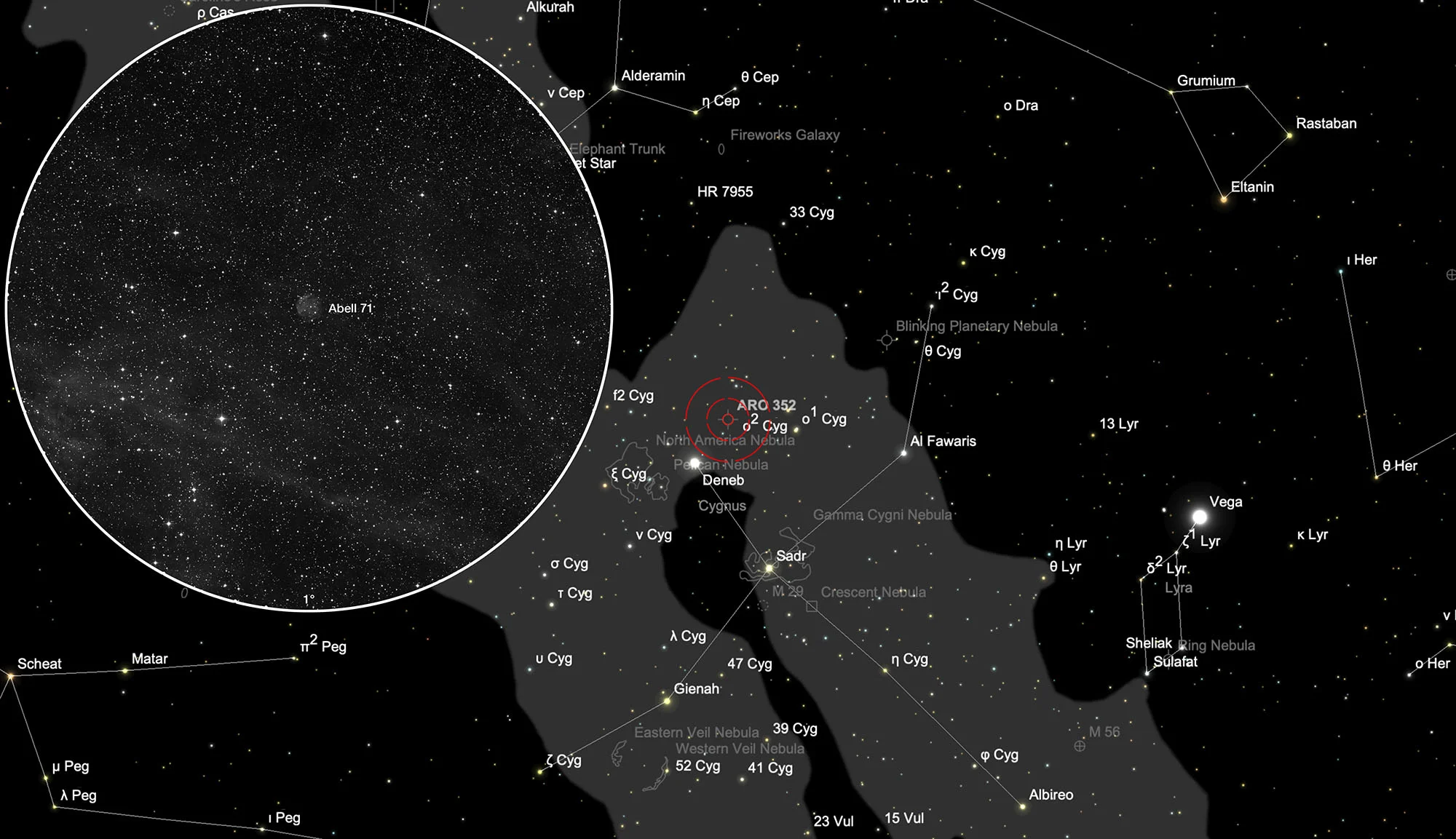
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Abell 71 is located in the constellation Cygnus. On 29 July it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is April to December.