Open Cluster Messier 23

Object Description
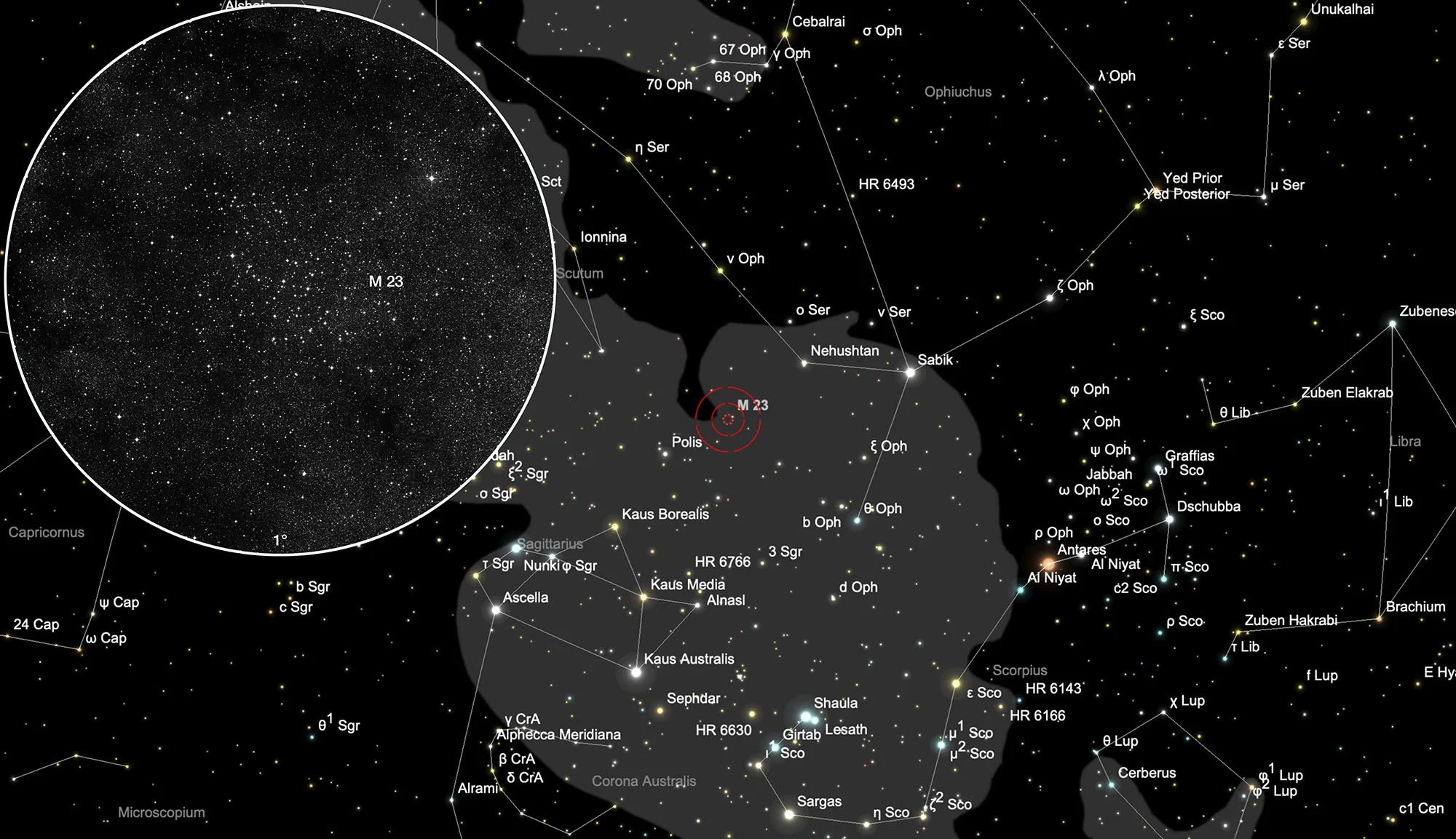
The galactic star cluster Messier 23 was probably first sighted by Charles Messier in June 1764. Although Messier described it as a cluster 15 arc minutes in diameter with stars very close together, he added M 23 to his list of comet-like objects. John Herschel found around 100 stars from 9th to 13th magnitude in this group, which appear more or less evenly scattered with a slight concentration towards the centre. A number of stars are formed into curved arcs and chains, which suggest the shape of a Chinese temple to the imaginative observer or which look something like oriental calligraphy.
According to the colour-brightness diagram, the majority of stars appear to be reddish main sequence stars. The brightest members are of type B9. Several G-type giant stars exist in the group - the brightest example in the main mass of the cluster can be found in the small elliptical formation of six stars in the centre: it is the westernmost star of this flat ring. The star density in the centre is estimated at around 31 stars per cubic parsec. M 23 is in front of an extensive dark cloud. The distance of the cluster is a little more than 2000 light years, the diameter about 15 light years. [4]
| Designation | NGC 6494 |
| Type | OCL (III1m) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 17h 56m 56.0s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -19° 00' 42" |
| Diameter | 25 arcmin |
| Visual magnitude | 5.5 mag |
| Metric Distance | 0.628 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | Cl, B, vL, pRi, lC, st 10… |
| Identification, Remarks | h 1990; GC 4346; M 23; OCL 30; ESO 589-SC22 |
Finder Chart
The star cluster Messier 23 is located in the constellation Sagittarius. It can best be seen in the months of February to November. Then the constellation is highest above the southern horizon.