Planetary Nebula Abell 13


History
The planetary nebula Abell 13 (PK 204-8.1) was discovered by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell on the photo plates of the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS) in 1955. Most of the 86 PNs discovered on the POSS photo plates are large and have one low surface brightness, which suggests an advanced age of their developmental stage. [331, 332]
Physical Properties
The PN is located at a distance of about 1.2 kpc. The brightness of the nebula, which is around 2.5 arc minutes in size, is 19.87 mag in the V-band and 19.87 mag in the B-band 06/20 mag. [145]
| Designations | PN G204.0-08.5: A 13, PK 204-08.1, A55 9, ARO 124, VV' 38, YM 28 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 06h 04m 47s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +03° 56' 27" |
| Dimensions | 153." (optical) |
| Expansion Velocity | 20. (O-III) 22.5 (N-II) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 58, CSI +03 -06022, UBV 6150 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 19.06, B: 20.06, V: 19.87 |
| Discoverer | ABELL 1955 |
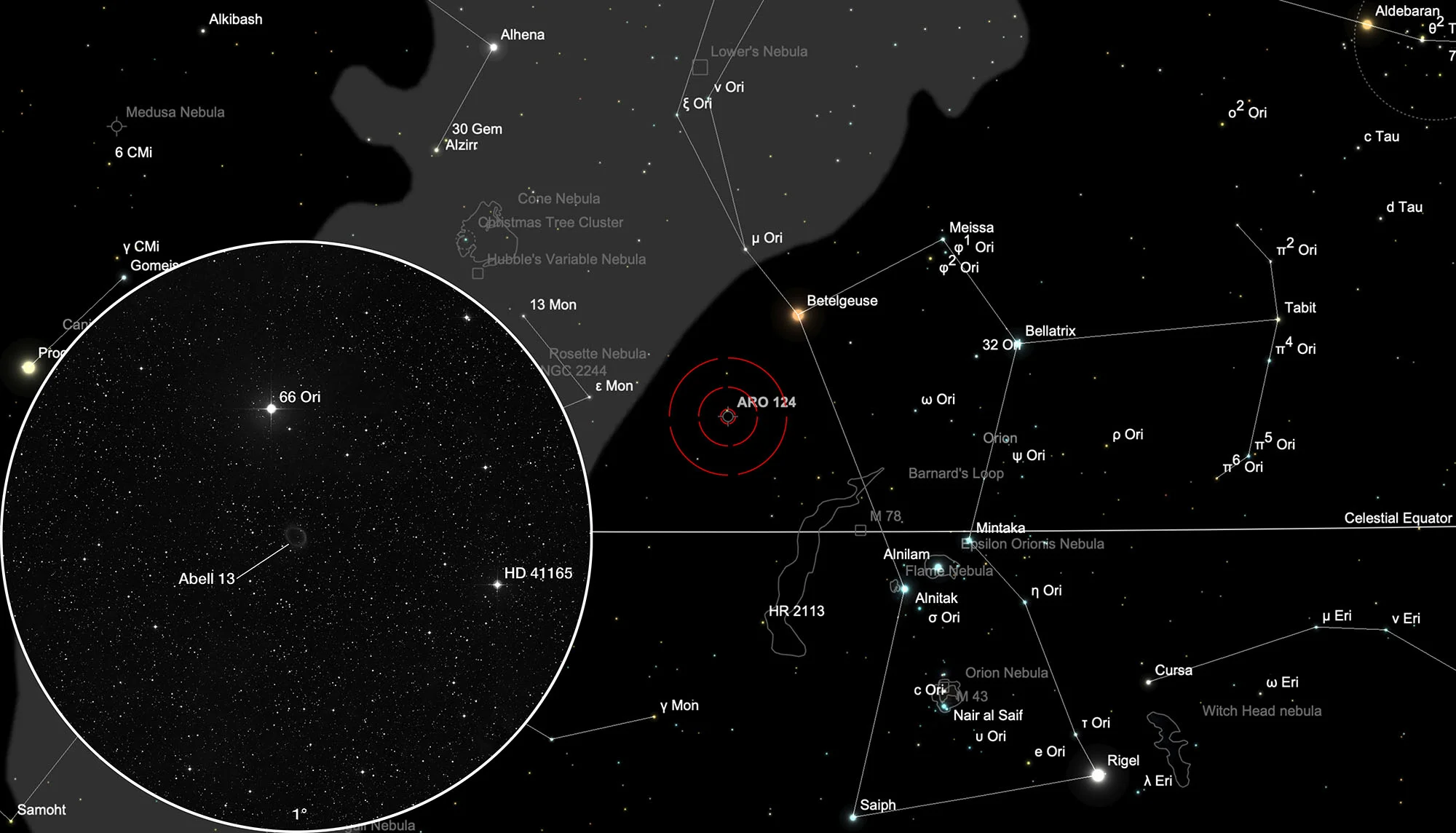
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Abell 13 is located in the constellation Orion, about 13 arc minutes south of the 5.6 mag bright star 66 Orionis. On 23 December it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is August to May.
Visual Observation
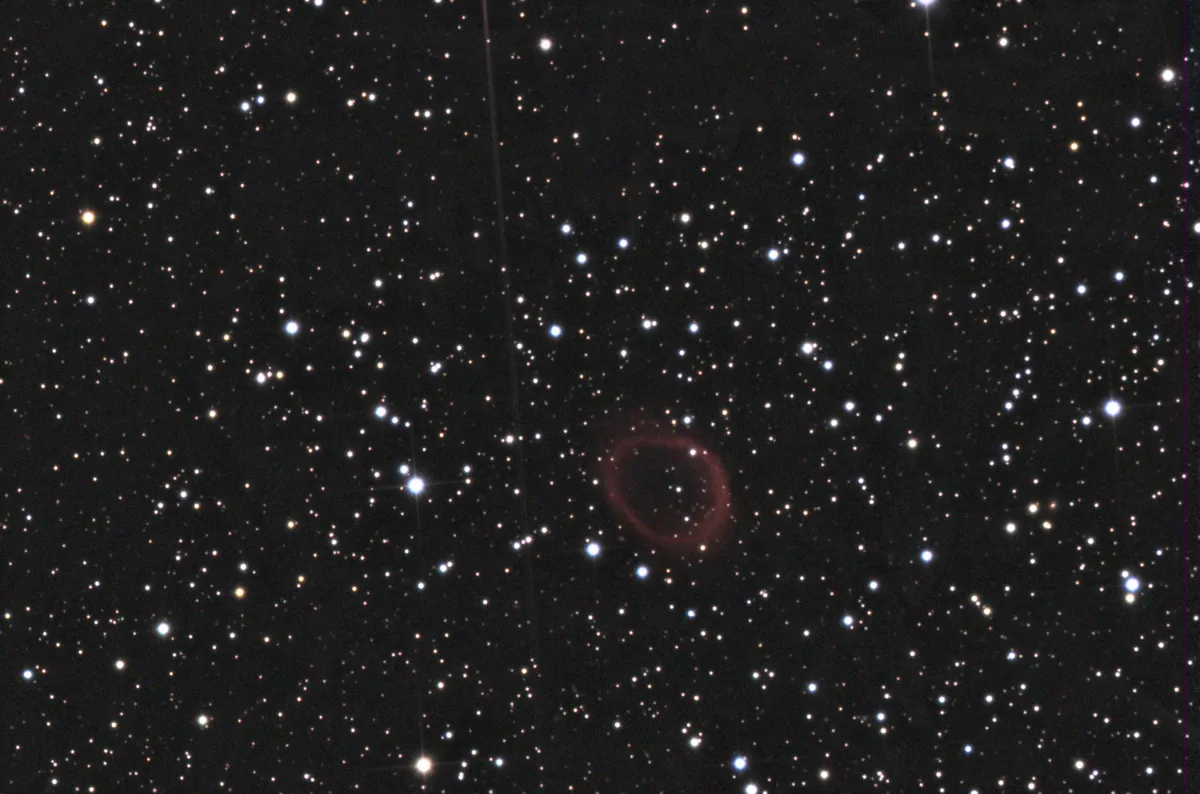
762 mm Aperture: Unfortunately only photographically, because Abell 13 does not show up visually, only on 34 stacked EAA single exposures of 8 seconds each at ISO 40'000 can a red ring-like glow be made out. — 30" f/3.3 SlipStream Dobsonian, Hasliberg, 27. 12. 2024, SQM-L 20.80, Elena + Eduard von Bergen