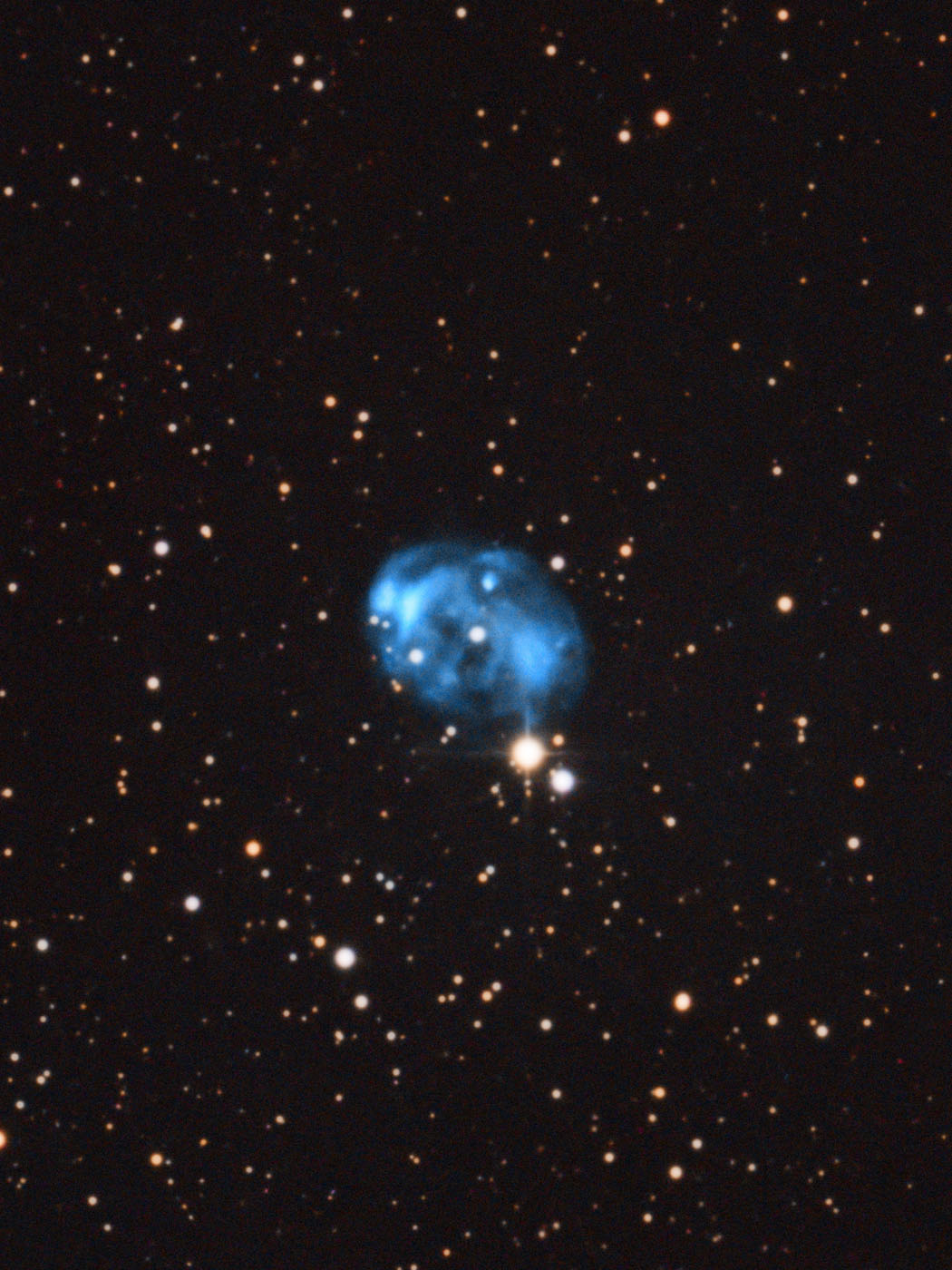
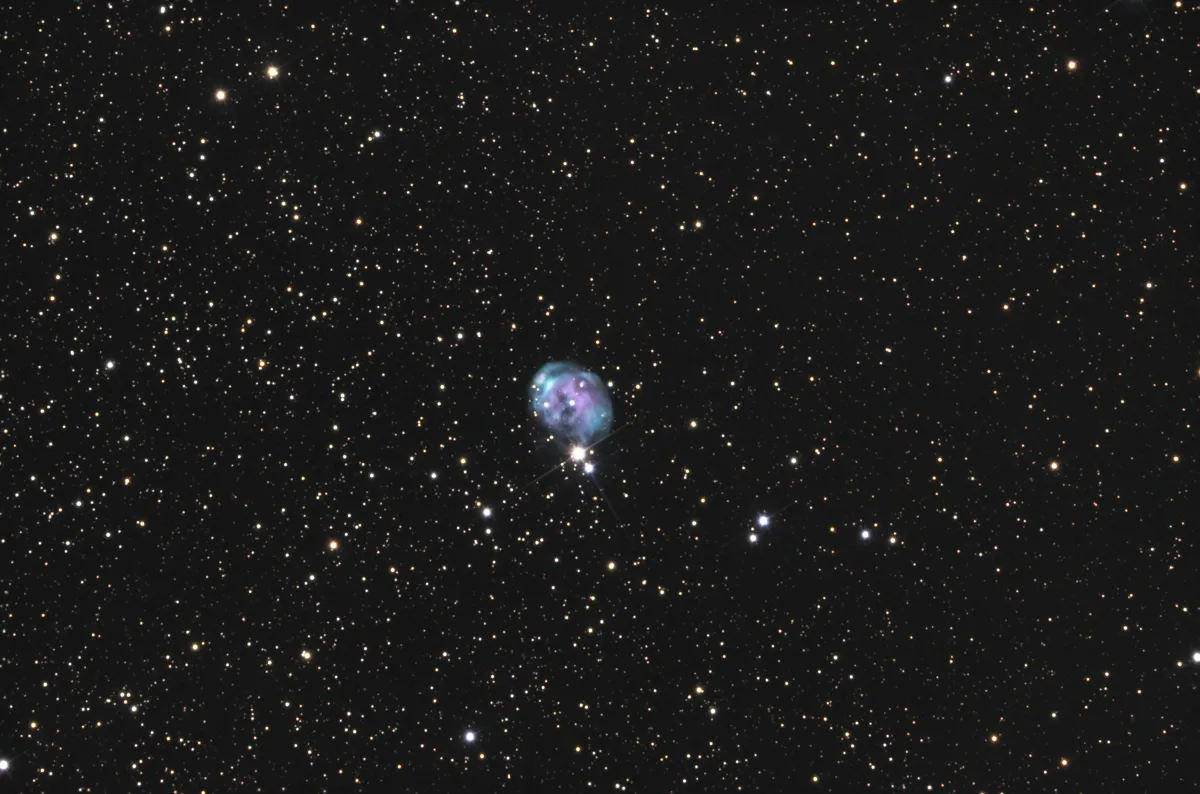
Fetus Nebula (NGC 7008)


History
This nebula was discovered by William Herschel on 14 October 1787 and cataloged as I 192 with the description: «Considerably bright of irregular figure, 3' long, 2.5' broad nebulosity.» [464] In 1888 John L. E. Dreyer cataloged it as NGC 7008 in his «New General Catalogue». [313]
Between 1911 to 1916 the American astronomer Francis G. Pease took a picture with the 60 inch f/5 reflector on Mount Wilson and recognized the nature of NGC 7008 as a planetary nebula. He described the picture as follows: «This planetary nebula is elliptical in shape, 95"x75", p=5°, containing much detail. The strongest bits of nebulosity are two condensations just E of the N end of the major axis. On the south following side the elliptical form seems eaten away, but traces of nebulosity may be seen connecting with a star which lies p=156°. A number of stars a magnitude or two fainter than the nucleus appear in the nebula. Except for one, they are surrounded by a dark ring which un turn opens directly on a dark region. As the nucleus itself presents this appearance, it is suggested that these stars lie within the nebula. One of the stars, p=240°, 23", appears elongated; it may be a double star or a very bright bit of nebulosity. One star at p=65°, 29", with respect to the nucleus, is but partly surrounded by the dark ring. Huggins found the spectrum to be gaseous.» [601]
Physical Properties
NGC 7008 is the shed shell of a red giant that has used up all its hydrogen and has evolved into a white dwarf in the final stage. The apparent magnitudes of the nebula measured with different filters are: R 13.2 mag, J 11.8 mag, H 11.5 mag, K 11.4 mag. The distance from Earth is 869 parsecs, around 2800 light years. [145]
South of NGC 7008 is another binary star system. The main star HD 235422 of spectral type K7 has an apparent visual magnitude of 9.5 mag and its companion HJ 1606 appears 11.6 mag bright. The two 18.7 arc seconds separated stars are at a distance of 469 parsecs, about 1500 light-years and are therefore unrelated to the planetary nebula. [145]
| Designations | PN G093.4+05.4: NGC 7008, PK 93+05.2, ARO 39, VV 258, VV' 540 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 21h 00m 33s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +54° 32' 29" |
| Dimensions | 86." (optical), 95." (radio) |
| Distance | 1.3 kpc |
| Radial Velocity | -74.2 ± 2.0 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 40.0 (O-III) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 417, CSI +54 -20591, GCRV 13203, PLX 5049 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 12.99, B: 13.75, V: 13.23 |
| C-Star Spectral Type | O7, O(H) |
| Discoverer | PEASE 1917 |
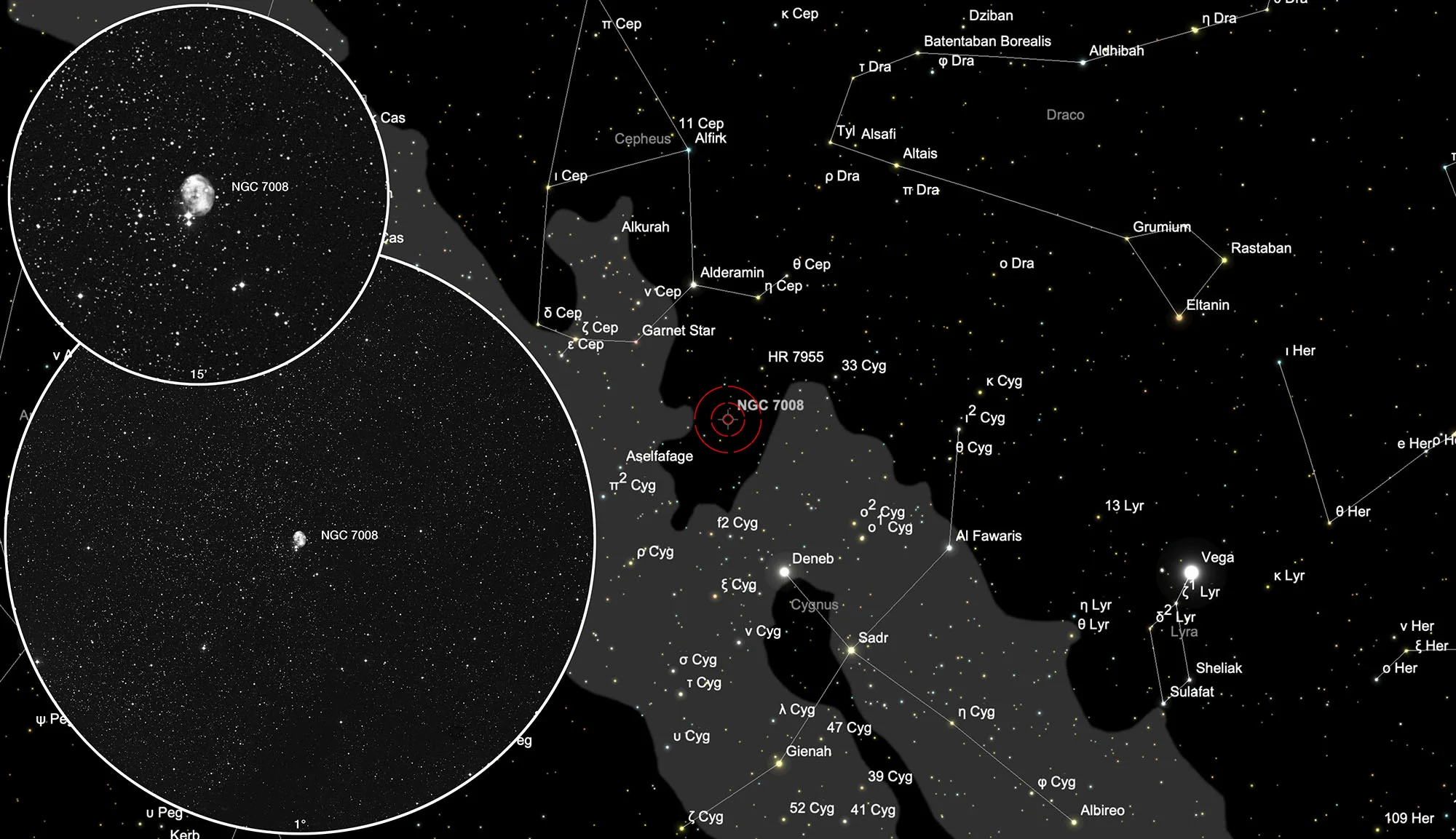
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula NGC 7008 is located in the constellation Cygnus. On 6 August it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observing time is April to January, when the PN is highest in the night sky.
Visual Observation
762 mm Aperture: The Foetus Nebula NGC 7008 appears like a thick croissant or in a similar shape, as the name suggests. A somewhat brighter flat trapezium appears at the lower end of the C. — 30" f/3.3 SlipStream Dobsonian, Hasliberg, 20. 06. 2025, SQM-L 21.27, Eduard von Bergen