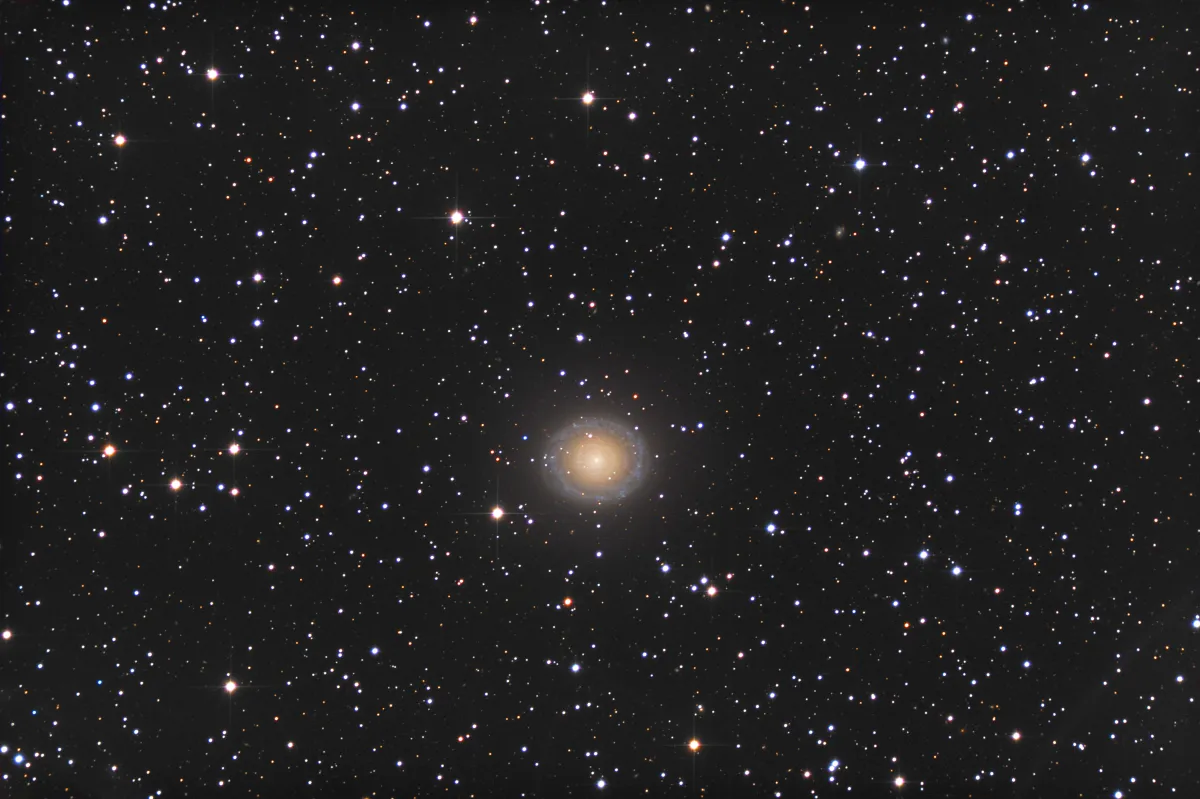
Galaxy NGC 7217

History
On 7 September 1784 William Herschel discovered a «faint nebula» which he logged as II 207 and recorded: «Considerably large, round, gradually much brighter in the middle, easily resolvable.» [463] John Herschel made the single observation, measured an accurate position, logged it as h 2149 and recorded: «bright; round; 30"; gradually brighter in the middle.» [466] The Birr Castle team observed the nebula 14 times with the giant 72-inch telescope and logged on 16 September 1854: «There can hardly be a doubt that this nebula is a cluster.» [486]
Physical Properties
It is a galaxy of morphological type (R)SA(r)ab with a LINER-type active core. Distance specifications range from 16 Mpc to 18.4 Mpc. [145]
| Designation | NGC 7217 |
| Type | Gx (Sb) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 22h 07m 52.1s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +31° 21' 34" |
| Diameter | 4 × 3.4 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 11.0 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 10.1 mag |
| Surface brightness | 12.7 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 83° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.003176 |
| Distance derived from z | 13.42 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 17.200 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | B, pL, gbM, er |
| Identification, Remarks | WH II 207; h 2149; GC 4760; UGC 11914; MCG 5-52-1; CGCG 494-2; KARA 947; IRAS 22056+3106 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 7217 is located in the constellation Pegasus. On 23 August it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is April to January, when it is highest at night.