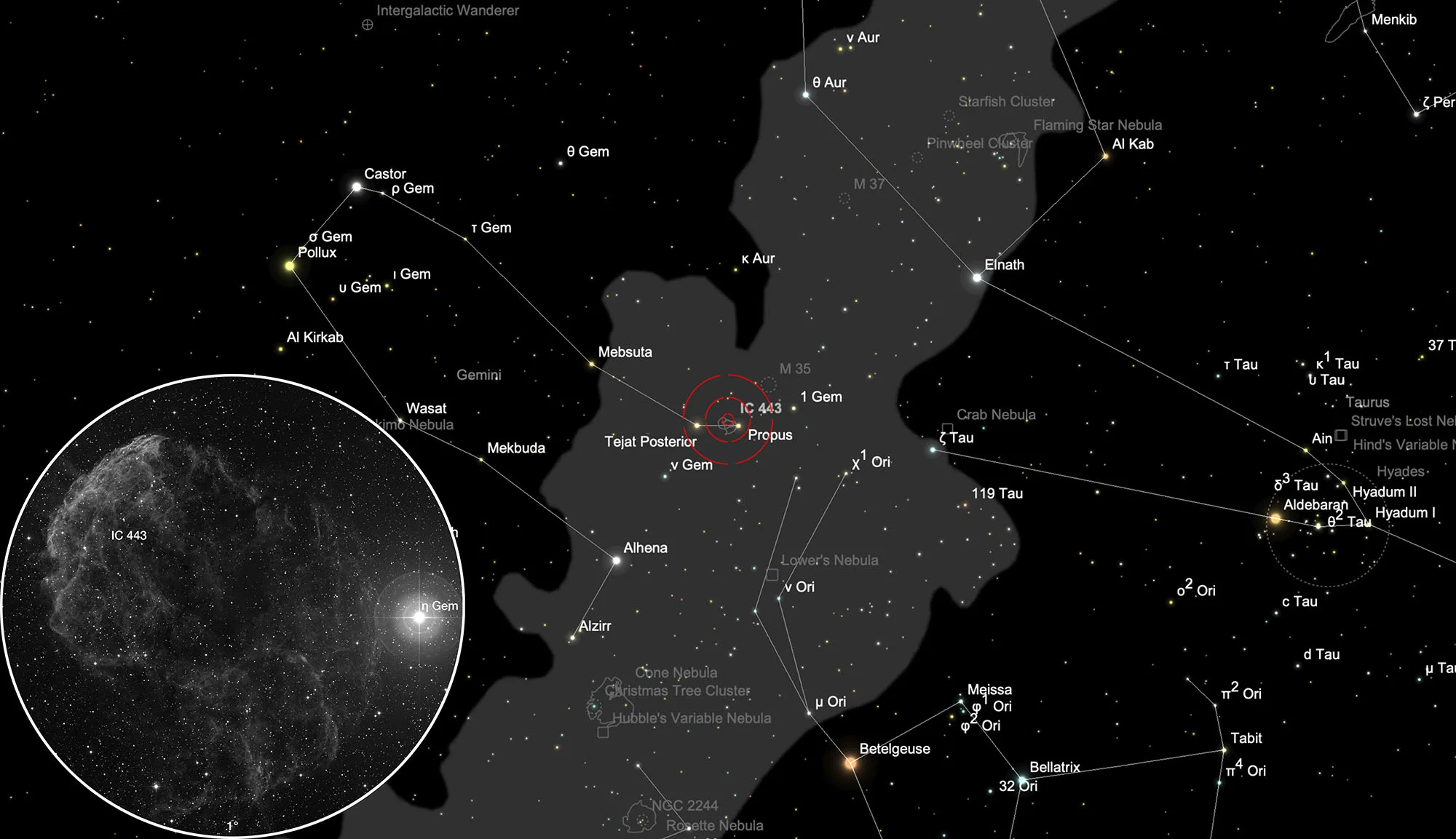
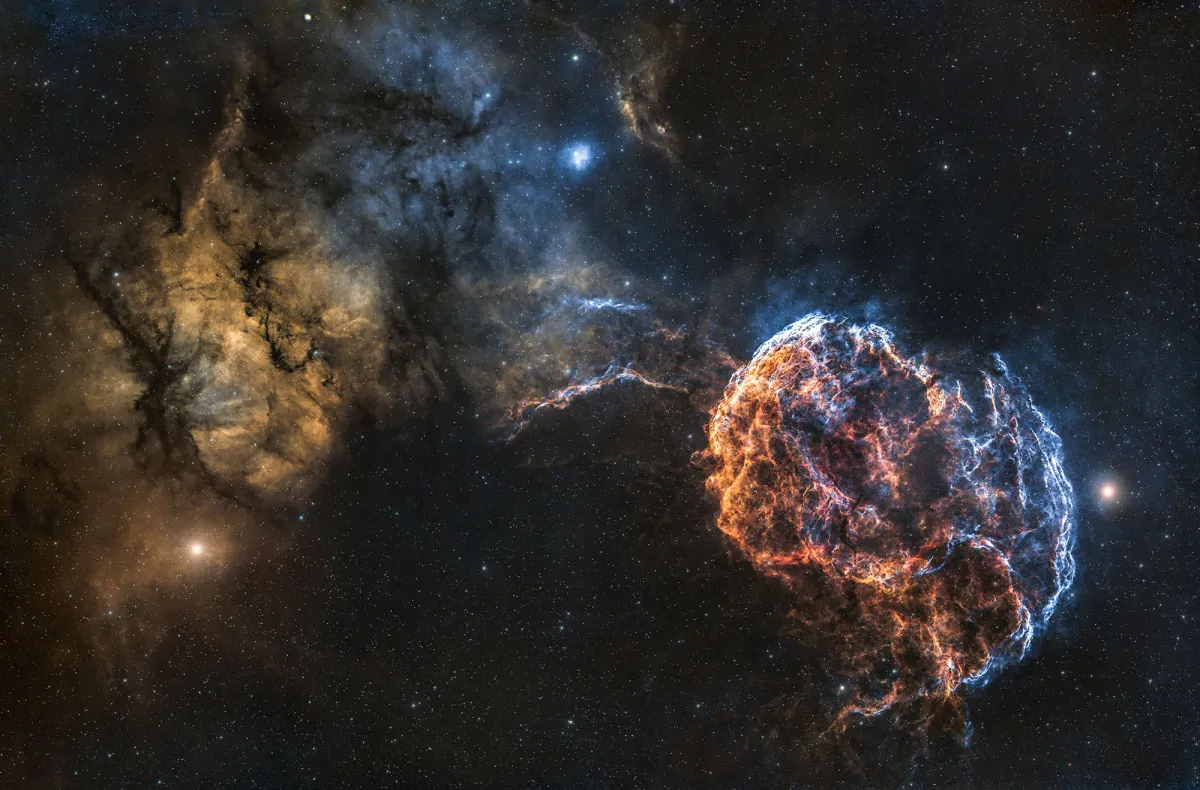
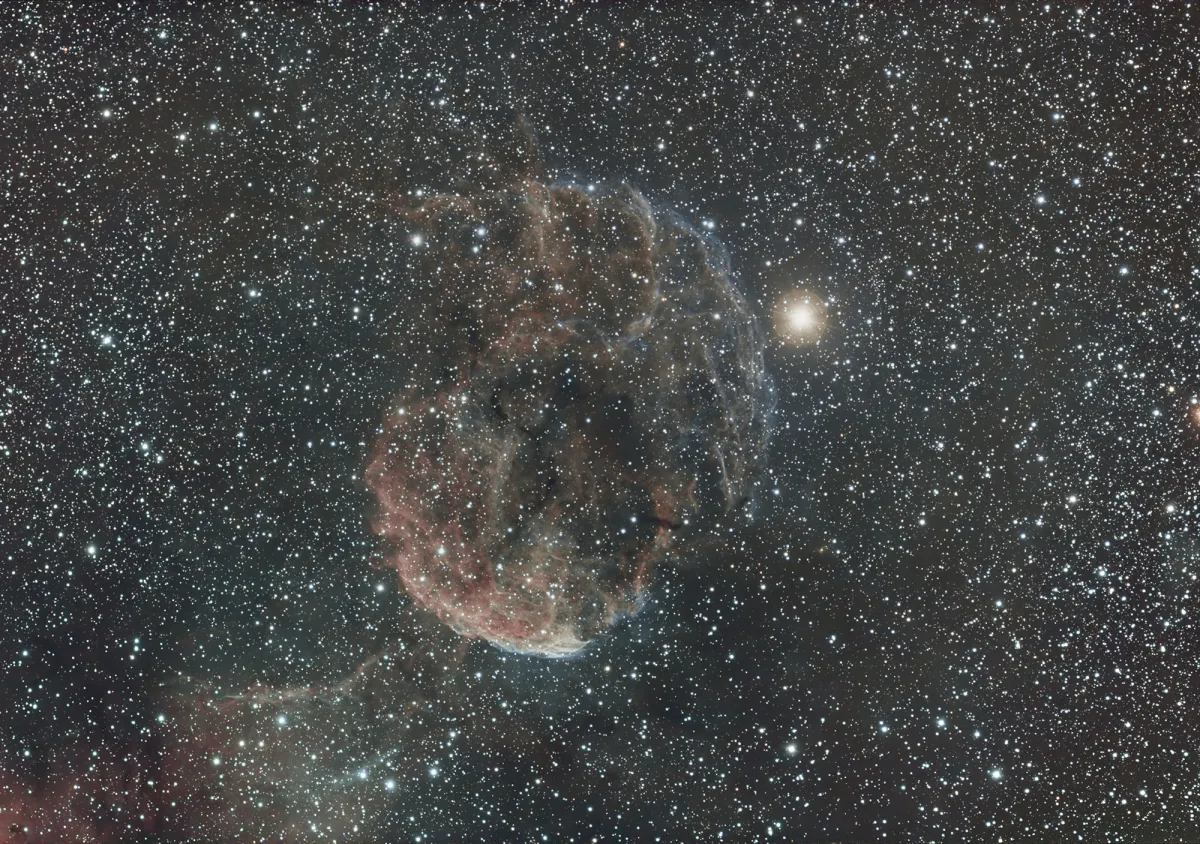
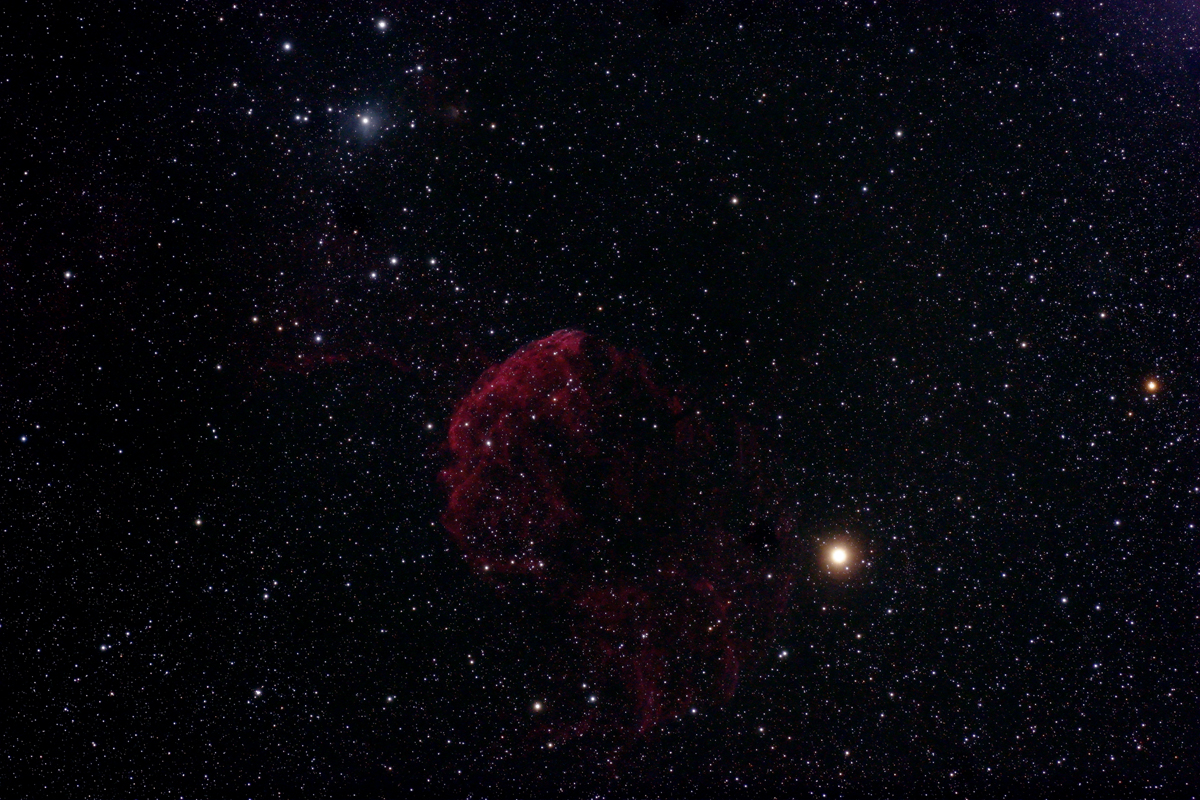
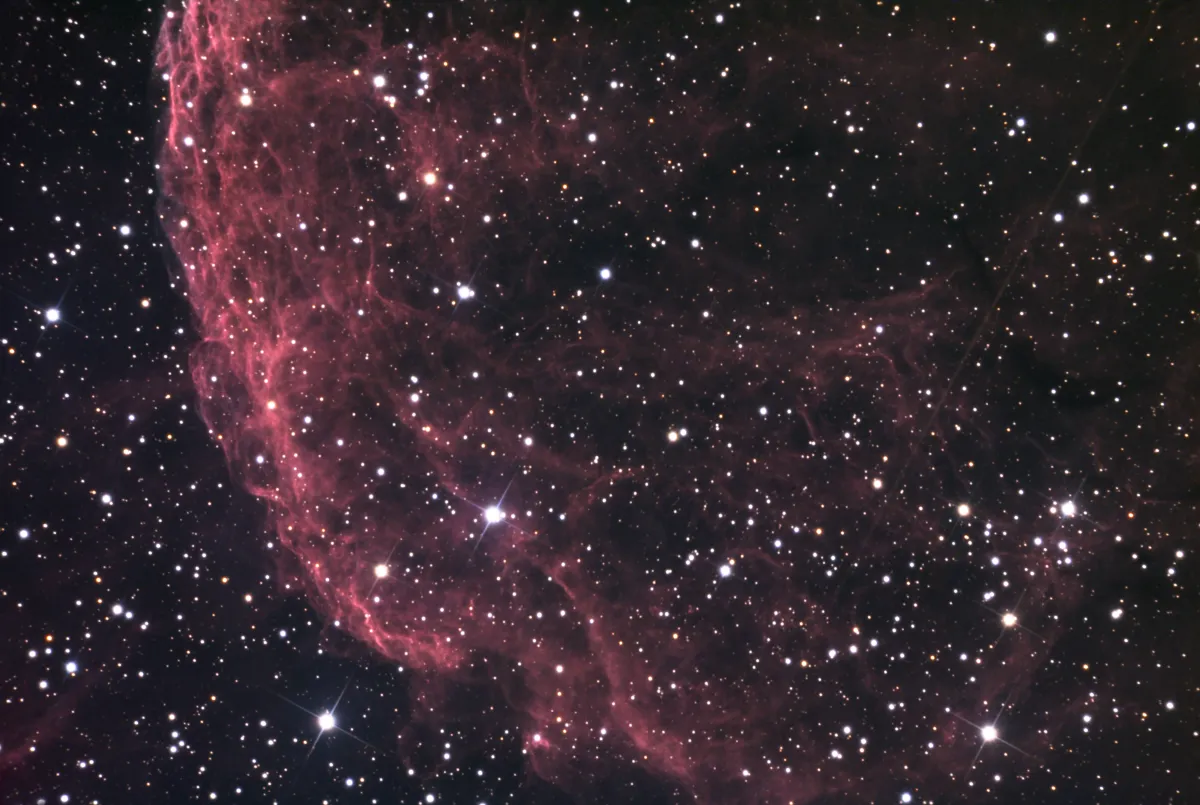
Jellyfish Nebula (IC 443)




History
Max Wolf took on 25 September 1892 a photography of the Nova of T Aurigae using a Hermagis 2¼" lens and discovered close to the stars μ and η Geminorum two «very large and bright nebula [IC 443, IC 444] that look promising.» [227] E. E. Barnard independently discovered these two nebulae in 1894. He reported in «Astronomy and Astro-Physics», Vol 8, No. 3, «On this same plate [taken on 1 Feb 1894 with a 2h 10m exposure] is a faint narrow curved nebulosity [IC 443] in about, 1860.0, 6h 8m + 23° 0'. It is nearly ½° long, extending north and south and convex to the east.» [364]
Because of its appearance, the nebula was nicknamed the «Jellyfish Nebula», not to be confused with the Medusa Nebula (Abell 21). Not only do both objects have a similar name (Medusa is the scientific name for jellyfish), they also have a similar appearance.
Physical Properties
In contrast to Abell 21, IC 443 is a supernova remnant and not a planetary nebula. The pulsar wind nebula with the neutron star CXOU J061705.3+222127 was identified as the origin of the supernova. A jet-like structure was discovered in IC 443, which appears to emanate from the neutron star. The distance to IC 443 is about 1.9 kpc (6200 light years) and the age is estimated to be about 30'000 years. [307, 359]
| Designation | IC 443 |
| Type | SNR |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 06h 16m 36.0s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +22° 31' 00" |
| Diameter | 50 × 40 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 12.0 mag |
| Metric Distance | 1.500 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | F, narrow, curved |
| Identification, Remarks | LBN 844; VMT 9; Sh2-248 |
Finder Chart
The galactic nebula IC 443 is located at the star Propus (η Gem) in the constellation Gemini, which is best visible from August to May.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: With O-III filter and 21 mm Ethos eyepiece the brightest sickle shaped part of this nebula is visible only with averted vision. It looks a bit like the Medusa Nebula (Abell 21) but much fainter. Without filter and with H-beta no nebula can be seen. Larger aperture or darker sky required. — Taurus T400 f/4.5 Dobsonian, Glaubenberg Langis, 28 February 2022, Bernd Nies
762 mm Aperture: The brightest part of the supernova remnant IC 443 is clearly visible with an OIII filter as Peperoni slice. From the very bright star in the direction of the slice, isolated finer nebula parts of the entire Jellyfish Nebula can be glimpsed. — 30" SlipStream-Dobson f/3.3, Hasliberg, 28. 12. 2024, SQM-L 21.05, Elena + Eduard von Bergen