Galaxy NGC 7292

History
The galaxy was discovered on 29 August 1872 by the French astronomer Jean Marie Édouard Stephan using the 31" Foucault reflector at Marseille observatory. [277] In 1888 Dreyer added the galaxy as NGC 7272 with the description «extremely faint, small, oval, faint star involved.» [313]
Physical Properties
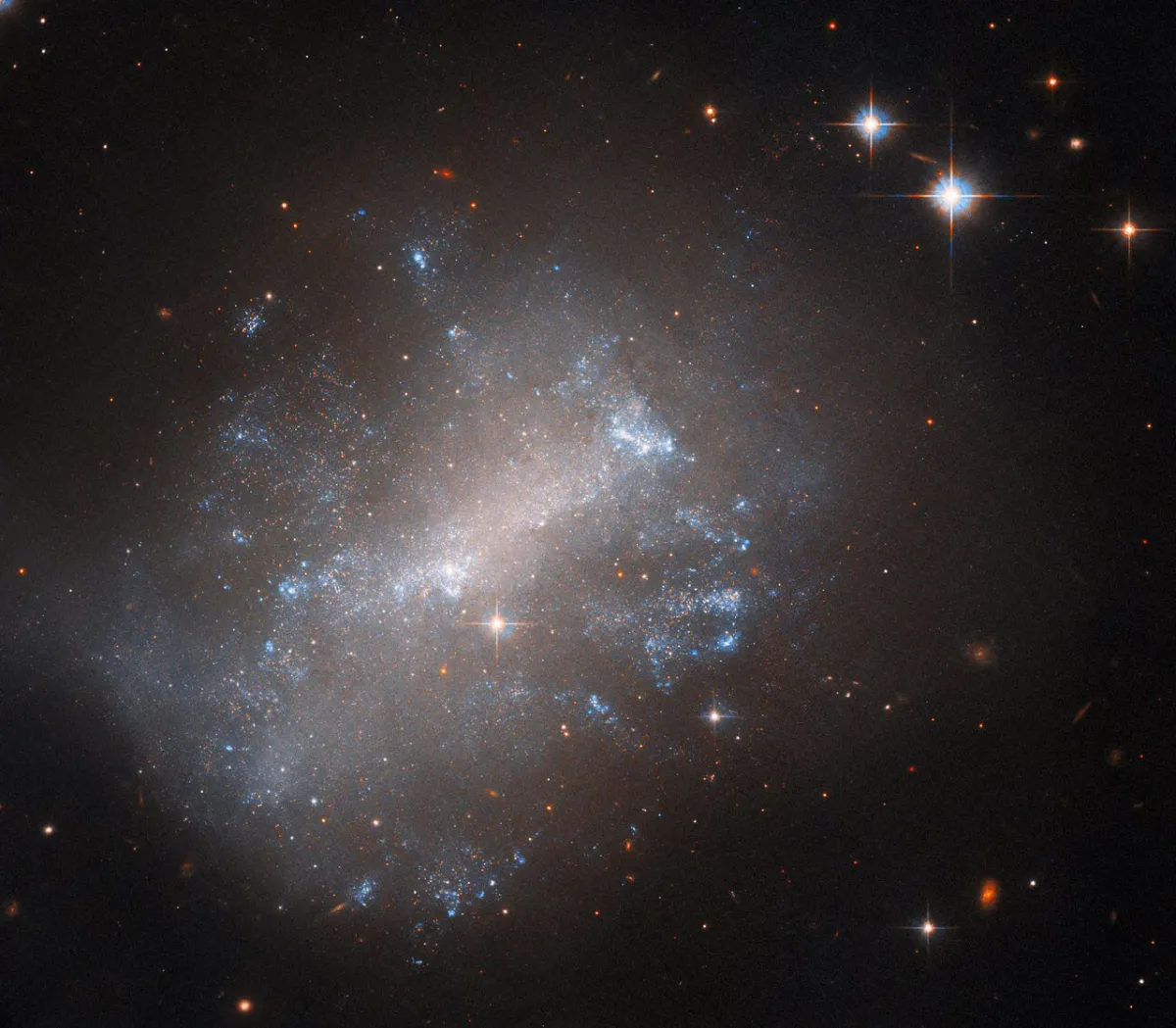
NGC 7292 is an irregular galaxy. Unusually to irregular galaxies its core is stretched out into a distinct bar, a feature seen in many spiral galaxies. It is a low surface brightness galaxy, which is typically dominated by gas and dark matter rather than stars. [629] Apparent magnitudes through different filters: u 17.286; B 13.1; g 17.154; r 17.099; i 17.081; z 16.891. Estimated distances range from 6 Mpc to 13 Mpc. [145]
| Designation | NGC 7292 |
| Type | Gx (IBm) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 22h 28m 25.7s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +30° 17' 35" |
| Diameter | 2.1 × 1.6 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 13.0 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 12.5 mag |
| Surface brightness | 13.8 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 117° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.003289 |
| Distance derived from z | 13.89 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 11.510 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | eF, S, oval, F * inv |
| Identification, Remarks | GC 6056; UGC 12048; MCG 5-53-3; CGCG 495-3; IRAS 22261+3002; KARA 967; KAZ 290 |
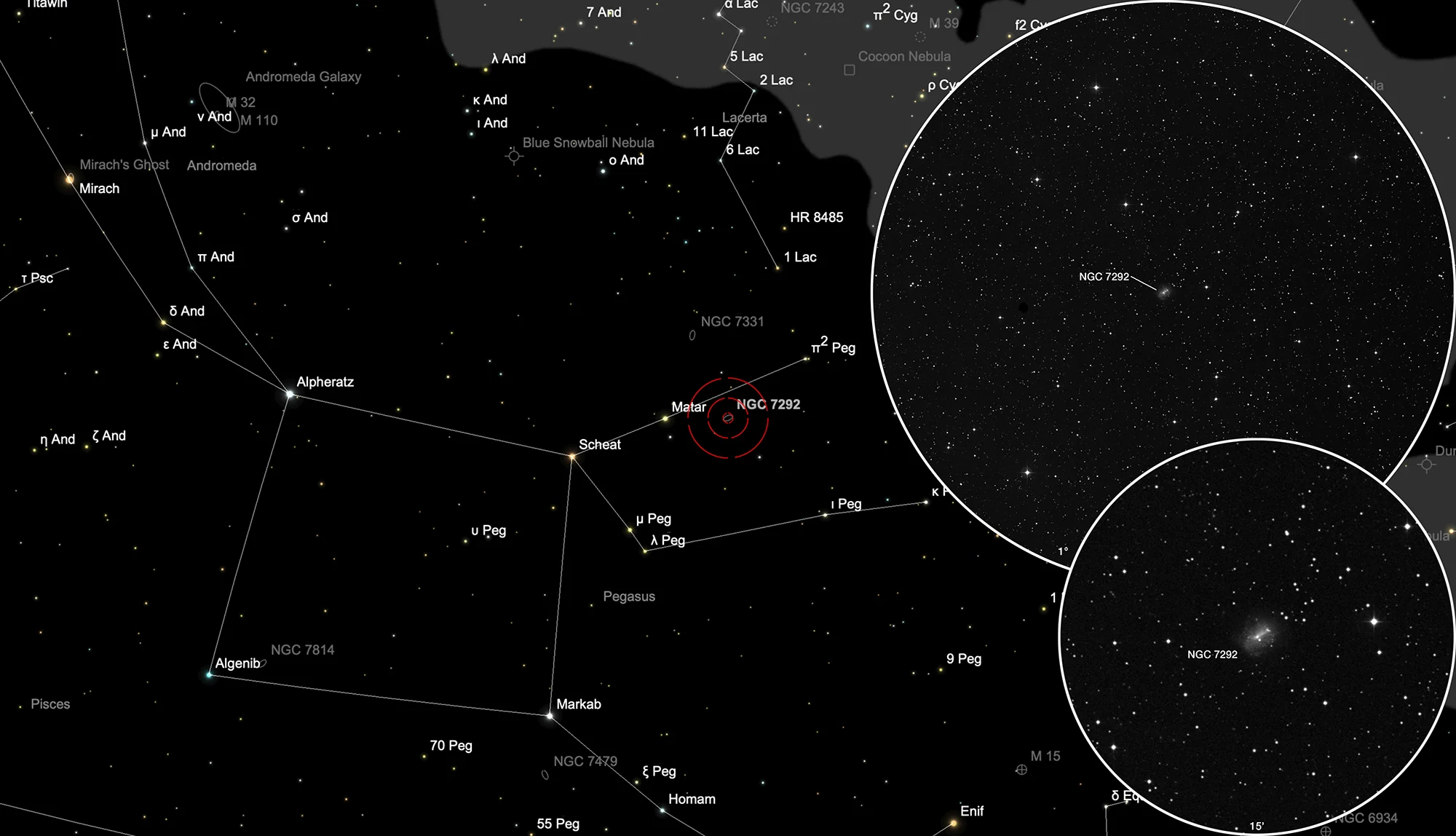
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 7292 can be found in the constellation Pegasus. On 29 August it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time for observation ist in the months from May to January, when it is highest in the sky.
Visual Observation
762 mm Aperture: This galaxy was a chance observation, actually the Helix Nebula should be approached with a number higher or NGC 7293. Nevertheless, we observe the shapeless, irregular galaxy, which shows a stellar, punctate core. — 30" SlipStream-Dobson f/3.3, Hasliberg, 18. 8. 2023, Eduard von Bergen