Pair of Galaxies NGC 770/2 (Arp 78)

History
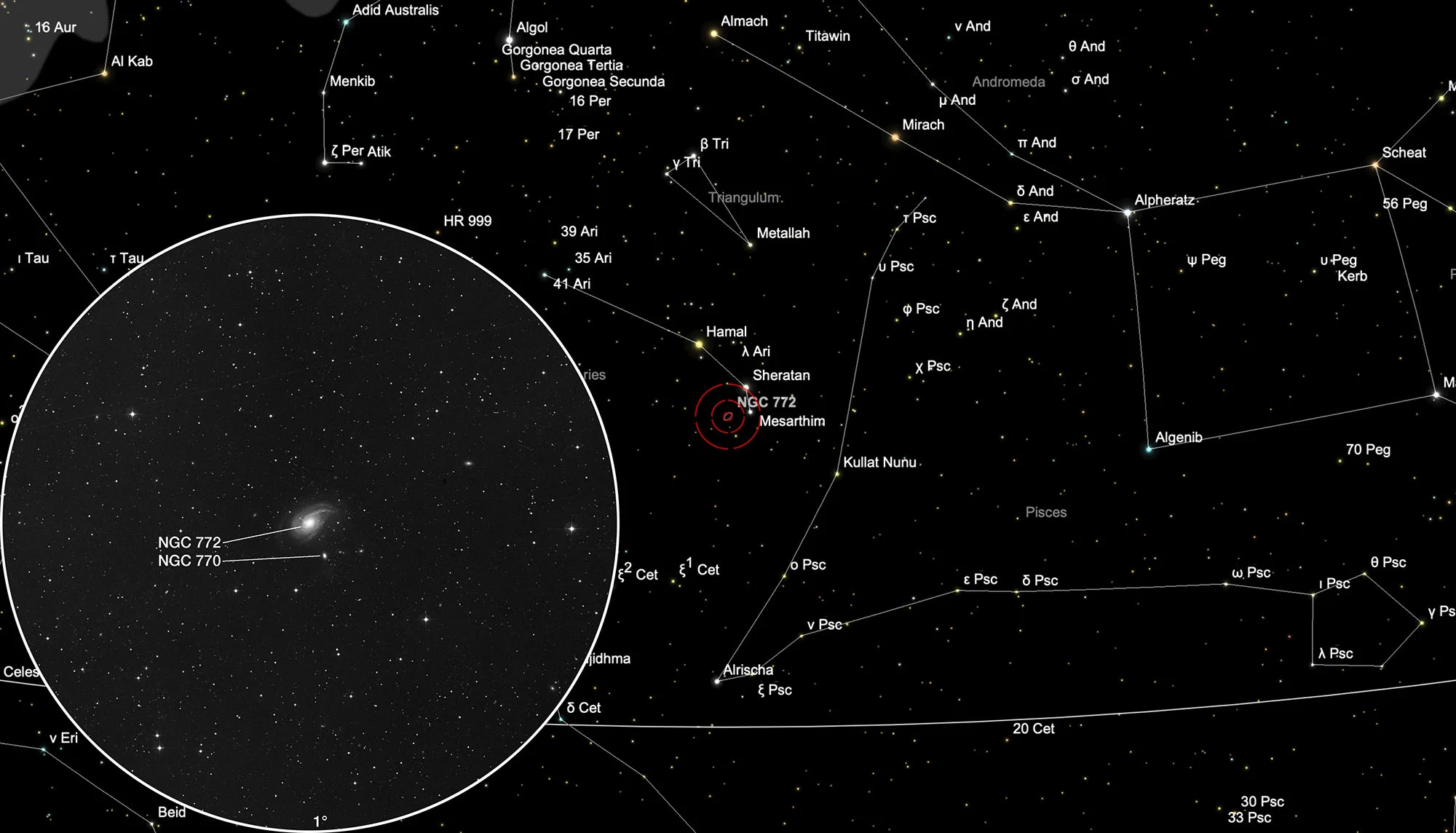
The galaxy NGC 772 was discovered on 29 November 1785 by the German-British astronomer William Herschel with his 18.7 inch reflector telescope. The small companion galaxy NGC 770 remained undiscovered until 3 November 1855. During that night it was discovered by the Irish astronomer RJ Mitchell using Lord Rosse's large 72 inch reflector telescope. [196, 277]
In Halton Arp's 1966 Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies, the two galaxies are listed as Arp 78, a spiral galaxy with a small companion with high surface brightness. [199]
Physical Properties
The two galaxies interact gravitationally with one another and are about 36 Mpc away. [145, 439]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 770 | 01 59 13.5 | +18 57 18 | Gx (E1) | 13.8 | 12.8 | 1.0 | 12.3 | 1.1 × 0.8 | 15 | 0.008199 | 34.63 | 32.300 | vF, S, R, sp I 112 | GC 461=464; UGC 1463; MCG 3-6-10; CGCG 461-16; Arp 78 |
| NGC 772 | 01 59 19.5 | +19 00 27 | Gx (Sb) | 11.1 | 10.3 | 0.8 | 13.9 | 7.2 × 4.3 | 130 | 0.008246 | 34.83 | 30.310 | B, cL, R, gbM, r | WH I 112; h 181; GC 463; UGC 1466; MCG 3-6-11; CGCG 461-18; KARA 80; Arp 78; IRAS 01565+1845 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 772 is located in the constellation Sternbild Aries. On 26 October it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best time to observe is June to March, when it is highest at night.
Visual Observation
635 mm Aperture: NGC 772 is recognizable as a faint, oval spot. There is no sign of one of its brighter arms. The small neighboring galaxy NGC 770 presents itself as a small, round, diffuse spot. — 25" f/4 Obession Dobsonian, Astrofarm Tivoli, Namibia, 15. 9. 2023, Bernd Nies