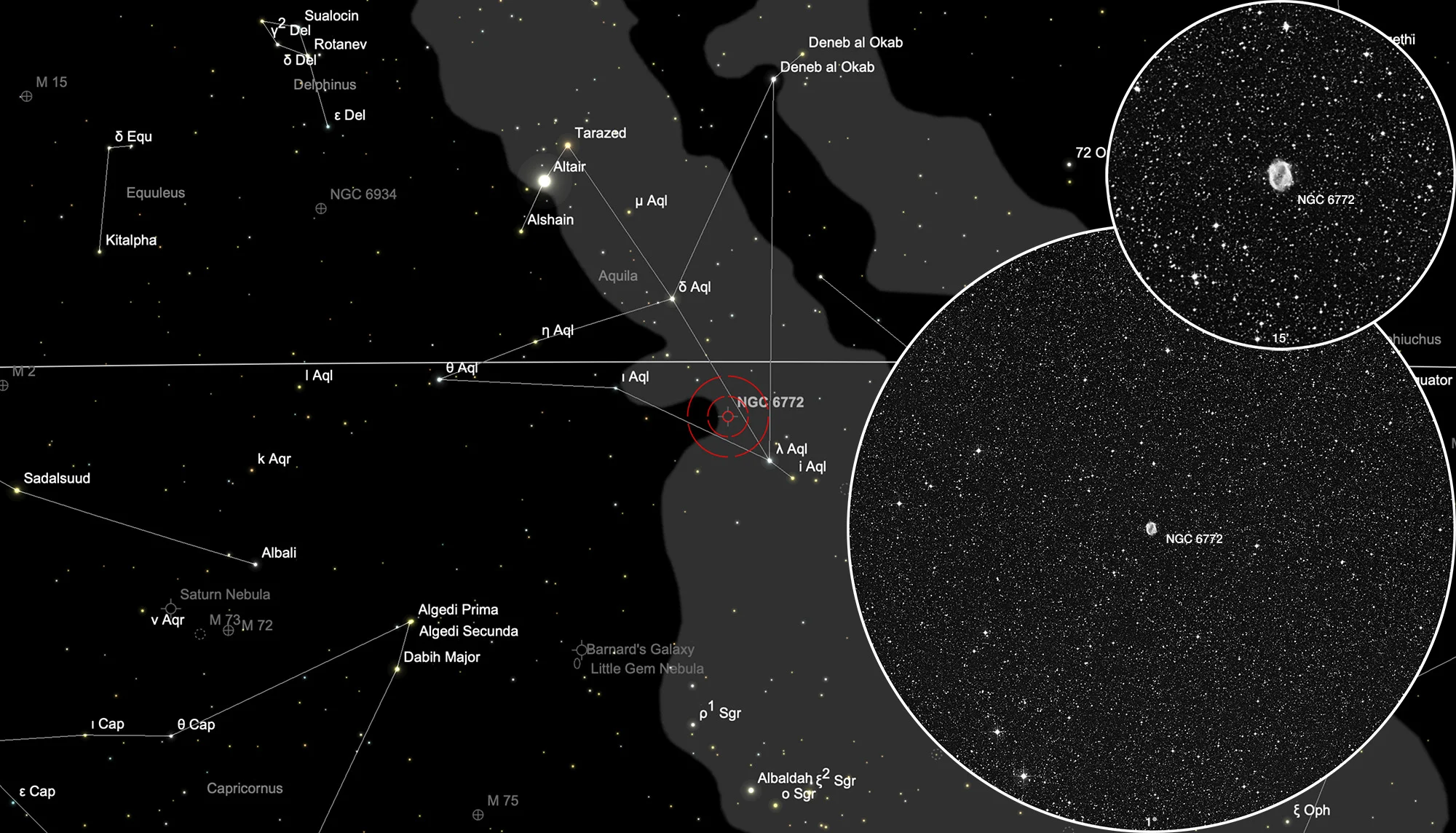
Planetary Nebula NGC 6772
History
The planetary nebula was discovered by William Herschel on 21st July 1784 using his 18.7" reflecting telescope. He cataloged it as IV 14 (class IV = planetary nebula) and noted: «Very faint of equal light. resolvable 1' diameter in the midst of numberless stars of the milky way» [463] J. L. E. Dreyer listed it 1888 as NGC 6772 in his famous «New General Catalogue» [313]
Physical Properties
NGC 6772 is with a dynamical age of circa 11'000 years one of the older planetary nebulae. It's morphology is that of an elliptical shell with apparent distortion along the north-east to south-west axis. This structure may be a result of interactions between the expanding shell and the interstellar medium (ISM) [538]
| Designations | PN G033.1-06.3: NGC 6772, PK 33-06.1, ARO 102, Sa 2-384, VV 224, VV' 486 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 19h 14m 28s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -02° 42' 26" |
| Dimensions | 64." (optical), 90." (radio) |
| Distance | 1.3 : kpc |
| Radial Velocity | 0.0 ± 4.0 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 10.2 (O-III) 25. (N-II) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 355 |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 19.02, V: 18.68 |
| Discoverer | PICKERING 1879 |
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula NGC 6772 is located in the constellation Aquila. On 10 July it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time to observe it is during the months of March to December.