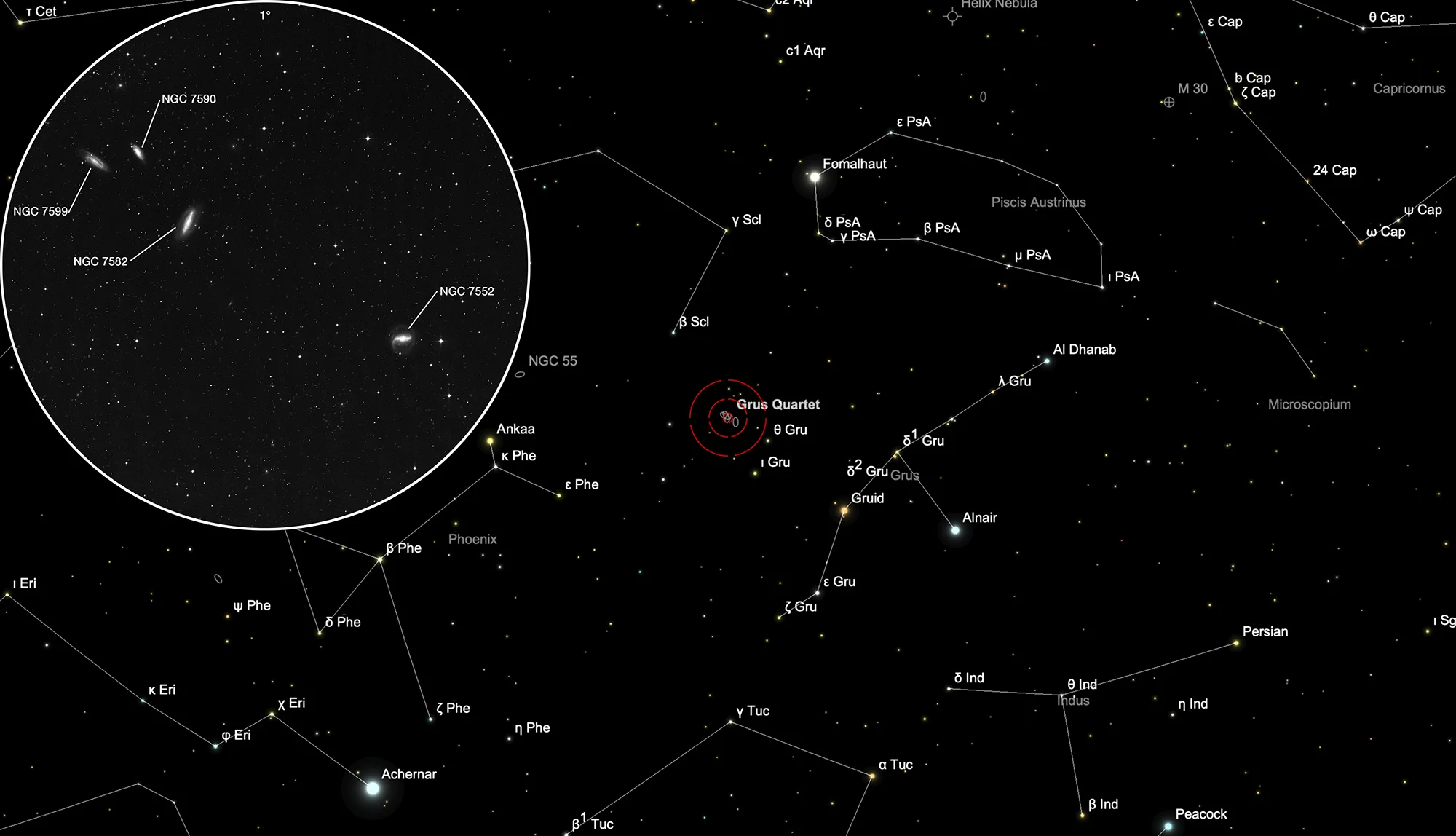
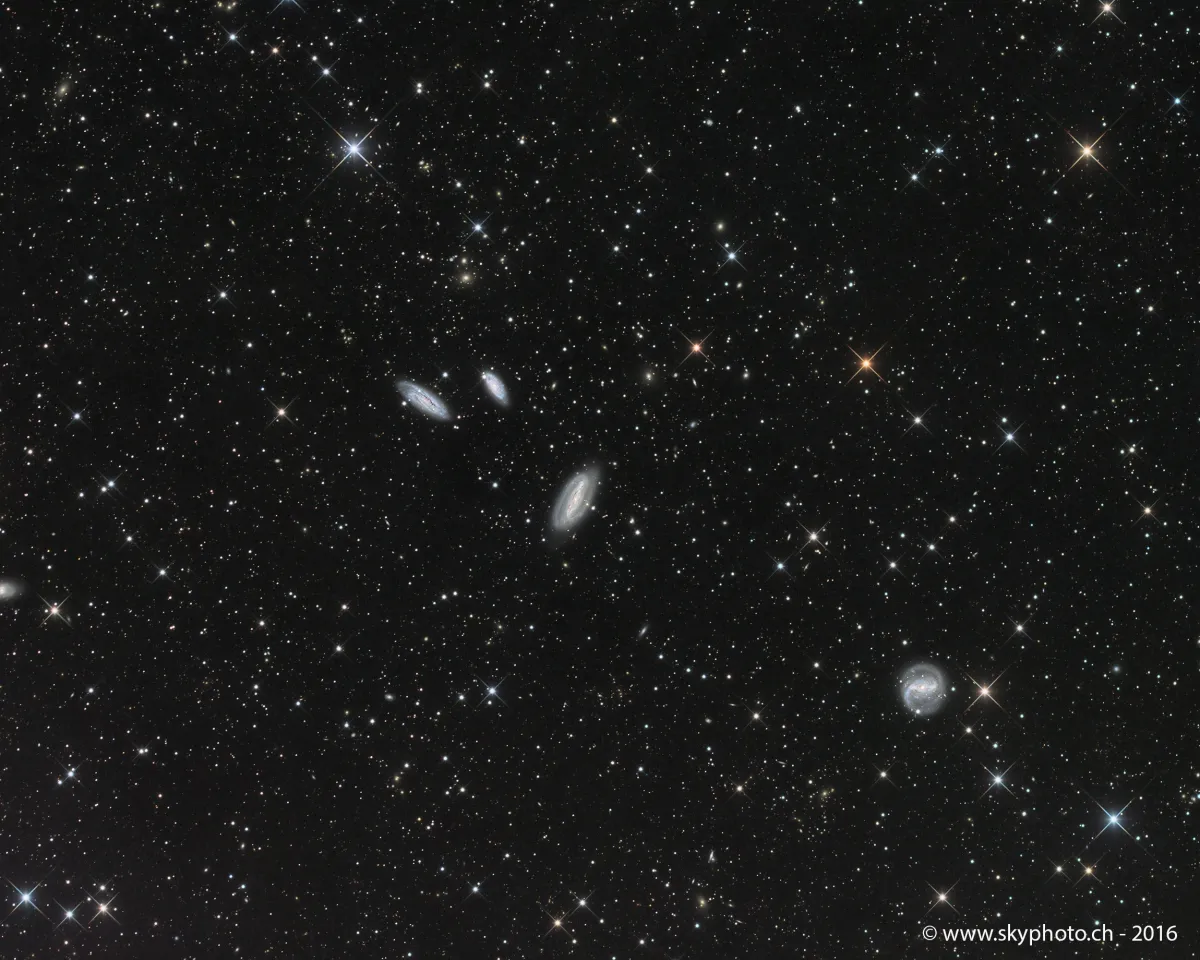
Grus Quartet (NGC 7552/82/90/99)

History
James Dunlop discovered NGC 7552 and NGC 7582 on 7 July 1826 using his 9-inch speculum reflector at Parramatta, New South Wales in Australia. For NGC 7552 (D 475) he noted after four observations: «A small faint nebula, rather elongated in the parallel of the equator, about 30" broad, and 40" long; there is a pretty bright point situated near the centre of the nebula: a small star precedes it.» For NGC 7582 (D 476) he made two observations and noted: «A small faint round nebula, about 30" diameter: a double nebula follows this.» The double nebulae (NGC 7590, NGC 7599 = D 477) he observed one week later and described them follows: «Two very small round nebulae, nearly the same AR, and differing about 1' in polar distance.» [50, 277]
On 22 October 1897 Lewis Swift found a nebula (Sw 11-226) and reported it as «pretty bright, pretty smal, round, 8m star preceding». This nebula was added by Dreyer as IC 5294. With a position just 9 seconds of time west of NGC 7552 it is a duplicate entry. [364]
Physical Properties
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 7552 | 23 16 10.6 | -42 35 05 | Gx (SBab) | 11.3 | 10.6 | 0.7 | 12.9 | 3.4 × 2.7 | 1 | 0.005365 | 22.66 | 17.150 | B, S, mE 90° ±, vsbM * 13 | h 3977; GC 4916; IC 5294; ESO 291-12; MCG -7-47-28; IRAS 23134-4251; VV 440; Grus quartet |
| NGC 7582 | 23 18 23.5 | -42 22 11 | Gx (SBab) | 11.4 | 10.6 | 0.8 | 13.0 | 5 × 2.3 | 157 | 0.005254 | 22.19 | 20.620 | pB, L, pmE, gbM | h 3978; GC 4927; ESO 291-16; MCG -7-47-29; AM 2315-423; IRAS 23156-4238; Grus quartet |
| NGC 7590 | 23 18 54.6 | -42 14 21 | Gx (Sbc) | 12.1 | 11.5 | 0.6 | 12.5 | 2.6 × 1 | 36 | 0.005255 | 22.20 | 25.270 | pB, pL, pmE, gbM, p of 2 | h 3980; GC 4929; ESO 347-33; MCG -7-47-30; IRAS 23161-4230; Grus quartet |
| NGC 7599 | 23 19 20.8 | -42 15 29 | Gx (SBc) | 12.1 | 11.5 | 0.6 | 13.3 | 4.4 × 1.4 | 57 | 0.005508 | 23.27 | 20.960 | F, pL, pmE, gbM, f of 2 | h 3981; GC 4931; IC 5308; ESO 347-34; MCG -7-47-33; IRAS 23166-4231; Grus quartet |
Finder Chart
The galaxy quartet is located on the southern celestial hemisphere in the constellation Grus. On 12 September it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight.