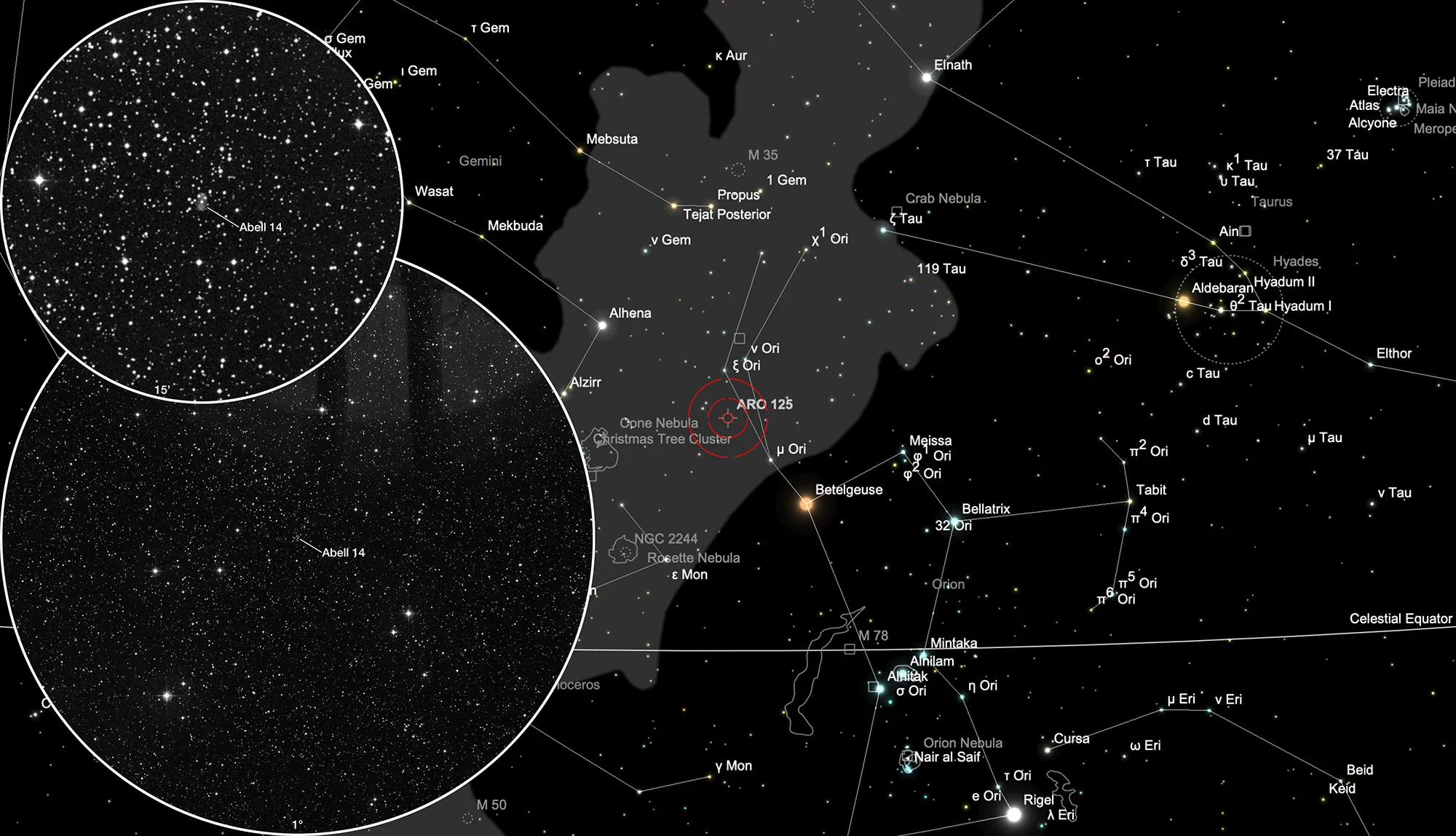
Planetary Nebula Abell 14

History
The planetary nebula Abell 14 (PK 197-3.1) was discovered in 1955 by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell on the photo plates of the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS). In 1955 he published a first list of 13 globular clusters and the positions of 73 planetary nebulae. The PN first had the number 10 (A55 10). In 1966 Abell published a completed list including the size and description of the 86 planetary nebulae discovered on the POSS photo plates. The PN was then listed as number 14 (A66 14). He described the morphological appearance of the PN as «D» (a ring of variable thickness). [331, 332]
The designation PK 197-3.1 originates from the two Czechoslovak astronomers Luboš Perek and Luboš Kohoutek, who in 1967 compiled a catalog of all the planetary nebulae of the Milky Way known at the time. [146]
Physical Properties
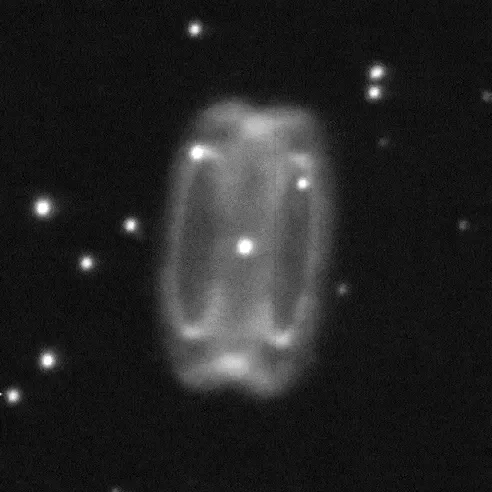
Abell 14 is a highly evolved, bipolar nebula with a kinematical age of ∼19'400 yr for a distance of 4 kpc. The progenitor probably had 5 solar masses and experienced the third dredge-up and hot bottom burning phases. The stellar parameters of the central source reveal a star at a highly evolved stage near to the white dwarf cooling track. [173]
| Designations | PN G197.8-03.3: A 14, PK 197-03.1, A55 10, ARO 125, VV' 39 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 06h 11m 09s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +11° 46' 47" |
| Dimensions | 33." (optical) |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 59, CSI +11 -06084, UBV 6225 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 15.74, B: 15.75, V: 15.24 |
| C-Star Spectral Type | F7 V? |
| Discoverer | ABELL 1955 |
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Abell 14 is in the constellation Orion. On 25 December it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. It is best observed from August to May.
Visual Observation
762 mm Aperture: Unfortunately, no. Abell 14 appears neither visually, nor on a single EAA image, nor on stacked 34 x 6 second images. — 30" f/3.3 SlipStream Dobsonian, Hasliberg, 26. 12. 2024, SQM-L 21.17, Elena + Eduard von Bergen