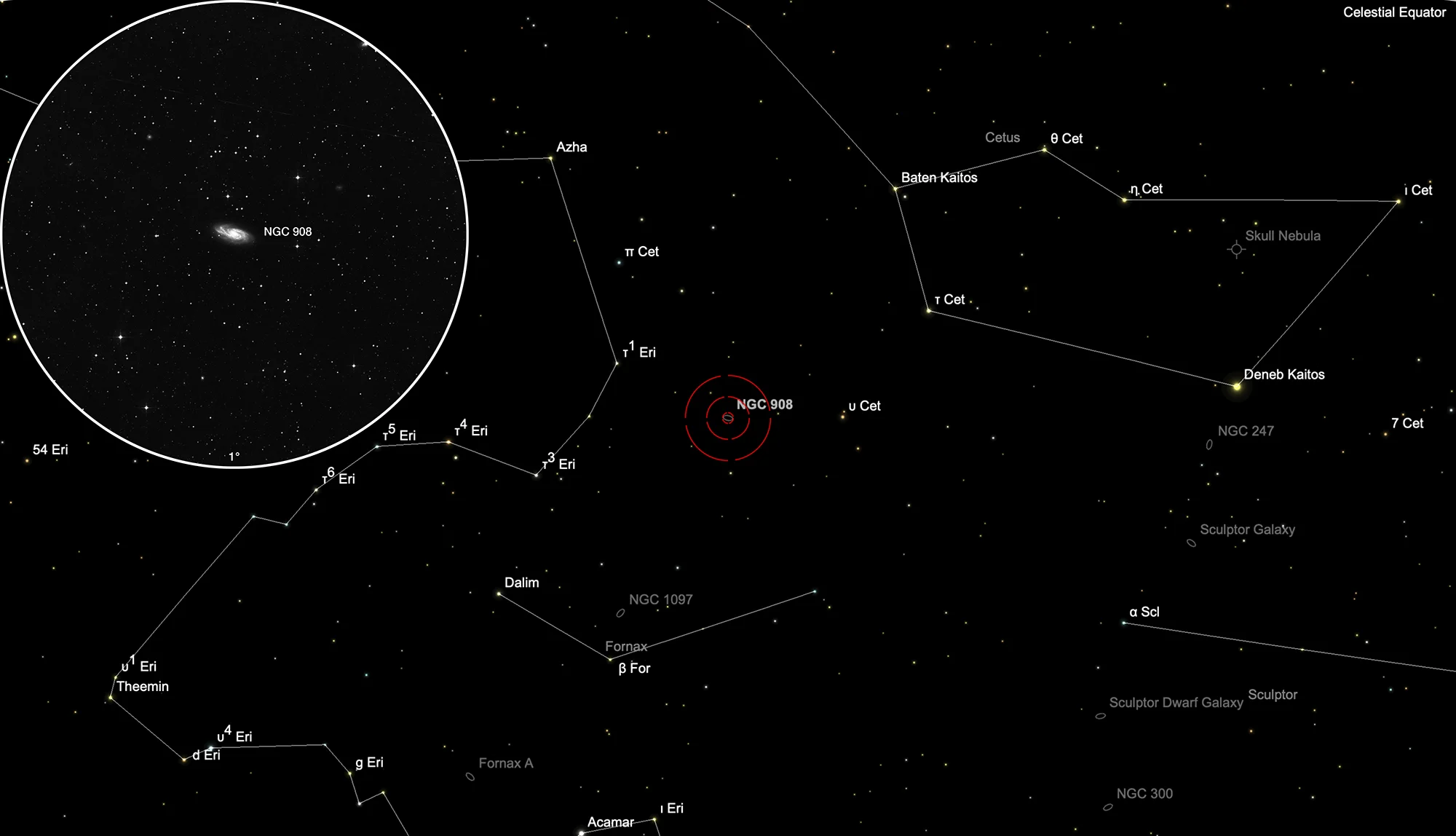
Galaxy NGC 908

History
This galaxy was discovered by William Herschel on 20 September 1789 using his 18.7 inch reflector. He cataloged it as I 153 and noted: «Considerably bright, very large, extended, south proceeding, north following, above 15' length.» [463] Dreyer added it as NGC 908 to his «New General Catalogue» published in 1888. [313]
Physical Properties
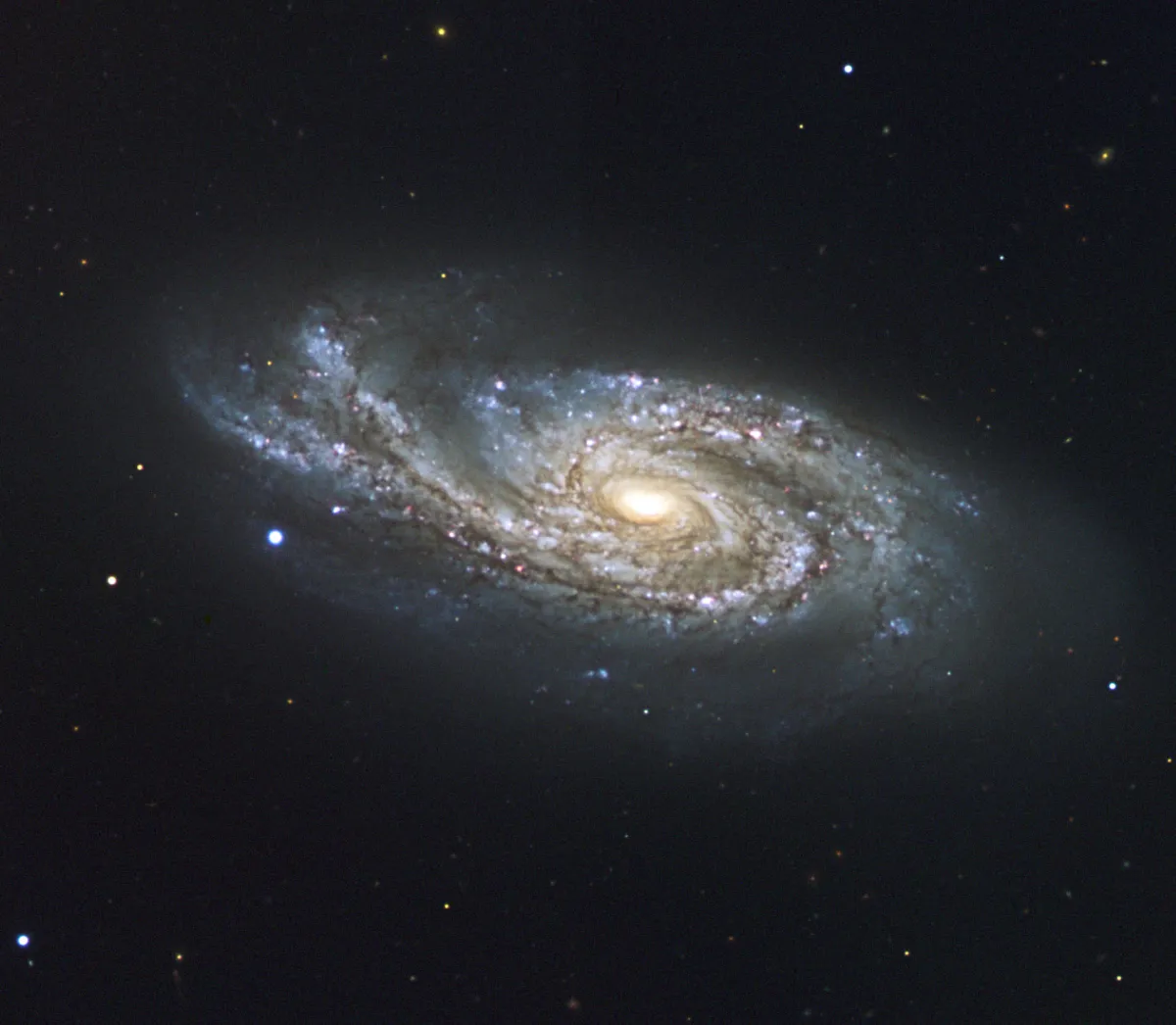
NGC 908 is a spiral galaxy in a distance of 65 million light-years and 75 000 light-years in size. It is a starburst galaxy that is undergoing a phase where many stars are born at a high rate. Clusters of young and massive stars can be seen in the spiral arms. The galaxy also presents uneven and thick spiral arms, indicating that it suffered a close encounter with another galaxy, even none is visible today. [640]
| Designation | NGC 908 |
| Type | Gx (SBc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 02h 23m 04.6s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -21° 14' 00" |
| Diameter | 6.1 × 2.7 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 10.8 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 10.2 mag |
| Surface brightness | 13.0 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 75° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.005033 |
| Distance derived from z | 21.26 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 17.620 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | cB, vL, E |
| Identification, Remarks | WH I 153; GC 536; ESO 545-11; MCG -4-6-35; UGCA 29; IRAS 02207-2127 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 908 is located in the constellation Cetus, close to Eridanus and Fornax. On 1 November it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is June to April.