Footprint Nebula, Minkowskis Footprint (Minkowski 1-92)

History
The nebula Minkowski 1-92 was discovered in 1946 by the German-American astronomer Rudolph Minkowski. He detected objects with little or no continuous H-α spectrum on objective-prism survey plates obtained by W. C. Miller using the 10-inch telescope at Mount Wilson. Further examination of its appearance on direct photographs, taken at the Newtonian focus of the 60-inch or 100-inch telescope on Mount Wilson, revealed its nature as a planetary nebula. Minkowski listed it in Table 2 for diffuse and peculiar nebulae, noting: «Binuclear nebula without central star. The north preceding mass has a diameter of about 3" and is separated from the south following fainter mass by a dark lane. The spectrum is that of apeculiar star, showing M-type bands, strong emission lines of H with P Cygni-type absorptions and numerous emission lines of Fe-II and [Fe-II]. The nebula is probably not an emission nebula, but a reflexion nebula which obscures the peculiar star by which it is illuminated.» [397]
The PN does not have a PK number, but Kohoutek's 2000 edition of the «Catalogue of Galactic Planetary Nebulae» [146] lists it as a possible pre-planetary nebula in Table 5. It is known under the following names: «Minkowski's Footprint» or «Footprint Nebula».
Physical Properties
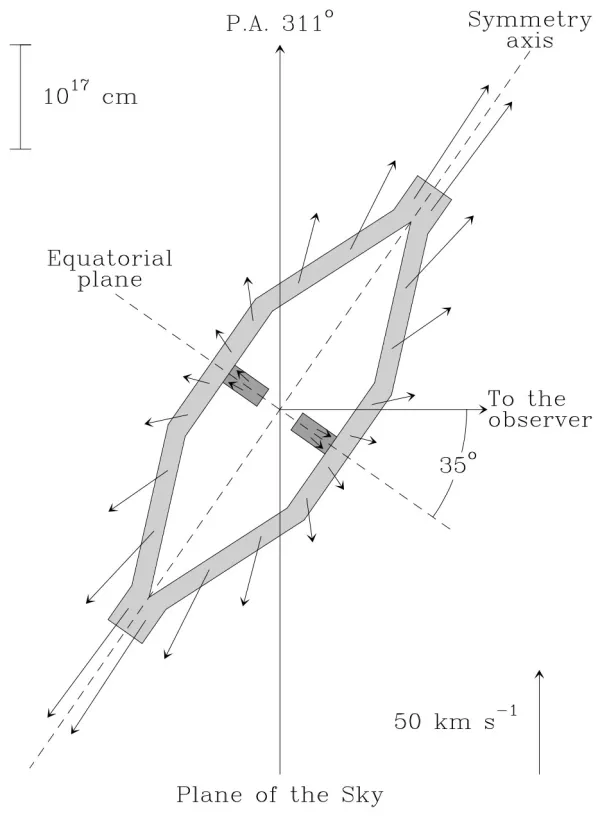
This protoplanetary nebula features two vast onion-shaped structures either side of an ageing star, giving it a very distinctive shape. Protoplanetary nebulae have short lives, being a preliminary stage to the more common planetary nebula phase. The central star, soon to be a white dwarf, puffing out material due to intense surface pulsations. Charged particle streams, called stellar winds, are shaping this gas into the interesting shapes.

Technically speaking Minkowski’s Footprint is currently a reflection nebula as it is only visible due to the light reflected from the central star. In a few thousand years the star will get hotter and its ultraviolet radiation will light up the surrounding gas from within, causing it to glow. At this point it will have become a fully fledged planetary nebula. [496] The northern lobe is inclined about 35° towards the observer. Distance to the nebula is about 2.5 kpc [497]
| Name | Min 1-92 |
| Object Type | Post-AGB Star |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 19h 36m 19s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +29° 32' 50" |
| Parallaxes | 0.6285 mas |
| Radial velocity | -7.08654 km/s |
| Redshift z | -0.000024 |
| Spectral type | B0.5IV[e] |
| Magnitudes | U 12.13; B 12.35; V 11.75; G 14.084518; R 11.54; J 9.91; H 7.929; K 6.209 |
| Identifiers | 2MASS J19361890+2932500; AKARI-FIS-V1 J1936183+293302; AKARI-IRC-V1 J1936189+293249; ALS 17351; AP J19361890+2932500; EM* VES 20; GEN# +6.20055020; GSC 02150-00266; GSC2 N0301023650; Gaia DR2 2032364166432389760; Gaia DR3 2032364166432389760; HBHA 2702-04; IRAS 19343+2926; LF 2 +29 230; MSX6C G064.0964+04.2563; Min 1-92; NAME Footprint Nebula; NAME Min Footprint; NAME Minkowski's Footprint; OH 064.0+04.2; PDS 581; PN M 1-92; TIC 213414497; UBV M 44475; UCAC3 240-190929; UCAC4 598-087069; WISE J193618.97+293250.0; WISEA J193618.91+293249.7; [KW97] 38-25; [LFO93] 1934+29; [TVH89] 410 |
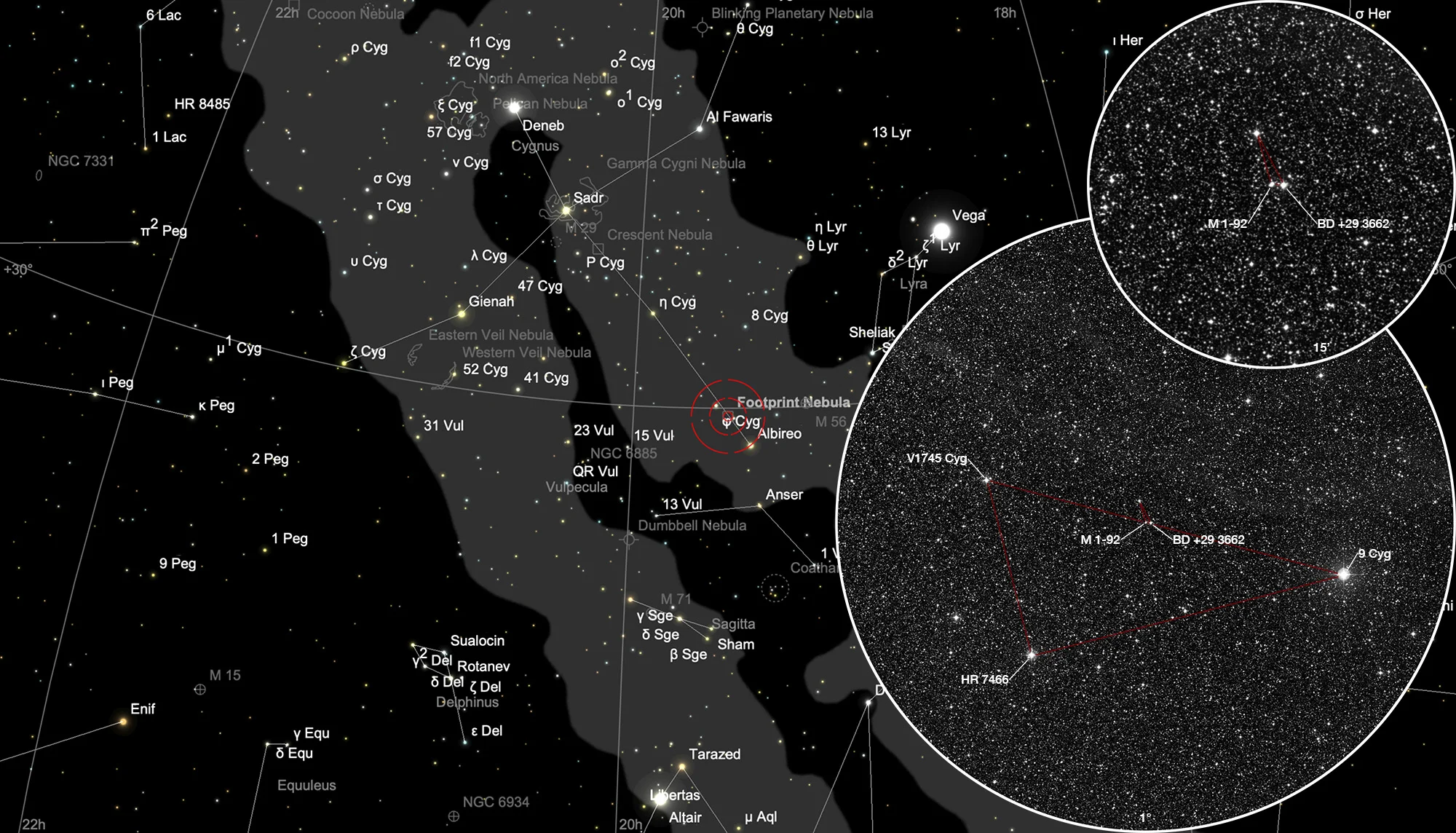
Finder Chart
The proto-planetary nebula Minkowski 1-92 is located in the constellation Cygnus and is quite easy to find despite its tiny size. Aim the outermost 4° Telrad circle at the bright star Albireo (β Cygni) so that the centre aligns with the line Albireo — η Cygni. There is a right triangle formed by binary star 9 Cygni (5.4 mag), binary star HR 7466 (6.46 mag and 11 mag) and variable star V1745 Cygni (7.44 mag). In the middle of the hypotenuse, which is about 35 arc minutes long, is the mag 9.7 star BD +29 3662 (TYC 2150-142-1) and about 20 arc seconds next to it is the protoplanetary nebula Minkowski 1-92. The best observation time is from March to December.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: The position of the proto-planetary nebula Minkowski 1-92 is easy to find using the location map in the 21 mm Ethos eyepiece (85x). The small, acute-angled triangle is quite conspicuous. The star BD +29 3662 is reddish and the proto-PN appears bluish. At higher magnification (11 mm Delite, 163x) the proto-PN appears diffuse and elongated when seen indirectly. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Glaubenberg, 2. 8. 2022, SQM 21.21, Bernd Nies