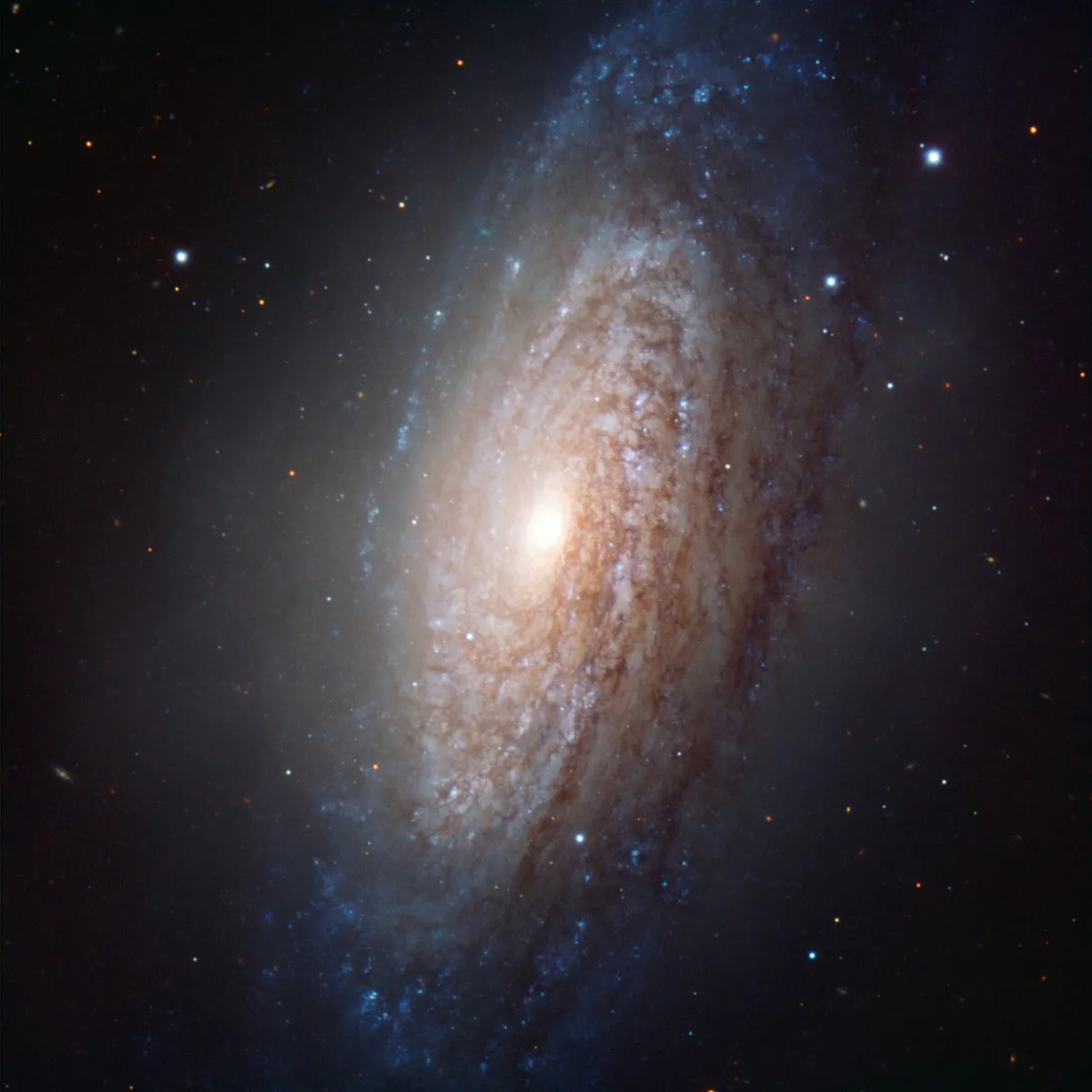
Bubble Galaxy (NGC 3521)

History
The galaxy NGC 3521 was discovered by William Herschel on 22 February 1784. He listed it as I 13 and described it with: «Very bright, much elongated, mer. fairly much brighter in the middle, 7 or 8' long.» [463] On 13 April 1828 (sweep 144) John Herschel described listed this galaxy as h 818 and noted: «Very bright, large, much extended (position by diagonal = 140° ±) 4' long, 1' broad, very suddenly very much brighter in the middle. The nucleus is rather excentric, being rather towards the south preceding side.» [466]
On 29 March 1856 Lord Rosse's assistant R. J. Mitchell observed the galaxy using Lord Rosse's 72-inch reflector, the «Leviathan of Parsonstown» and compared the galacy with NGC 7331 He noted: «The nucleus projects into the space along south preceding edge; outside this dark space there is faint nebulosity, which I see joining the nebula at north. A faind star at the opposite extremity.» [486]
Physical Properties
| Designation | NGC 3521 |
| Type | Gx (SBbc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 11h 05m 48.8s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -00° 02' 13" |
| Diameter | 11.2 × 5.4 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 9.8 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 9.0 mag |
| Surface brightness | 13.2 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 163° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.002672 |
| Distance derived from z | 11.29 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 12.080 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | cB, cL, mE 140° ±, vsmbMN |
| Identification, Remarks | WH I 13; h 818; GC 2301; UGC 6150; MCG 0-28-30; CGCG 10-74; KARA 461 |
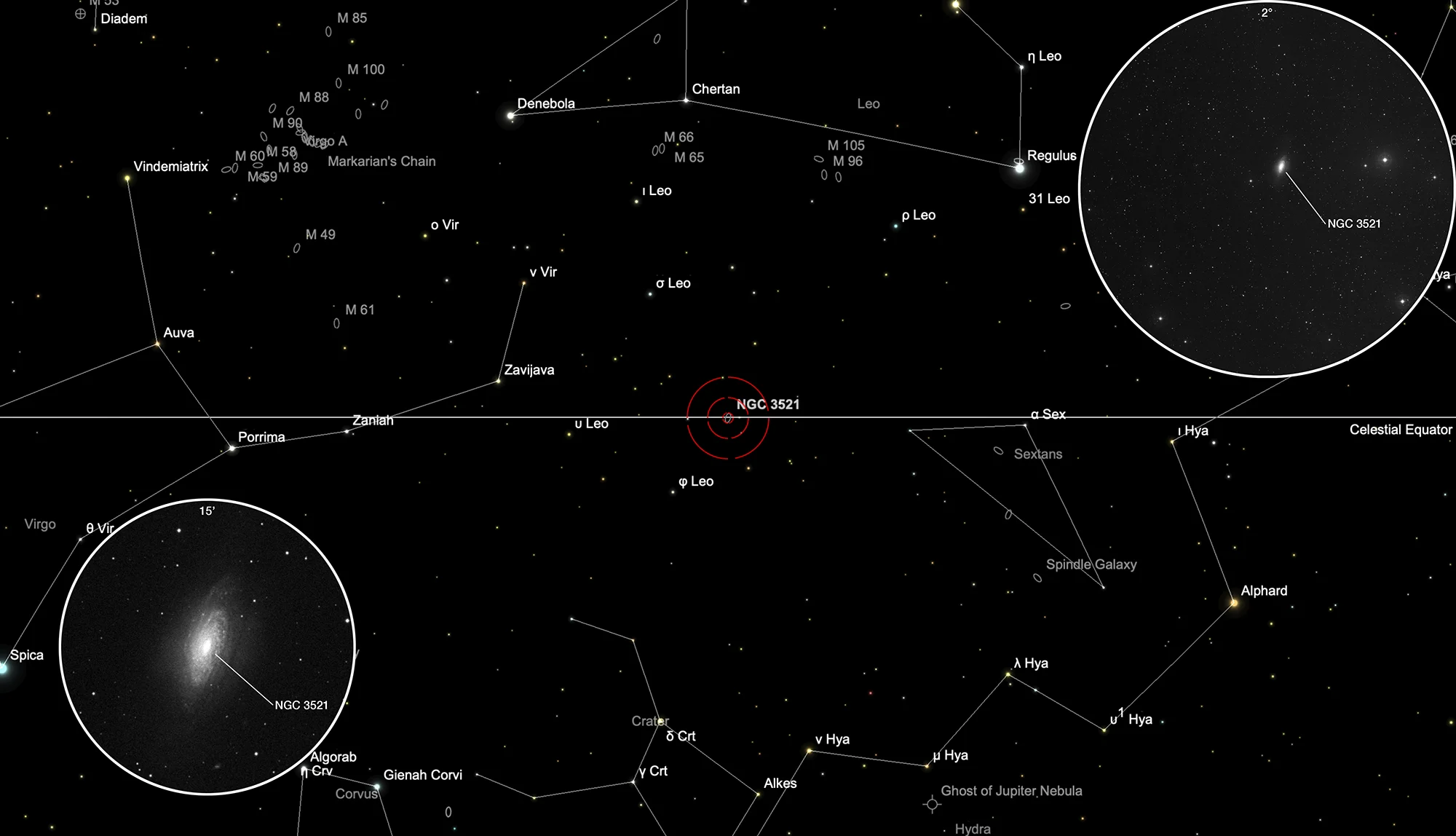
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 3521 is located in the constellation Leo. On 6 March it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. It can best be observed from November to August.
Visual Observation
762 mm Aperture: The Bubble Galaxy NGC 3521 appears crescent-shaped, extending from a brighter nucleus. — 30" f/3.3 SlipStream Dobsonian, Hasliberg, 05. 03. 2025, SQM-L 21.62, Eduard von Bergen