Galaxy NGC 3310 (Arp 217)

History
The galaxy NGC 3310 was discovered by William Herschel on 12 April 1789. It is a spiral galaxy of morphological type SA(rs)bc pec. In Halton Arp's 1966 «Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies», NGC 3310 is listed under the number Arp 217 as an example of a galaxy with an attached bow. The escape velocities measured since 2000 range from 952 km/s to 993 km/s and the distances determined from them range from 17 Mpc to 20 Mpc. [145, 196, 199]
On 20 March 2021, a type II supernova was discovered: SN2021gmj. It reached magnitude 15.1. See Fig. 1. Previous known supernovae in this galaxy are: SN1991N, SN1974C. [303, 304]
Physical Properties

NGC 3310 is a well-studied starburst galaxy thought to have earlier merged with a companion. It shows various tidal formations surrounding the main disc and two large H-I tails extending north and south. [305] Observations with the Hubble Space Telescope showed a rotating disk of gas at its centre, suggesting a supermassive black hole of about 5 to 42 million times the mass of the Sun. [306]
| Designation | NGC 3310 |
| Type | Gx (SBbc/P) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 10h 38m 45.6s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +53° 30' 12" |
| Diameter | 3.1 × 2.4 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 11.2 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 10.8 mag |
| Surface brightness | 12.8 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 156° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.003312 |
| Distance derived from z | 13.99 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 18.100 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | cB, pL, R, vg, vsmbMN 15" |
| Identification, Remarks | WH IV 60; h 731; GC 2158; UGC 5786; MCG 9-18-8; CGCG 267-4; IRAS 10356+5345; VV 356; VV 406; PRC D-15; Arp 217 |
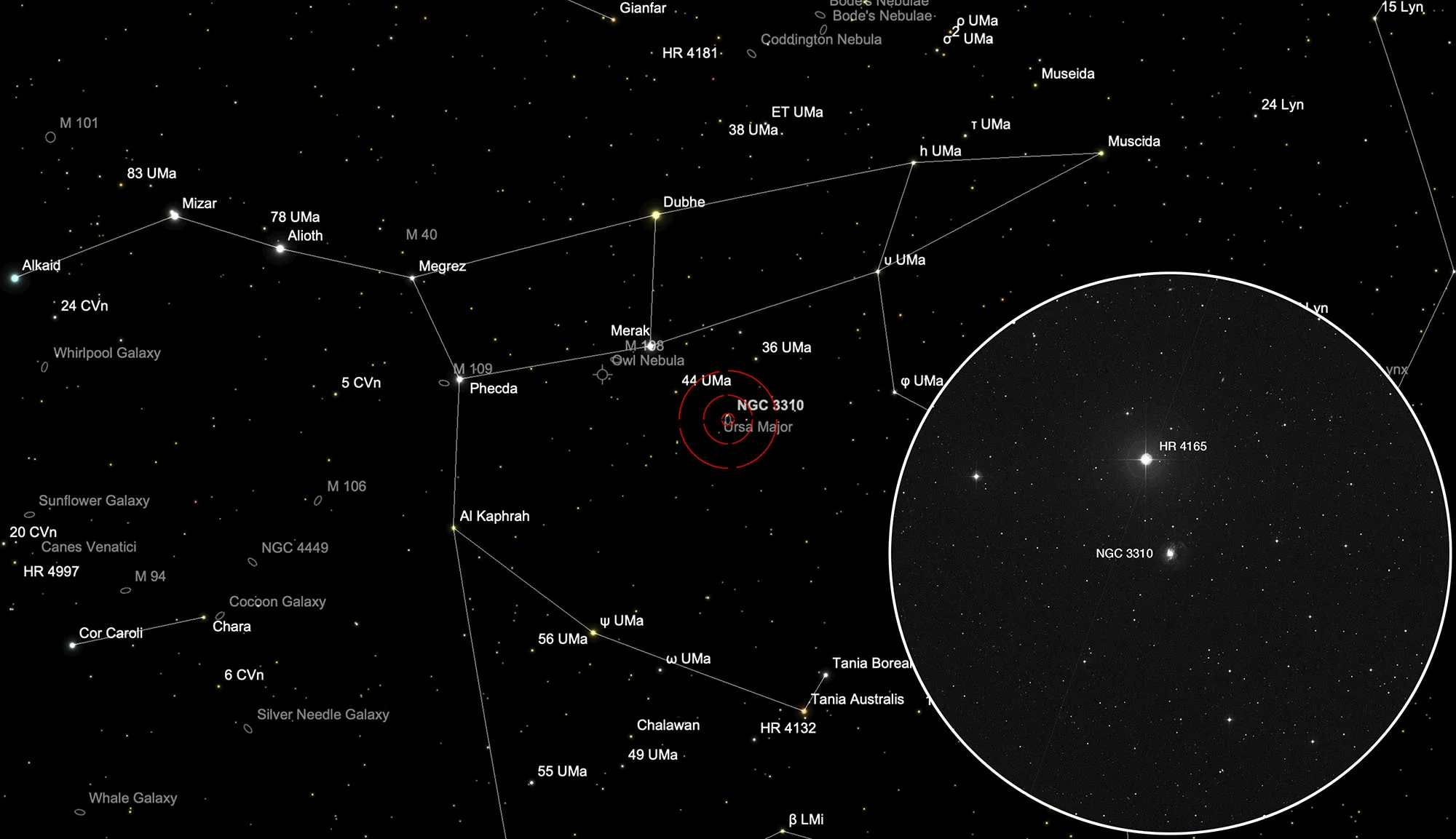
Finder Chart
NGC 3310 is located in the constellation Ursa Maior, about 10 arc minutes south of the 5.5 mag bright star HR 4156, which on a dark night still is visible to the eye. It is circumpolar and is highest in the sky at night from November to August.
Visual Observation
762 mm aperture: Current supernova (SN2021gmj) in galaxy visually clear and well visible. — 30" SlipStream-Dobson f/3.3, Hasliberg, 3. 4. 2021, Eduard von Bergen