Planetary Nebula Abell 24

History
The planetary nebula Abell 24 was discovered in 1955 by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell on the photo plates of the «Palomar Observatory Sky Survey» (POSS). This survey was exposed on photographic plates with the 48 inch Oschin Schmidt Telescope on Mount Palomar in Southern California. In 1966 he published a second list of a total of 86 planetary nebulae discovered on the POSS photo plates. Most of the 86 PNs discovered on the POSS photo plates are large and have one low surface brightness, which suggests an advanced age of their developmental stage. [331, 332]
The designation PK 217+14.1 originates from the two Czechoslovak astronomers Luboš Perek and Luboš Kohoutek, who in 1967 compiled a catalog of all the planetary nebulae of the Milky Way known at the time. [146]
The lesser known designation ARO 137 originates from 1971 survey of microwave radiation from planetary nebulae conducted by Canadian radioastronomer Lloyd A. Higgs using the 46-metre Algonquin Radio Observatory in Ontario, Canada. [136, 137]

Physical Properties
The white dwarf star in the centre of the nebula has about 0.7 solar masses, a surface temperature of 137,000 K and an evolutionary age of about 11'000 years. The nebula began to form around 20'000 years ago. [411] Distances range from 530 pc to 700 pc. Apparent Magnitudes: B 16.97 mag, V 17.18 mag. [145]
| Designations | PN G217.1+14.7: A 24, PK 217+14.1, A55 17, ARO 134, VV' 73 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 07h 51m 39s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +03° 00' 27" |
| Dimensions | 355." (optical), 296." (radio) |
| Radial Velocity | +12.7 ± 4.0 km/s |
| Expansion Velocity | 14.0 (O-III) km/s |
| C-Star Designations | AG82 93, CSI +03 -07491, UBV 7572 |
| C-Star Magnitude | U: 15.82, B: 16.97, V: 17.18 |
| Discoverer | ABELL 1955 |
Finder Chart
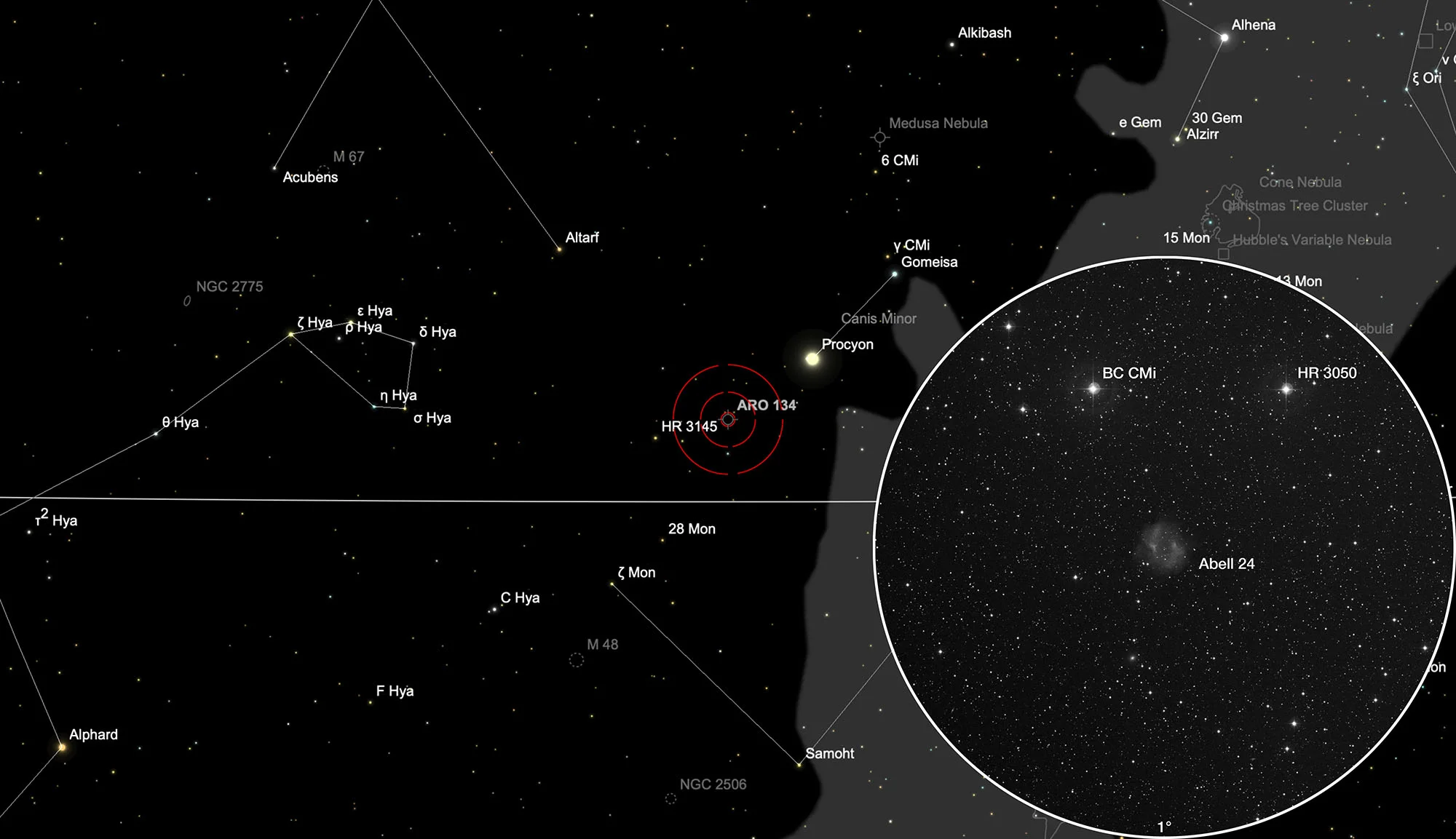
The planetary nebula Abell 24 (PK 217+14.1) is located in the constellation Canis Minor (Lesser Dog). It lies south of the two 6 mag stars HR 3050 and BC Canis Minoris and forms an isosceles triangle with them. On 17 January it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is September to June.