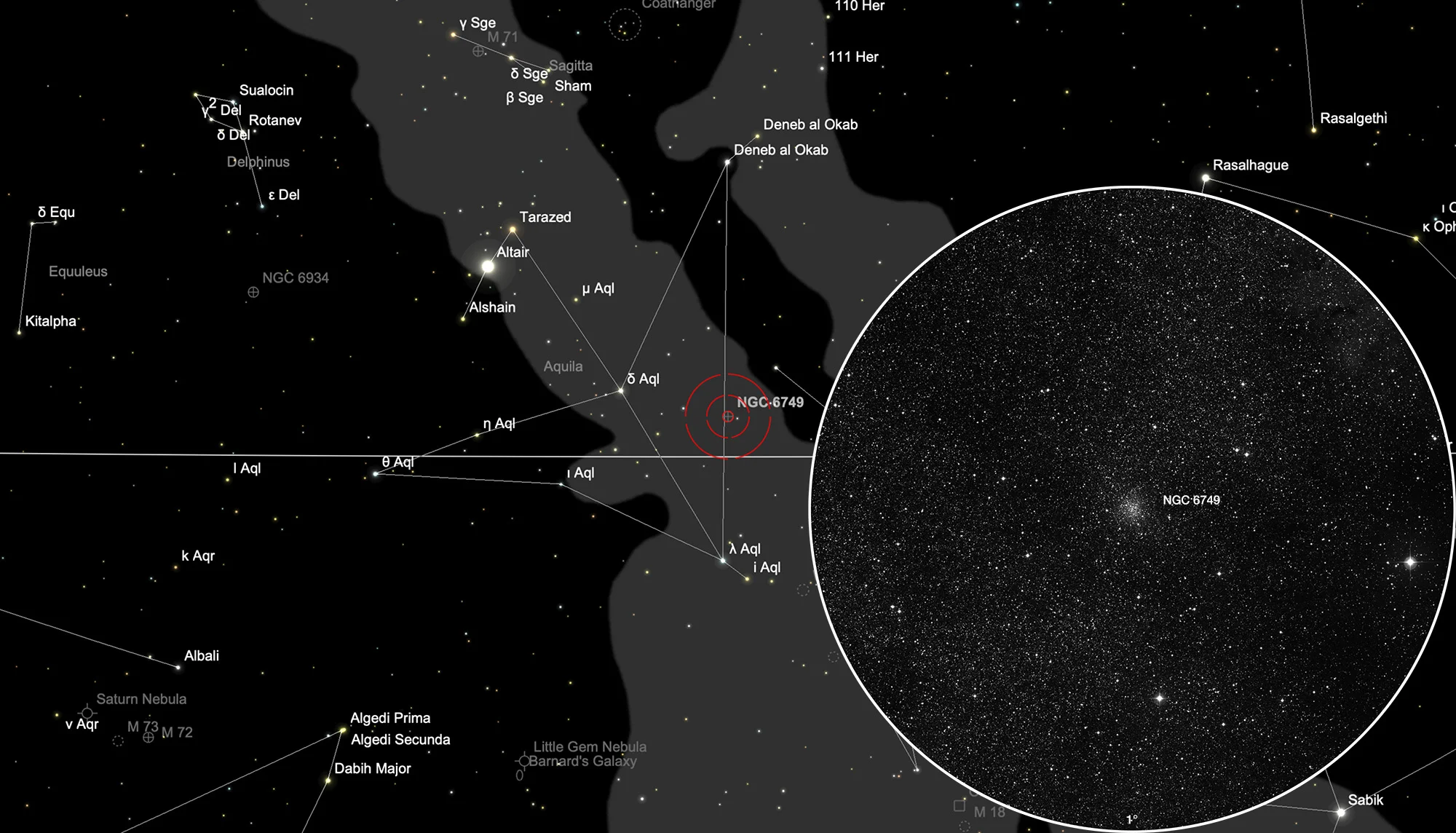
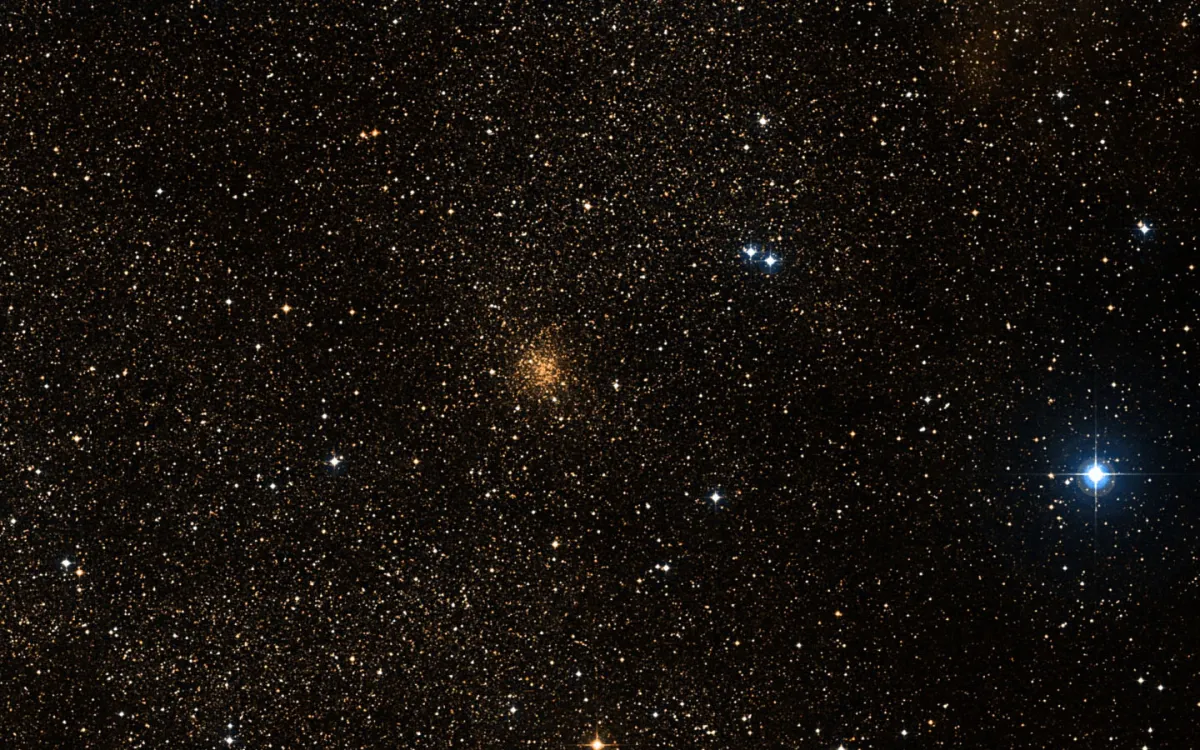
Globular Cluster NGC 6749

History
This cluster of stars was discovered by John Herschel on 15th July 1827. He cataloged it as h 2029 (GC 4466). He noted: «A cluster of loose small stars of various magnitudes; fills the field.» [466] In his «General Catalogue» appeared in 1864 he described GC 4466 as «Cluster; large; little compressed; stars large & small.» [467] John L. E. Dreyer added it as NGC 6749 in 1888. [313]
The cluster is also known as Berkeley 42 and was first misclassified as open star cluster of classification I3r consisting of «very faint stars». [542]
Physical Properties
NGC 6749 is a loose globular cluster. Its blue horizontal branch indicates that the stars are metal-poor, which is typical for globular clusters. Its distance from the Sun is estimated to 7.3 ± 0.9 kpc. It is a halo globular cluster close to the disc plane. [543]
| Designation | NGC 6749 |
| Type | GCL |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 19h 05m 15.3s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +01° 54' 05" |
| Diameter | 4 arcmin |
| Visual magnitude | 12.4 mag |
| Metric Distance | 7.900 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | Cl, L, lC, st L & S |
| Identification, Remarks | h 2029; GC 4466; GCL 107; OCL 91; Berkeley 42; not OCL (I3r) |
Finder Chart
The globular cluster NGC 6749 can be found in constellation Aquila. Only 1° 43' towards southeast you can find another globular cluster: NGC 6760. On 8 July it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time for observation is in the months March to December.