Constellation Columba (Dove)
Properties
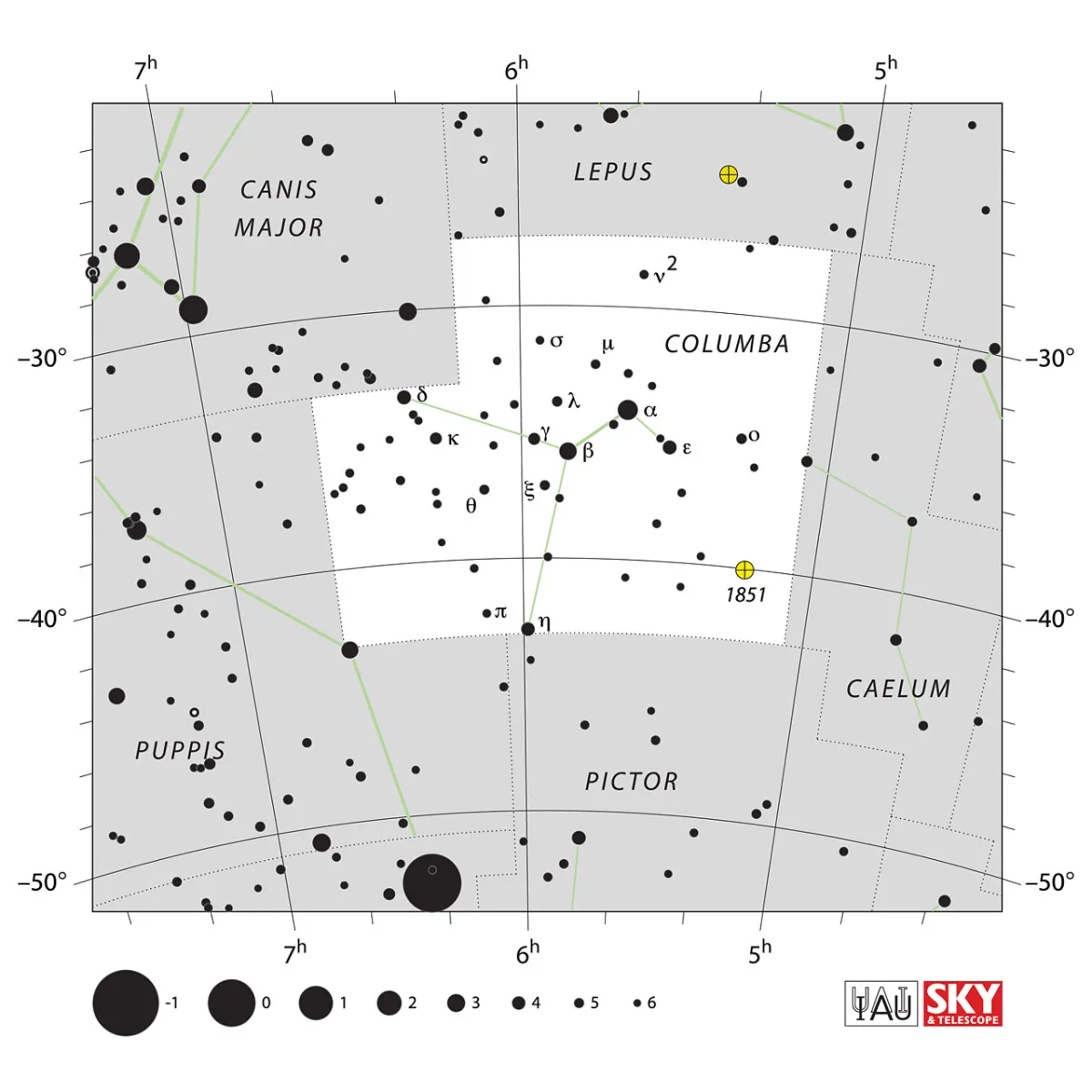
The constellation is south of Orion, separated by Lepus. It is a rather inconspicuous constellation, the most striking feature of which is a wavy line of six stars that runs from east to west. The constellation covers 270 square degrees of the sky and culminates around midnight on December 17th. [9, 15]
| α Col | Phaet, Phakt, Phact, Phad |
| β Col | Wezn, Wazn |
| IAU Name | Columba |
| IAU Genitive | Columbae |
| IAU Abbr. | Col |
| English Name | Dove |
| Culmination at local midnight | 20 December |
| Season (Latitude +0.0°) | August … May |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 05h 03m 54s … 06h 39m 37s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -43° 06' 42" … -27° 04' 38" |
| Area | 270 deg2 |
| Neighbours (N↻) | Lep, Cae, Pic, Pup, CMa |
Deep-Sky Object Descriptions
Catalogues
Mythology and History
Columba is a constellation related to Argo Navis (today divided into Carina, Vela, Puppis, Pyxis). Some see it as the dove that showed the Argonauts the way between deadly rocks at the entrance to the Black Sea, others see it as Noah's dove, which Noah sent out after the flood to look for land.
The constellation was introduced by Johann Bayer in his Uranometria from 1603 and taken into an official list by the French Augustin Royer in 1679. [7]