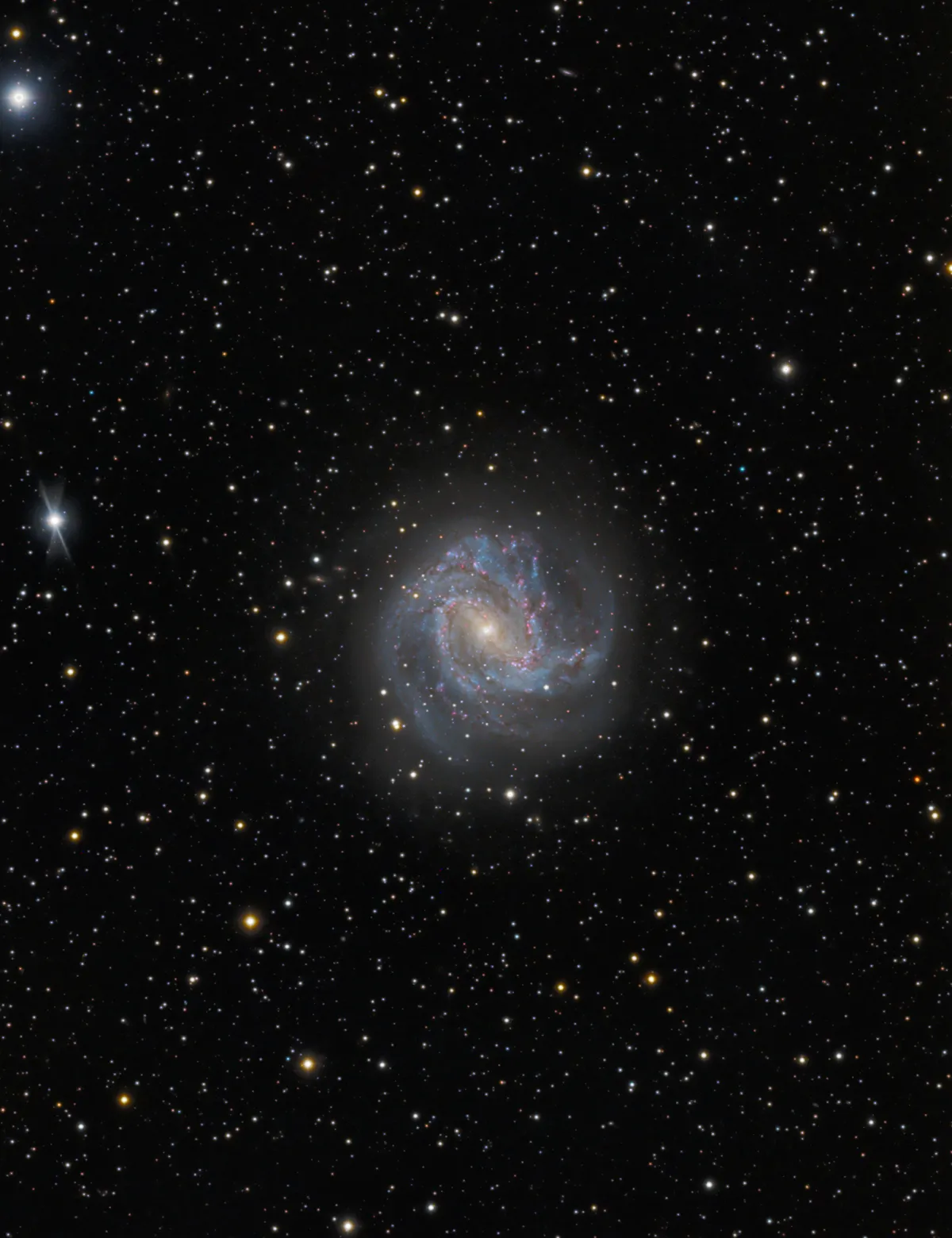
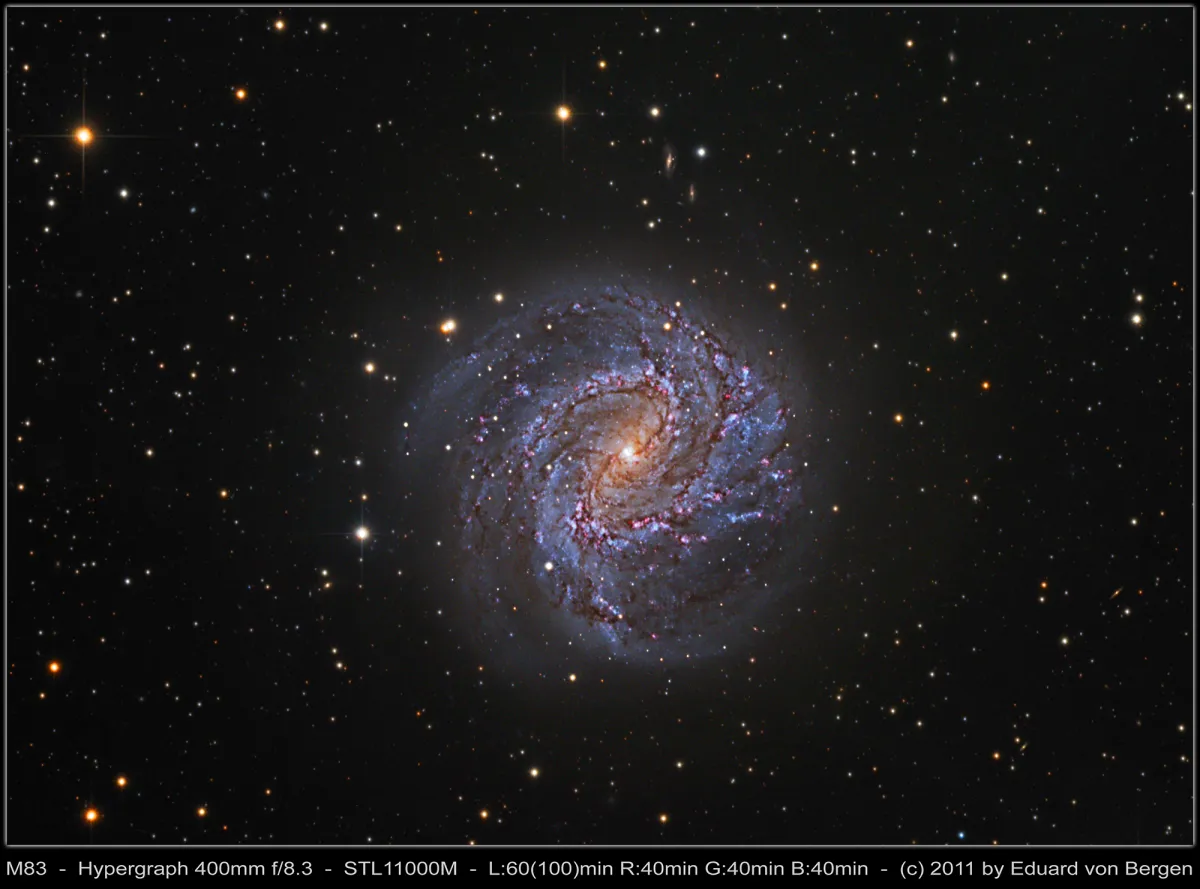
Galaxy Messier 83



History
This large galaxy was discovered by Lacaille in 1752 while he was staying at the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa and mapping the southern starry sky. In 1781 Charles Messier added them to his catalog.
Physical Properties
The two main arms of the galaxy form a mirror-inverted «S». A third, weaker arm arises south of the core and turns to the southwest. M 83 is of the morphological type SAB(s)c and an intermediate form of a spiral galaxy and a barred spiral galaxy. Due to the high rate of star formation and supernovae (six since 1923), M 83 is considered a starburst galaxy.
The measured radial velocities of the last 20 years range from 508 to 519 km/s and distances range from 4.5 Mpc to 5.1 Mpc (14.7 million to 16.6 million light years). [4, 145]
| Designation | NGC 5236 |
| Type | Gx (Sc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 13h 37m 00.2s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -29° 52' 02" |
| Diameter | 12.9 × 11.5 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 8.2 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 7.5 mag |
| Surface brightness | 12.8 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 44° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.001711 |
| Distance derived from z | 7.23 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 6.960 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | !!, (H, h) vB, vL, E 55°, esbMN, (L) 3 branched spiral |
| Identification, Remarks | h 3523; GC 3606; M 83; ESO 444-81; MCG -5-32-50; UGCA 366; IRAS 13342-2933 |
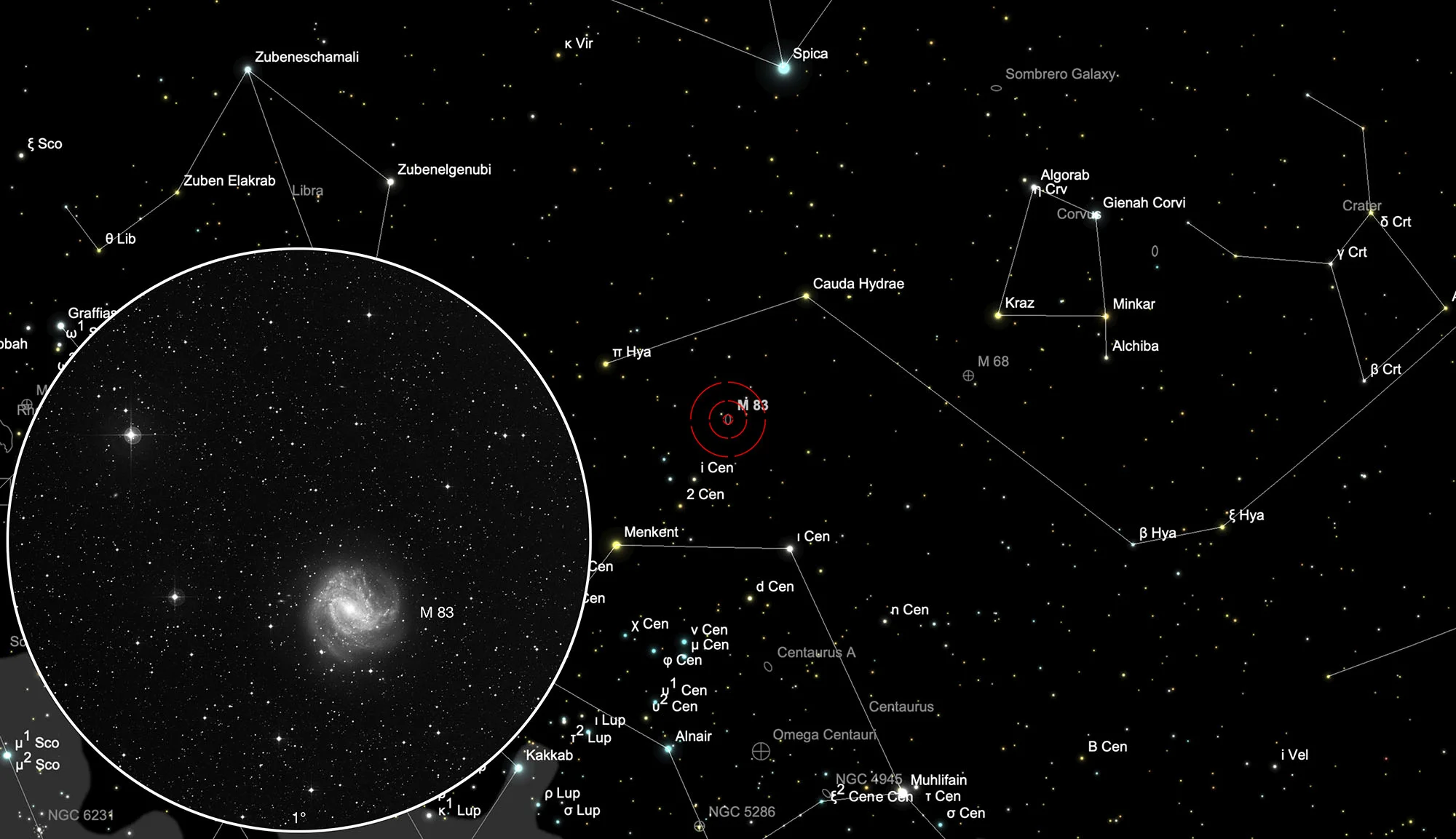
Finder Chart
M 83 is located in the constellation Hydra on the border with the constellation Centaurus, around 18° south of the bright star Spica (α Virginis) in the constellation Virgo. Connect the stars Menkent (θ Centauri) - Cauda Hydrae (γ Hydrae). M 83 lies almost exactly in the middle. Due to its southern position of -29° declination, the galaxy from Central Europe is highest above the southern horizon at night in the months of December to September.