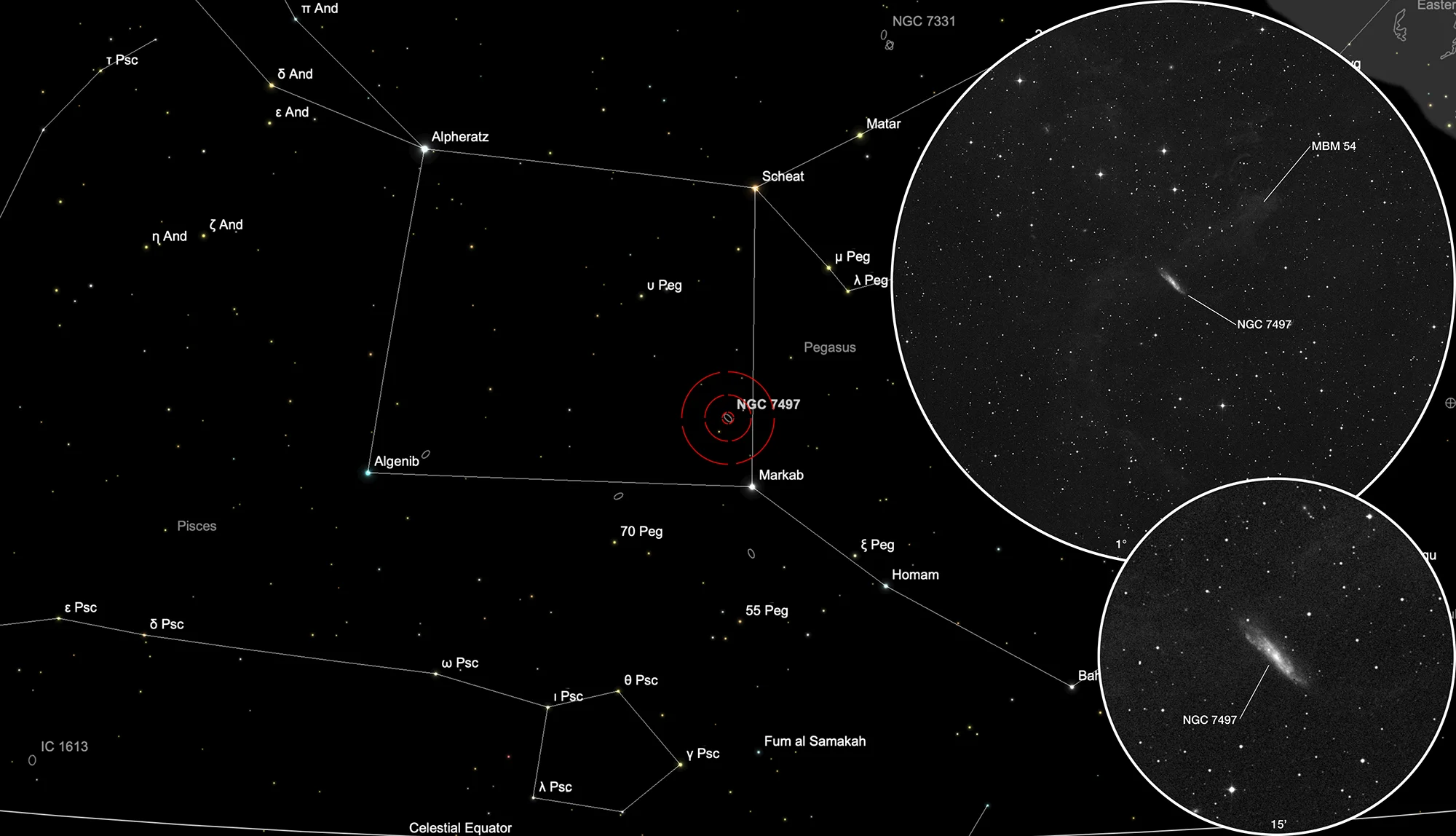
Galaxy NGC 7497 & Integrated Flux Nebula

History
The galaxy NGC 7497 was discovered on 15 October 1784 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7 inch reflecting telescope. He cataloged it as III 203 and noted: «Very faint, considerably large, extended, 2' long.» [463] John Herschel observed it twice and noted for sweep 11 (7 October 1825): «Extremely faint; extended like the tail of a comet; little brighter in the middle.» On sweep 92 (26 August 1827) he noted: «very faint; much extended; position 45° north following to south preceding; 4' long, 1' broad.» [466]
Physical Properties
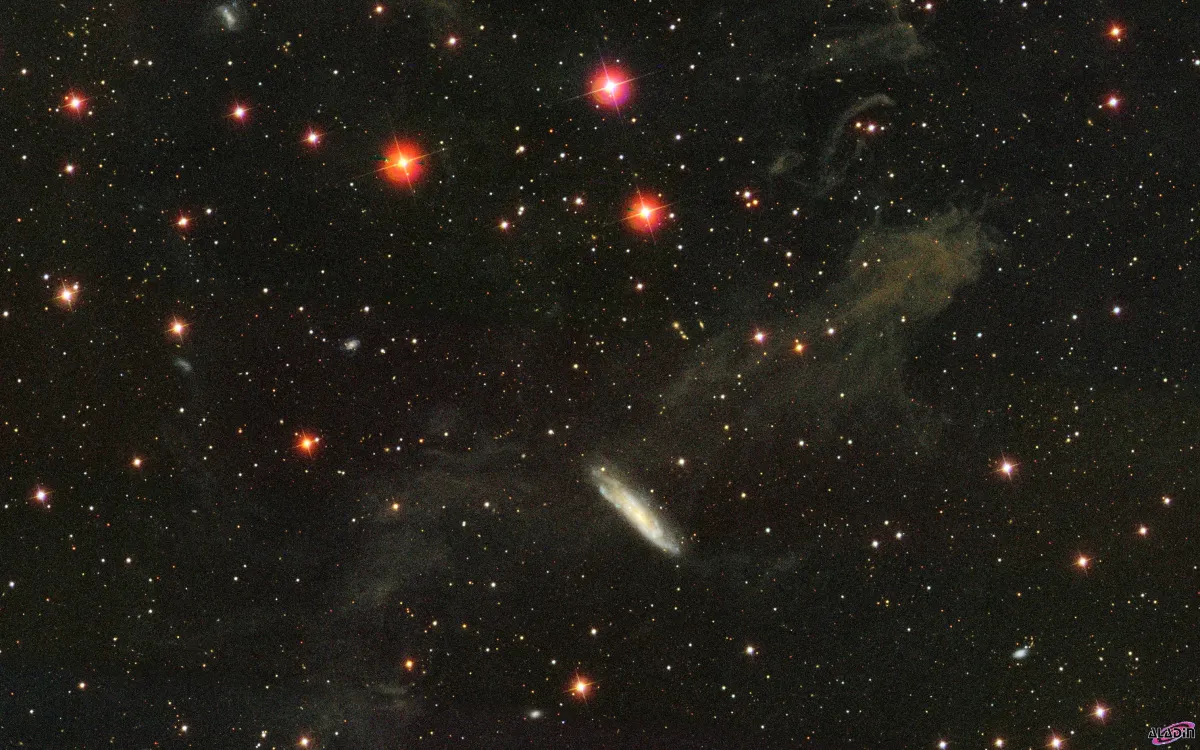
NGC 7497 is a barred spiral galaxy of morphological Type SBc. It is situated behind a filament of integrated flux nebula MBM 54. Integrated flux nebulae are high galactic latitude molecular clouds that are not illuminated by a single star but by the energy from all stars of The Milky Way, hence the term «integrated flux». Such nebulae are very faint. MBM 54 is part of a larger complex of molecular clouds, approximately 238 parsec away, slightly above the galactic plane. [37, 145, 271]
| Designation | NGC 7497 |
| Type | Gx (SBc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 23h 09m 03.5s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +18° 10' 39" |
| Diameter | 4.4 × 1.7 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 13.0 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 12.2 mag |
| Surface brightness | 14.0 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 48° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.005697 |
| Distance derived from z | 24.06 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 18.790 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | vF, L, pmE 45°, lbM |
| Identification, Remarks | WH III 203; h 2209; GC 4898; UGC 12392; MCG 3-59-2; CGCG 454-3; KUG 2306+179; IRAS 23065+1754 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 7497 is located in the constellation Pegasus. On 9 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is May to February, when it is highest at night.