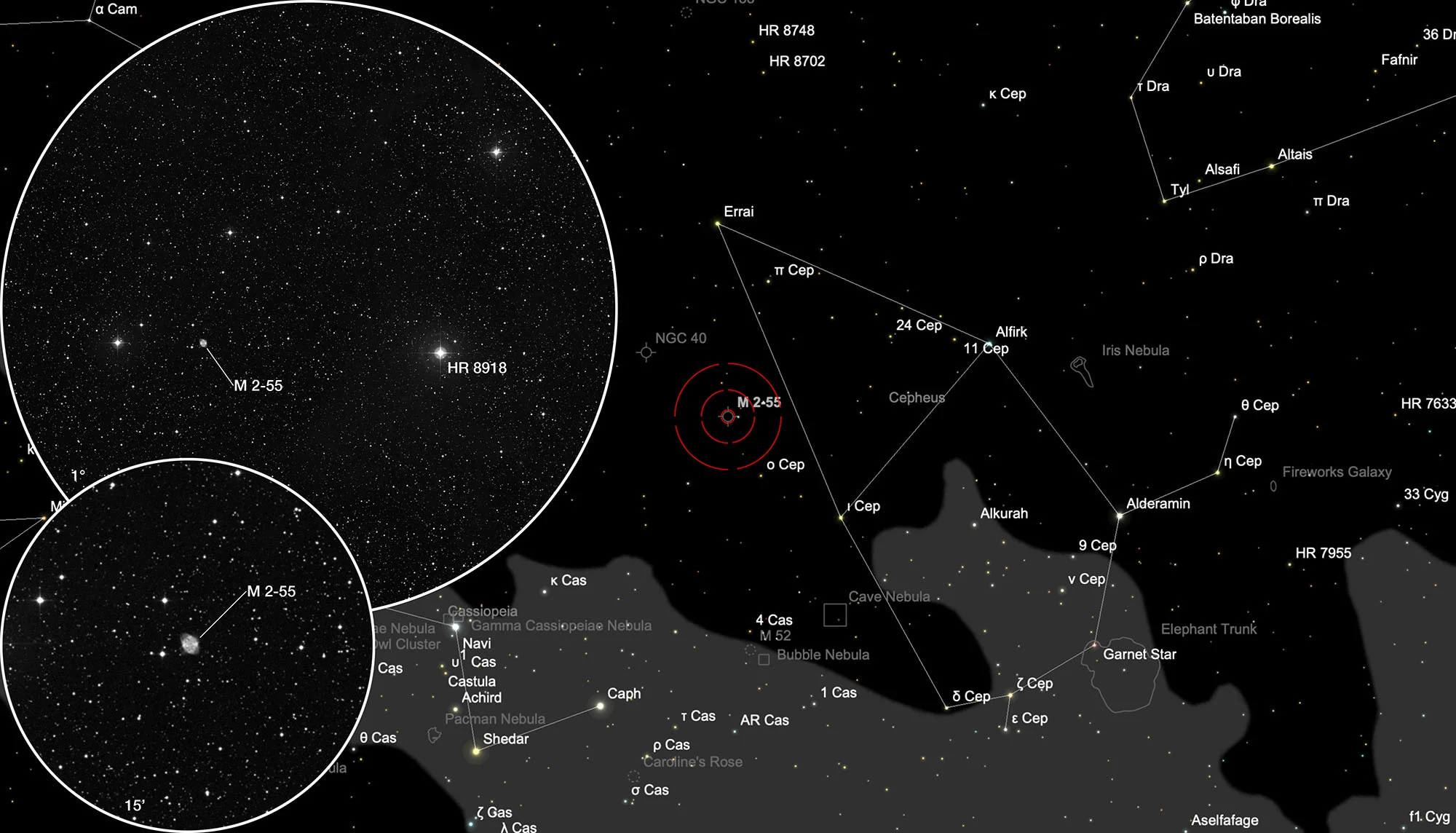
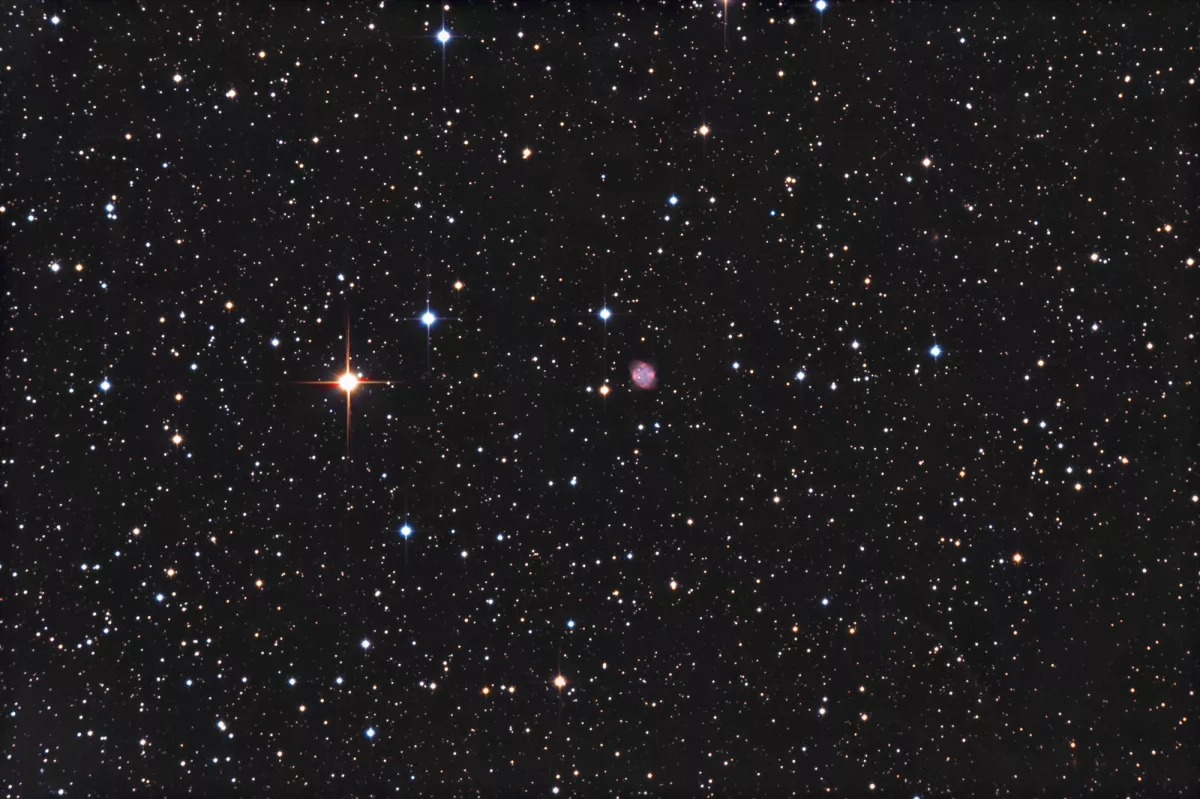
Planetary Nebula Minkowski 2-55

History
The planetary nebula was discovered in 1947 by the German-American astronomer Rudolph Minkowski. He detected objects with little or no continuous H-α spectrum on objective-prism survey plates obtained by W. C. Miller using the 10-inch telescope at Mount Wilson. Further examination of its appearance on direct photographs, taken at the Newtonian focus of the 60-inch or 100-inch telescope on Mount Wilson, revealed its nature as a planetary nebula. Minkowski also contributed to the creation of the National Geographic Society - Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS). [397, 454]
Physical Properties
The distance from M 2-55 is 2232 pc. [145]
| Designations | PN G116.2+08.5: M 2-55, PK 116+08.1, ARO 382, VV 287, VV' 577 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 23h 31m 51s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +70° 22' 14" |
| Dimensions | 39." (optical), 40." (radio) |
| Radial Velocity | -22.6 ± 2.9 km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 453 |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 21.2, V: 21.1 |
| Discoverer | MINKOWSKI 1947 |
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Minkowski 2-51 is located in the constellation Cepheus. The best time to observe is May to February, when it is highest at night.