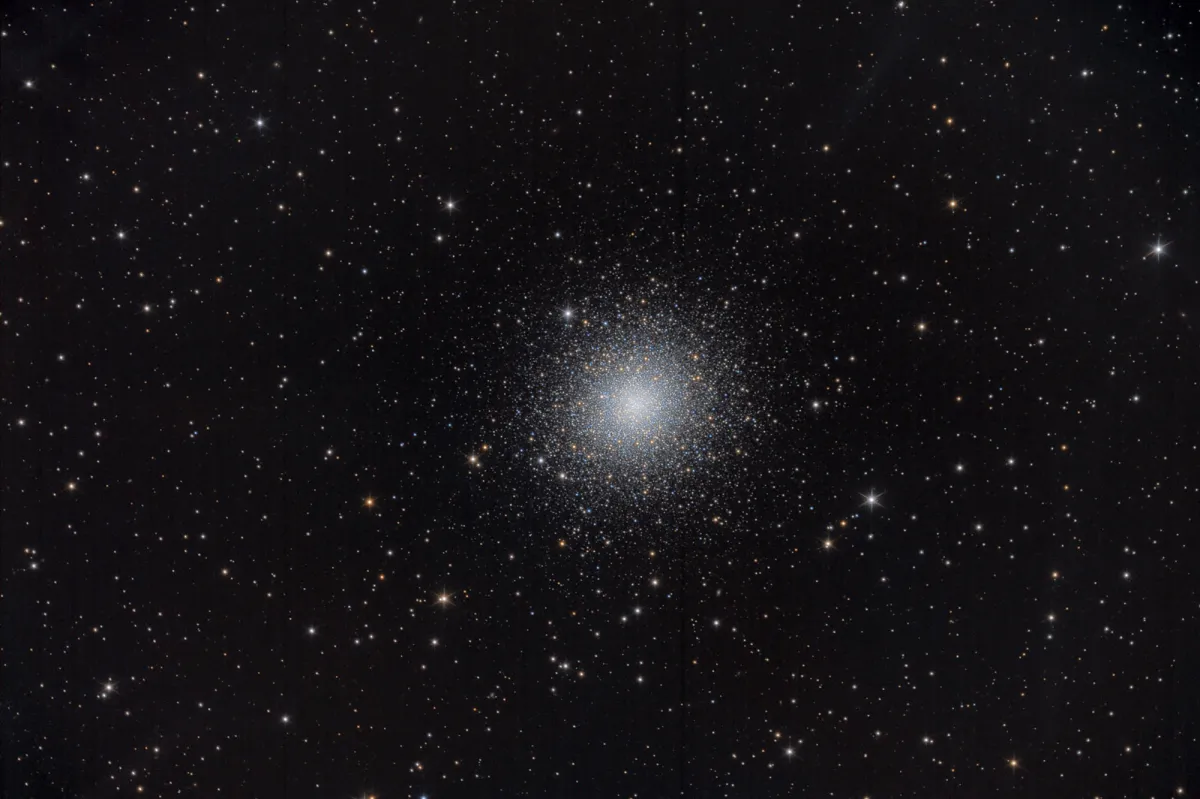
Globular Cluster Messier 2

History
This beautiful, bright globular cluster was first spotted by G. Maraldi in the year 1746, while he was searching for the comet Chéseaux. At that time, the appearance of fleeting tailed stars (comets) was more popular than it is today. Nebulous objects found during their search and tracking were entered into star charts solely to avoid the risk of confusing them with comets. On September 11, 1760, Charles Messier came across this globular cluster again and included it as the second object in his list. He wrote: «It resembles the beautiful nebula located between the head and the bow of Sagittarius and can be seen very well with a two-foot telescope aligned with the parallel of α Aquarii. Mr. Messier reported this nebula on the map of the comet’s path that he observed in 1759. Mém. Acad. year 1760, page 464. Mr. Maraldi had seen this nebula in 1746, while observing the comet that appeared that year.» [281]
About two decades later Sir William Herschel observed the objects found Messier and recognized the true nature of many of these «nebulae». He wrote: «The excellent collection of nebulae and clusters of stars which has lately been given in the Connoissance des Temps for 1783 and 1784, leads me next to a subject which, indeed, must open a view of the heavens. As soon as the first of these volumes came to my hands, I applied my former 20-feet reflector of 12 inches aperture to them; and saw, with the greatest pleasure, that most of the nebulae, which I had an opportunity of examining in proper situations, yielded to the force of light and power, and were resolved into stars. For instance the 2d, 5, 6, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 19, 22, 24, 28, 30, 31, 37, 51, 52, 53, 55, 56, 62, 65, 66, 67, 71, 72, 74, 92, all which are said to be nebulae without stars, have either plainly appeared to be noting but stars, or at least to contain stars, and to shew every other indication of consisting of them entirely.» [27]
Physical Properties
Visually, M 2 appears as a globular cluster with an angular diameter of about 7 arcminutes - but stars up to a diameter of 11 arcminutes can still be seen in photographs. The total integrated brightness is about 6.4 mag, the brightest stars reach about 13.1 mag, which is about three magnitudes above that of the horizontal branch in the HR diagram.
At a distance of around 50'000 light years, the globular cluster is a good bit further away than Messier 13 in the constellation Hercules or Messier 5 in Serpentis Caput. The current diameter is given as about 150 light years. With around 100'000 members, it is one of the richer globular clusters. With a Shapley/Sawyer concentration class of 2, M 2 is one of the more compact star clusters. It is particularly impressive due to its location in a region of the sky that is relatively poor in stars. The brightest stars are yellow and red giants with an absolute magnitude of -3 mag. The total absolute brightness of M 2 is -10 mag. The integrated spectral class of the cluster is F0. The radial speed is very low at around 3 km/s. [4]
| Designation | NGC 7089 |
| Type | GCL (II) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 21h 33m 27.2s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -00° 49' 22" |
| Diameter | 16 arcmin |
| Visual magnitude | 6.6 mag |
| Metric Distance | 11.500 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | !!, globular, B, vL, gpmbM, rrr, st eS |
| Identification, Remarks | h 2125; GC 4678; M 2; GCL 121 |
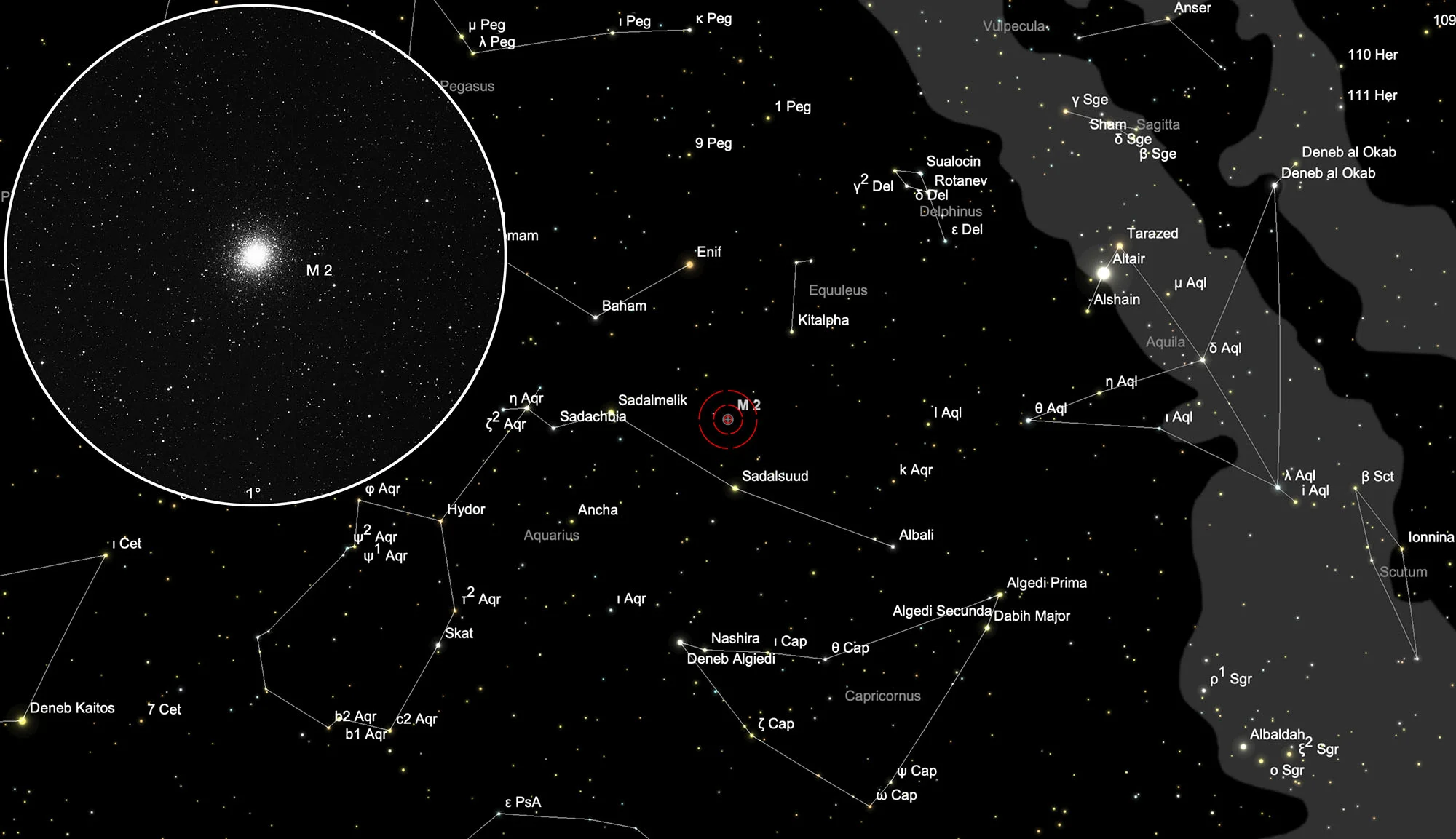
Finder Chart
The globular cluster Messier 2 is located in the constellation Aquarius, roughly five degrees north of the 2.9 mag bright star Sadalsuud (β Aquarii) about the same declination as the two stars Sadalmelik (α Aquarii, 3.0 mag) and Sadachbia (γ Aquarii, 3.8 like). As with almost all retrieval procedures, the choice of a large field eyepiece with the highest possible field of view (more than one degree) is recommended. In the months of April to January, M 2 is highest in the sky at night.