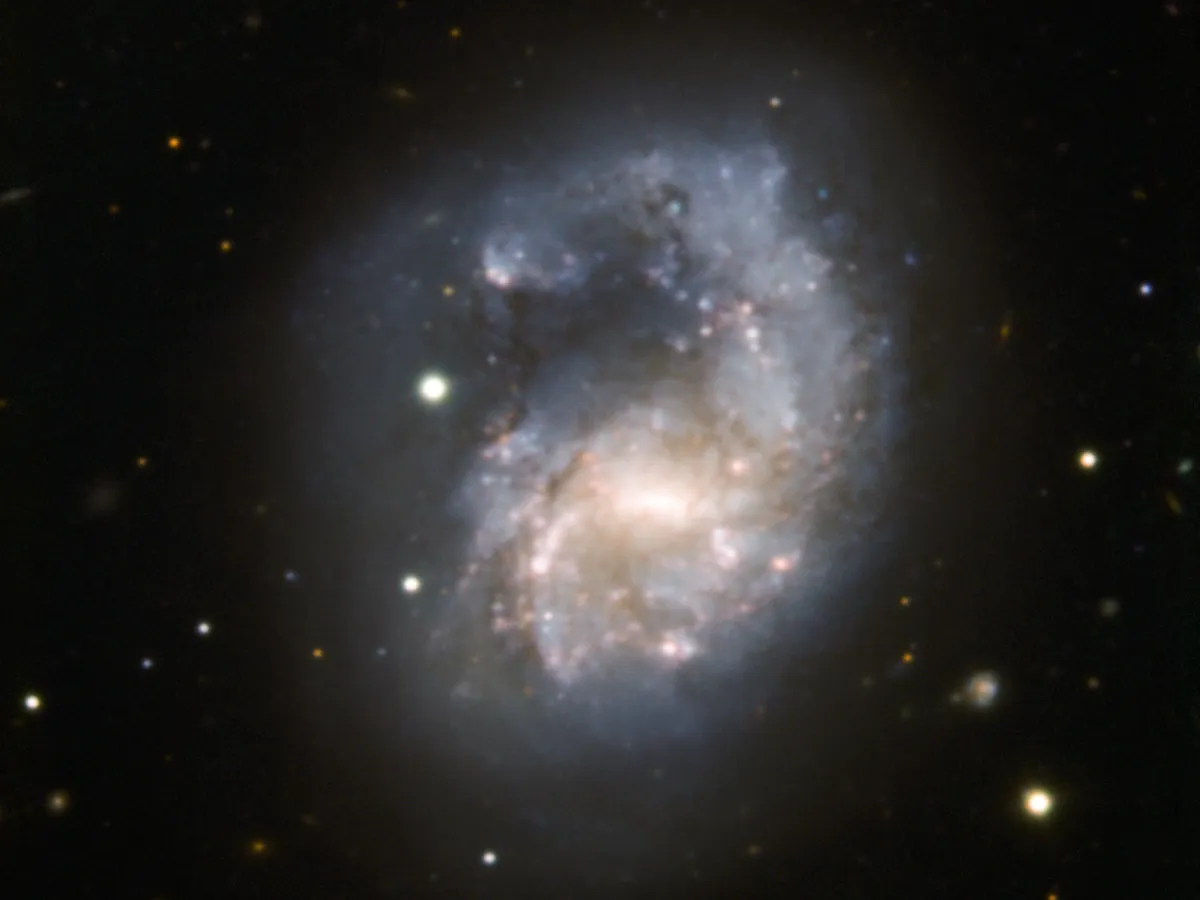
Galaxy NGC 4027 (Arp 22)

History
The galaxy NGC 4027 was discovered by William Herschel on 7 February 1785. He listed it as II 296 and recorded: «Pretty bright, pretty large.» [463] John Herschel observed it on 23 March 1835 (sweep 561) from Cape of Good Hope, listed it as h 3371 and noted: «Globular cluster, faint, pretty larg, resolvable 2', resolved, stars brely seen, but in a better night for definition would no doubt be clearly resolved into stars 16 magnitude.» [11]
In Halton Arp's 1966 «Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies», this galaxy is listed as Arp 22, a spiral galaxy with one arm. [199]
Physical Properties
NGC 4027, also known as Arp 22, stretches its single extended spiral arm towards north. This peculiar extended arm, thought to be the result of a collision with another galaxy millions of years ago — most likely a small galaxy ESO 572-36, also known as NGC 4027A. NGC 4027 is part of the NGC 4038/9 Group. [221]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 4027 | 11 59 30.5 | -19 15 57 | Gx (SBd) | 11.7 | 11.1 | 0.6 | 13.1 | 3.3 × 2.4 | 167 | 0.005574 | 23.54 | 25.600 | globular, pF, pL, R, rr, st 16 | WH II 296; h 3371; GC 2661; ESO 572-37; MCG -3-31-8; UGCA 260; VV 66; Arp 22; 1SZ 109; 8ZW 158; IRAS 11569-1859 |
| NGC 4027 A | 11 59 29.3 | -19 19 55 | Gx (IBm) | 14.9 | 14.5 | 0.4 | 13.7 | 0.9 × 0.6 | 159 | 0.005827 | 24.61 | globular, pF, pL, R, rr, st 16 | WH II 296; h 3371; GC 2661; ESO 572-36; MCG -3-31-7; VV 66; Arp 22 |
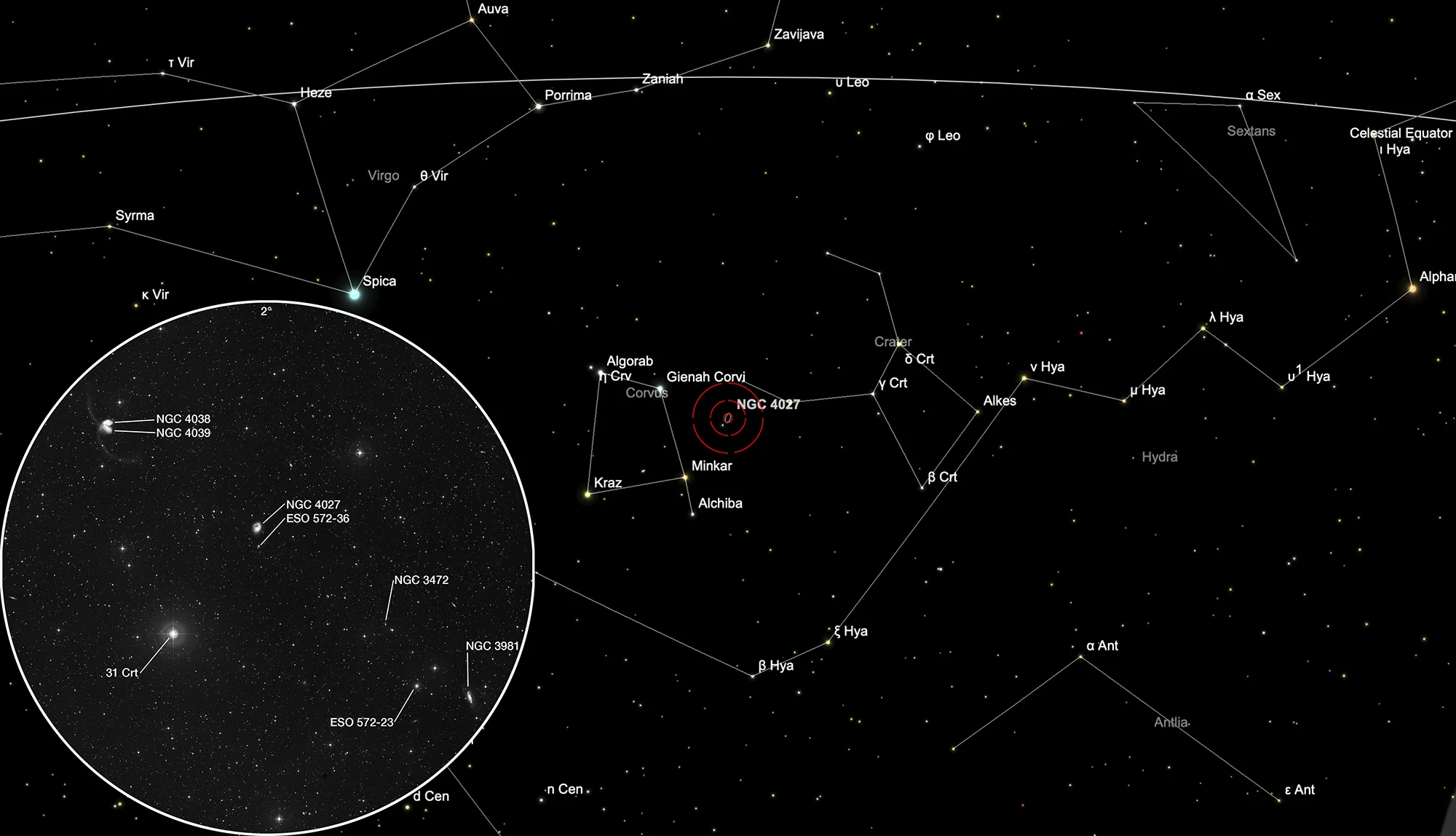
Finder Chart
West of the diamond-shaped asterism of the constellation Corvus, approximately half a degree north-west of the 5.2-magnitude bright star 31 Crateries, lies galaxy pair NGC 4027. On 20 March, the galaxy pair is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at midnight local time. The best time to observe it is during the months of November to August. Not far away lies the Antennae galaxy NGC 4038/9.