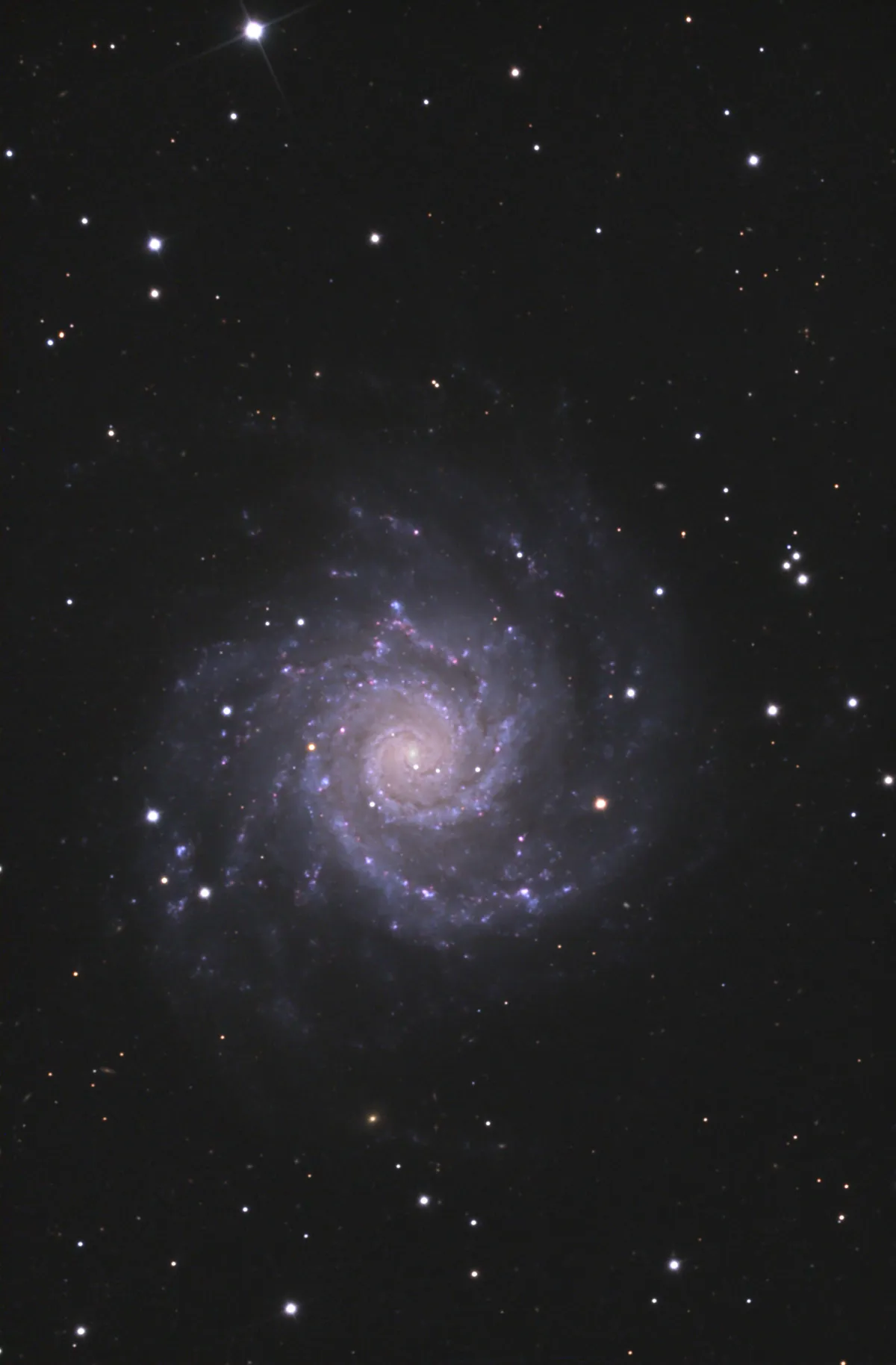
Galaxy Messier 74

History
M 74 was discovered by Pierre Méchain at the end of September and confirmed by Charles Messier on 18 October 1780, who noted: «Nebula without a star, next to the star η in the band of fish, seen by M. Méchain at the end of September 1780 and who wrote: This nebula does not contain any stars, it is quite large, very dark, extremely difficult to observe, we will be able to determine it more precisely on the beautiful winter nights.» [281]
In his «General Catalogue» published in 1864, John Herschel classified M 74 as a globular cluster. This mistake was copied in Dreyer's «New General Catalogue» published in 1888. Lord Rosse was probably the first to discover the spiral shape in 1848. [4]
Physical Properties
The galaxy M 74 is of the morphological type SA (s) c and we see it directly from above. It is similar to M 101, but has a more symmetrical shape. The heliocentric velocities measured over the last 20 years are 657 km/s and distances from 7 Mpc to 11 Mpc. [145]
| Designation | NGC 628 |
| Type | Gx (Sc) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 01h 36m 41.7s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +15° 47' 00" |
| Diameter | 10.5 × 9.5 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 10.0 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 9.4 mag |
| Surface brightness | 14.2 mag·arcmin-2 |
| Position Angle | 25° |
| Redshift (z) | 0.002192 |
| Distance derived from z | 9.26 Mpc |
| Metric Distance | 9.080 Mpc |
| Dreyer Description | globular, F, vL, R, vg, psmbM, rr |
| Identification, Remarks | h 142; GC 372; M 74; UGC 1149; MCG 3-5-11; CGCG 460-14; IRAS 01340+1532 |
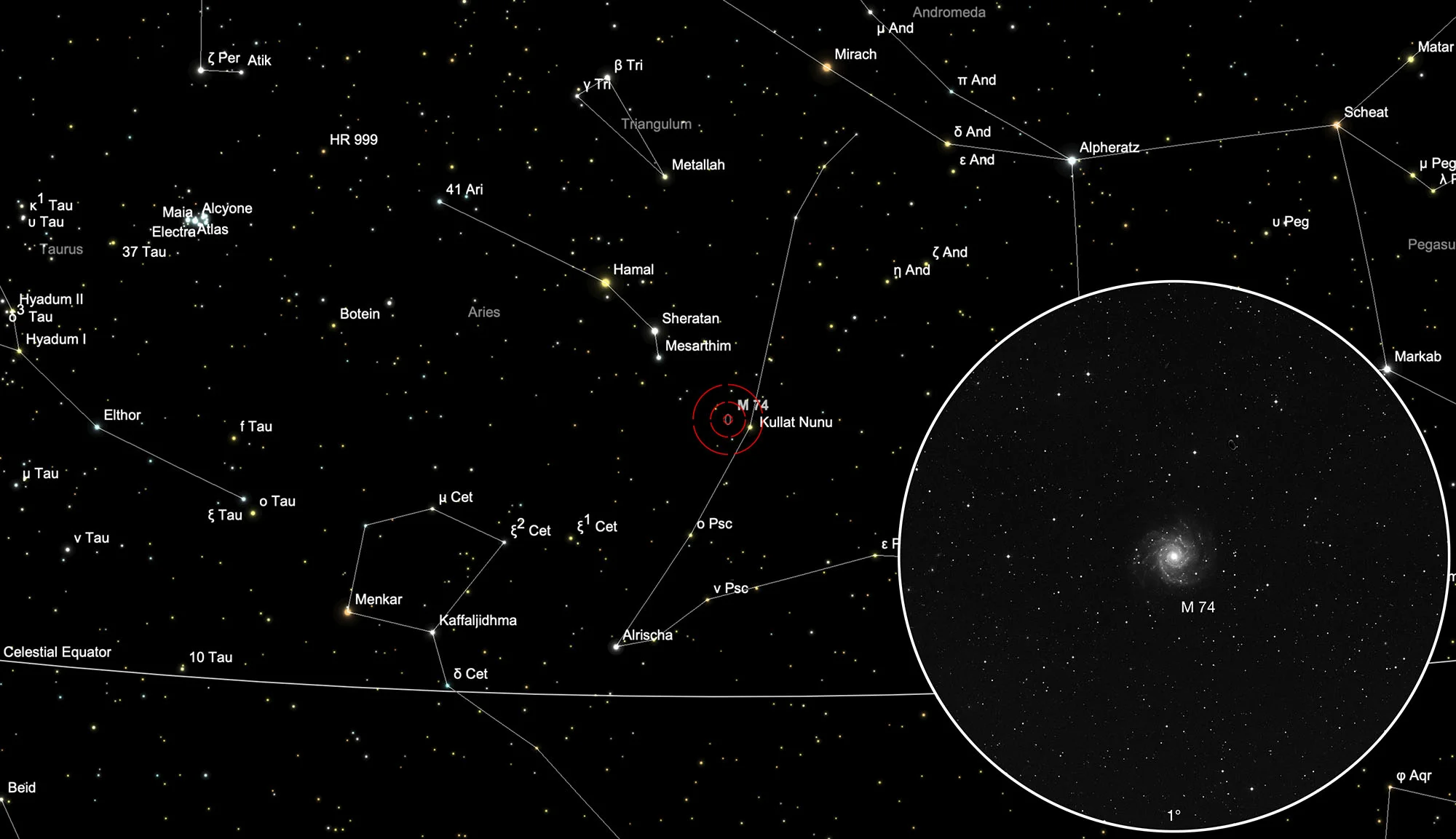
Finder Chart
M 74 is located in the constellation Pisces, about 1° 20' east of the star Kullat Nuni (η Piscium). The best observation time is June to March.
Visual Observation
400 mm Aperture: The galaxy M 74 was clearly visible, but its spiral structure could only just be discerned in the 13 mm Ethos eyepiece. — 400 mm f/4.5 Taurus Dobsonian, Falera, SQM 21.1, 20. 9. 2025, 01:06 MESZ, Bernd Nies