Globular Cluster Messier 92



History
M 92 was discovered on 27 December 1777 by J. E. Bode and about four years later, on 18 March 1781, again independently of Charles Messier. He wrote about it: «Nebula, beautiful, apparent, and of great light, between the knee and the left leg of Hercules, is seen very well with a telescope of one foot [focal length]. It contains no stars; the centre is clear and brilliant, surrounded by nebulosity and resembles the nucleus of a large comet: its light, its size, approaches very much the nebula which is in the belt of Hercules. See number 13 of this Catalog: its position has been determined by comparing it directly to the sigma star of Hercules, fourth magnitude: the nebula and the star on the same parallel.» [281]
While M 92 couldn't be resolved into separate stars neither with Bodes nor with Messiers small telescopes, W. Herschel recognized its true identity as a globular star cluster. Lord Rosse, with his large reflector in Parsonstown, Ireland, believed he saw a spiral structure in the core of M 92. [4, 277]
Physical Properties
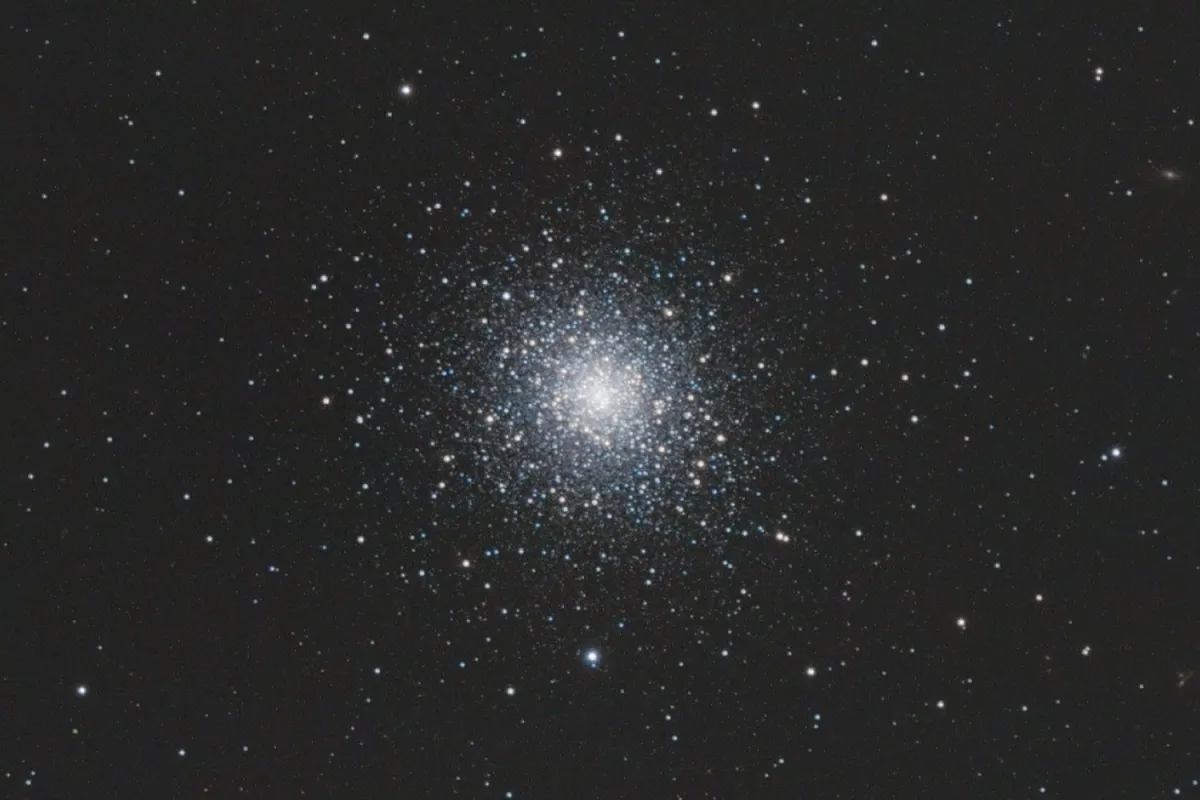
M 92 is a globular cluster only nine degrees away from the larger M 13 and thus ekes out a bit of a shadowy existence. Althoguh it is slightly smaller and weaker than M 13, but it is more concentrated. The integrated spectral type of M 92 is of type F2. The cluster contains several variable stars, most of them short-period pulsating variables of the RR Lyrae type. Only one star seems to be eclipsing. Presumably these are so rare because of the high star density and the resulting orbital disruption of a binary system in globular clusters. Most of the stars in M 92 are red giants with an apparent magnitude of about 12 mag and an absolute magnitude of about -3 mag. The total luminosity of the star cluster is about 250'000 times that of the sun.
The distance from M 92 is estimated to be around 26'000 to 35'000 light years and it is moving towards us at around 120 km/s. M 92 appears to be younger than M 13 with an age of more than 14 billion years. [4, 98]
| Designation | NGC 6341 |
| Type | GCL (IV) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 17h 17m 07.3s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +43° 08' 13" |
| Diameter | 14 arcmin |
| Visual magnitude | 6.5 mag |
| Metric Distance | 8.300 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | globular, vB, vL, eCM, rrr, st S |
| Identification, Remarks | GC 4294; M 92; GCL 59 |
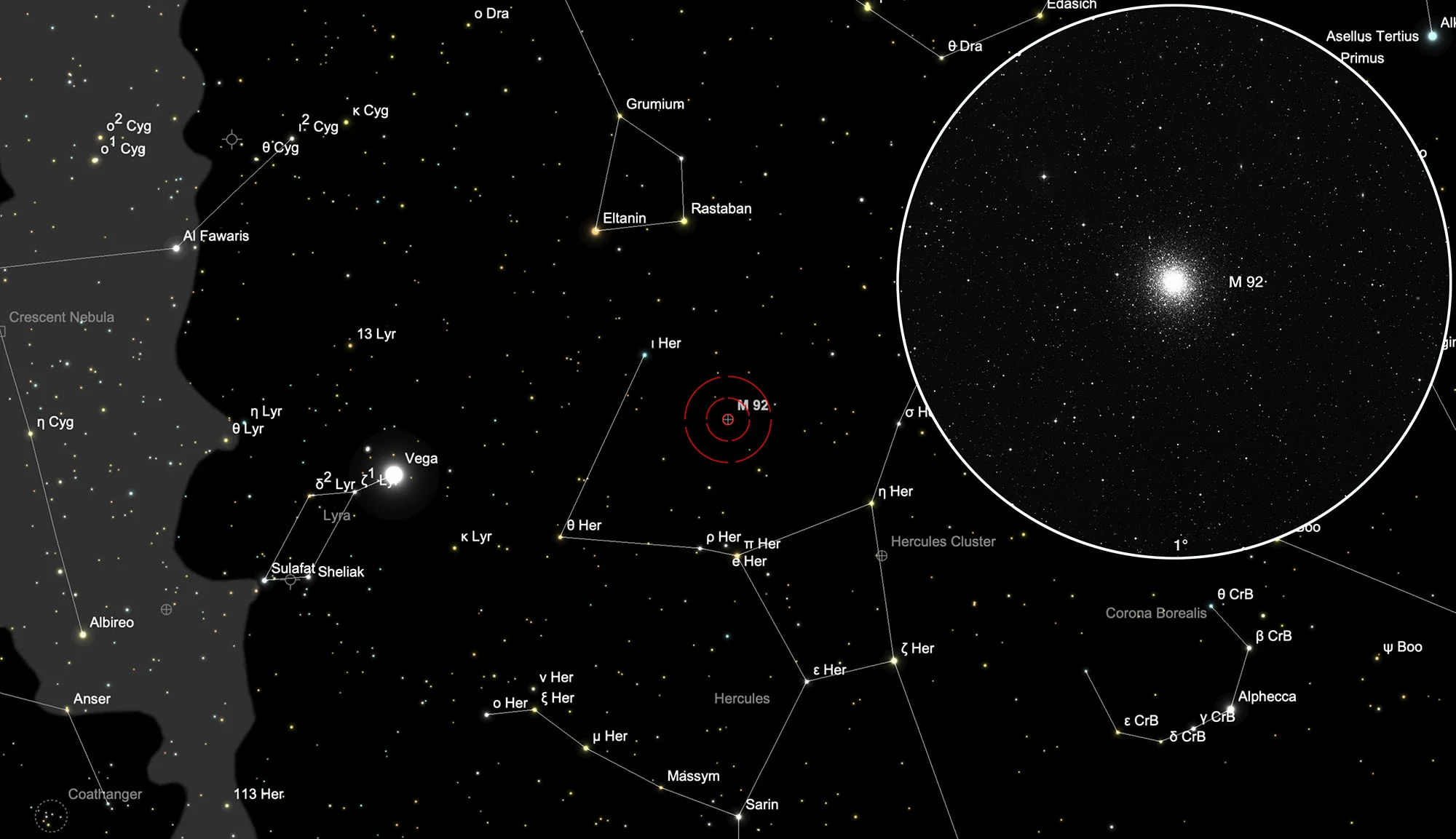
How to find M 92?
The globular cluster M 92 is located about six degrees north of the 3.4 mag bright star π Herculis, which forms the northeast corner of the well-known Hercules trapezoid, and about eight degrees east of σ Herculis. It is therefore easy to focus this globular cluster in the telescope, especially since it is barely visible to the eye even on a dark night.
Visual Observation

150 mm Aperture: In the shadow of its «bigger brother» M 13, this somewhat more difficult to find is often overlooked. M 92 is perhaps one of the most beautiful objects to be observed in the northern sky: As a globular star cluster, it reveals some irregular structures that are also visible in smaller devices: In a 6 inch refractor at around 130x magnification, a foggy spiral structure can be seen most clearly, which is interspersed with many star-like points of light. This spiral structure is unique. The core still appears foggy with two distinct thickenings. Only from approx. 180- twice the core appears to be dissolved, the two thickenings that are visible with smaller enlargements are also dissolved, but are lost in the core area. With even greater enlargements, these thickenings appear to dissolve completely and a relatively large core area is presented with approximately the same density of individual points of light. It is also interesting that the «foggy background» remains visible at all magnifications up to 680x; this could be many faint single stars that are below the visibility limit. The best magnification range is around 130 to 300x. — 150 mm refractor, 1996, Beat Kohler
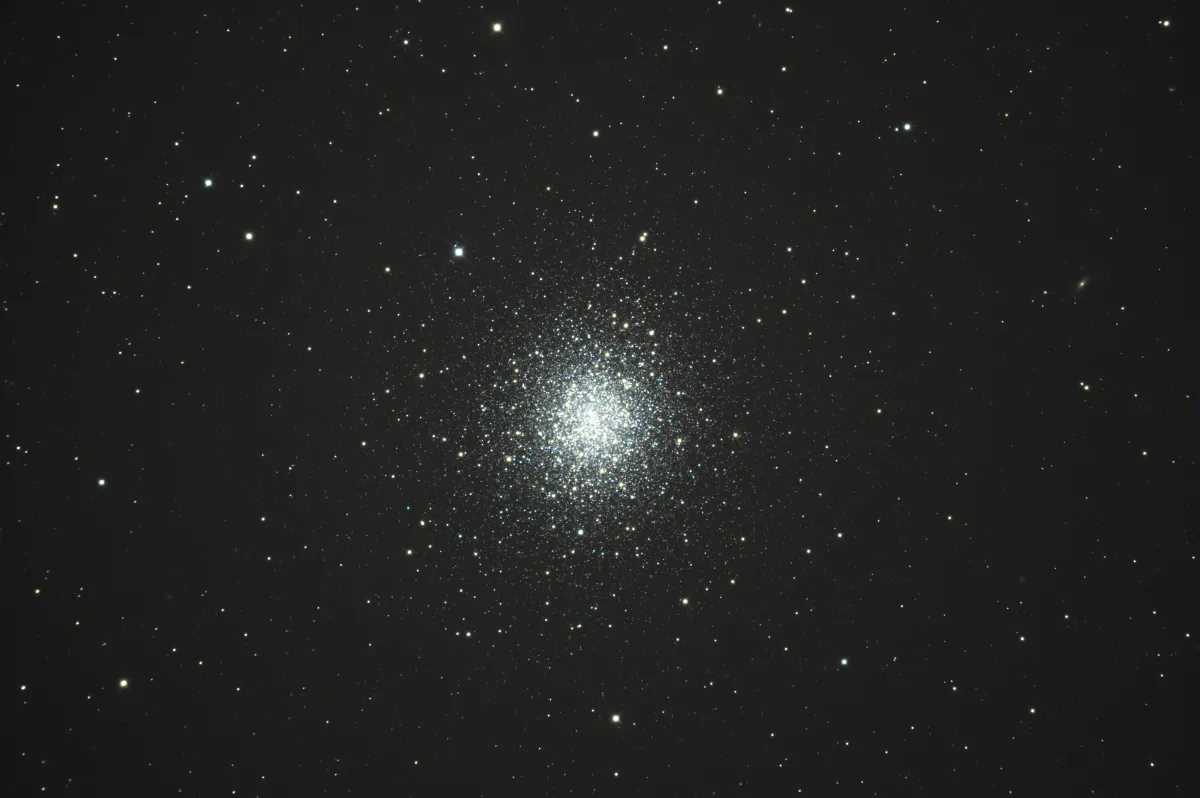
320 mm Aperture: The globular cluster M 92, compared to the previously observed M 15, has somewhat brighter stars that are much more scattered and not as densely arranged. The core, however, is twice as wide, with similar brightness to the surrounding stars. — 12.5" f/4.5 Ninja-Dobsonian, Zwirgi, 1021 m above sea level, 5. 10. 2024, Eduard von Bergen
400 mm Aperture: The globular cluster M 92 is always worth a detour after M 13. It does not need to hide and is also a pleasing sight. With increasing magnification, more stars can be teased out of the core region. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Glaubenberg, 17. 6. 2023, Bernd Nies